Abstract
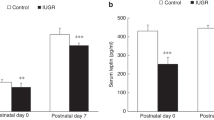
Neonates with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) are associated with reduced concentrations of IGF-I that might contribute to arterial wall thickening. Direct atherogenic effects of leptin have been described. We aimed to investigate the relationship among abdominal aortic intima-media thickness (aIMT), serum IGF-I, IGF binding protein-3, and leptin levels in neonates with IUGR. Abdominal aIMT was measured in 40 term neonates with IUGR and in 40 controls. Mean aIMT was significantly greater in neonates with IUGR (0.45 ± 0.03 mm) than in controls (0.39 ± 0.04 mm, p < 0.0001). Serum IGF-I and leptin levels were lower in neonates with IUGR than in controls. There was a significant positive correlation between aIMT and gestational age, whereas a significant negative correlation was determined between aIMT and IGF-I in the IUGR neonates. For aIMT, significant associations included serum IGF-I level (β = –0.406, p = 0.006) and gestational age (β = 0.331, p = 0.022) in a multiple stepwise linear regression analysis. In control neonates, serum IGF-I levels