Abstract
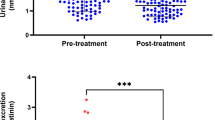
Newborn resuscitation with pure oxygen may be associated with long-term detrimental effects. Due to the change in attitude toward use of less oxygen upon resuscitation, there is a need to study effects of intermediate hyperoxia. The aim was to study dose-response correlation between inspiratory fraction of oxygen used for resuscitation and urinary markers of oxidative damage to DNA and amino acids. Hypoxemia was induced in newborn piglets following a standardized model; they were resuscitated for 15 min with either 21%, 40%, 60% or 100% oxygen and observed for 1 h. Urine samples were collected. Urinary elimination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG), 2′deoxyguanosine (2dG), ortho-tyrosine (o-Tyr) and phenylalanine (Phe) were determined by HPLC and tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Quotient of 8-oxo-dG/2dG and o-Tyr/Phe ratios were significantly and dose-dependant higher in piglets resuscitated with supplementary oxygen. 8-oxodG/dG: Mean (SD) 5.76 (1.81) versus 22.44 (12.55) p < 0.01 and o-Tyr/Phe: 19.07 (10.7) versus 148.7 (59.8)for 21% versus 100%, p < 0.001. Hypoxia and subsequent resuscitation for 15 min with graded inspiratory fraction of oxygen causes increased oxidative stress and a dose-dependant oxidation of DNA and Phenylalanine. The increase in the hydroxyl attack may lead to a pro-oxidative status and risk for genetic instability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- 8-oxodG:
-
8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine
- dG:
-
2′deoxyguanosine
- HPLC-MS/MS:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry
- o-Tyr:
-
ortho-tyrosine
- Phe:
-
phenylalanine
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
References
International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation 2005 2005 Committee on Resuscitation 2005 2005 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science with Treatment Recommendations. Part 7: Neonatal resuscitation. Resuscitation 67: 293–303.
Kondo M, Itoh S, Isobe K, Kondo M, Kunikata T, Imai T, Onishi S 2000 Chemiluminescence because of the production of reactive oxygen species in the lungs of newborn piglets during resuscitation periods after asphyxiation load. Pediatr Res 47: 524–527
Saugstad OD, Ramji S, Vento M 2005 Resuscitation of depressed newborn infants with ambient air or pure oxygen: a meta-analysis. Biol Neonate 87: 27–34
Vento M, Sastre J, Asensi MA, Vina J 2005 Room-air resuscitation causes less damage to heart and kidney than 100% oxygen. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172: 1393–1398
Naumburg E, Bellocco R, Cnattingius S, Jonzon A, Ekbom A 2002 Supplementary oxygen and risk of childhood lymphatic leukaemia. Acta Paediatr 91: 1328–1333
Spector LG, Klebanoff MA, Feusner JH, Georgieff MK, Ross JA 2005 Childhood cancer following neonatal oxygen supplementation. J Pediatr 147: 27–31
Shigenaga MK, Gimeno CJ, Ames BN 1989 Urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine as a biological marker of in vivo oxidative DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9697–9701
Wu LL, Chiou CC, Chang PY, Wu JT 2004 Urinary 8-OHdG: a marker of oxidative stress to DNA and a risk factor for cancer, atherosclerosis and diabetics. Clin Chim Acta 339: 1–9
Lubec G, Widness JA, Hayde M, Menzel D, Pollak A 1997 Hydroxyl radical generation in oxygen-treated infants. Pediatrics 100: 700–704
Munkeby BH, Borke WB, Bjornland K, Sikkeland LI, Borge GI, Halvorsen B, Saugstad OD 2004 Resuscitation with 100% O2 increases cerebral injury in hypoxemic piglets. Pediatr Res 56: 783–790
Cooke MS, Olinski R, Evans MD 2006 Does measurement of oxidative damage to DNA have clinical significance?. Clin Chim Acta 365: 30–49
Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Cooke MS 2004 Oxidative DNA damage and disease: induction, repair and significance. Mutat Res 567: 1–61
Biondi R, Ambrosio G, Liebgott T, Cardounel AJ, Bettini M, Tritto I, Zweier JL 2006 Hydroxylation of D-phenylalanine as a novel approach to detect hydroxyl radicals: application to cardiac pathophysiology. Cardiovasc Res 71: 322–330
de Zwart LL, Meerman JH, Commandeur JN, Vermeulen NP 1999 Biomarkers of free radical damage applications in experimental animals and in humans. Free Radic Biol Med 26: 202–226
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dove R, Rozalski R, Gackowski D, Siomek A, Lunec J, Olinski R 2005 DNA repair is responsible for the presence of oxidatively damaged DNA lesions in urine. Mutat Res 574: 58–66
Olinski R, Rozalski R, Gackowski D, Foksinski M, Siomek A, Cooke MS 2006 Urinary measurement of 8-OxodG, 8-OxoGua, and 5HMUra: a noninvasive assessment of oxidative damage to DNA. Antioxid Redox Signal 8: 1011–1019
Orhan H, Vermeulen NP, Tump C, Zappey H, Meerman JH 2004 Simultaneous determination of tyrosine, phenylalanine and deoxyguanosine oxidation products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as non-invasive biomarkers for oxidative damage. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 799: 245–254
Cooke MS, Lunec J, Evans MD 2002 Progress in the analysis of urinary oxidative DNA damage. Free Radic Biol Med 33: 1601–1614
Renner T, Fechner T, Scherer G 2000 Fast quantification of the urinary marker of oxidative stress 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with triple-stage quadrupole mass detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 738: 311–317
Tsukahara H, Jiang MZ, Ohta N, Sato S, Tamura S, Hiraoka M, Maeda M, Mayumi M 2004 Oxidative stress in neonates: evaluation using specific biomarkers. Life Sci 75: 933–938
Tsukahara H, Toyo-Oka M, Kanaya Y, Ogura K, Kawatani M, Hata A, Hiraoka M, Mayumi M 2005 Quantitation of glutathione S transferase-pi in the urine of preterm neonates. Pediatr Int 47: 528–531
Loft S, Svoboda P, Kasai H, Tjonneland A, Vogel U, Moller P, Overvad K, Raaschou-Nielsen O 2006 Prospective study of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine excretion and the risk of lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 27: 1245–1250
Greenberg JA, Wei H, Ward K, Boozer CN 2000 Whole-body metabolic rate appears to determine the rate of DNA oxidative damage and glycation involved in aging. Mech Ageing Dev 115: 107–117
Dizdaroglu M, Jaruga P, Birincioglu M, Rodriguez H 2002 Free radical-induced damage to DNA: mechanisms and measurement. Free Radic Biol Med 32: 1102–1115
Vento M, Asensi M, Sastre J, Garcia-Sala F, Pallardo FV, Vina J 2001 Resuscitation with room air instead of 100% oxygen prevents oxidative stress in moderately asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatrics 107: 642–647
Mansell AL, McAteer AL, Pipkin AC 1992 Maturation of interdependence between extra-alveolar arteries and lung parenchyma in piglets. Circ Res 71: 701–710
Standaert TA, Wilham BE, Mayock DE, Watchko JF, Gibson RL, Woodrum DE 1991 Respiratory mechanics of the piglet during the first month of life. Pediatr Pulmonol 11: 294–301
Pond WG, Boleman SL, Fiorotto ML, Ho H, Knabe DA, Mersmann HJ, Savell JW, Su DR 2000 Perinatal ontogeny of brain growth in the domestic pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223: 102–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Helse Sor.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solberg, R., Andresen, J., Escrig, R. et al. Resuscitation of Hypoxic Newborn Piglets With Oxygen Induces a Dose-Dependent Increase in Markers of Oxidation. Pediatr Res 62, 559–563 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318156e8aa
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318156e8aa
This article is cited by
-
Splanchnic oxygen saturation during reoxygenation with 21% or 100% O2 in newborn piglets
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Randomized trial of oxygen weaning strategies following chest compressions during neonatal resuscitation
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Free radicals and neonatal encephalopathy: mechanisms of injury, biomarkers, and antioxidant treatment perspectives
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
Oxygen therapy of the newborn from molecular understanding to clinical practice
Pediatric Research (2019)
-
Increased expression of inflammatory genes in the neonatal mouse brain after hyperoxic reoxygenation
Pediatric Research (2015)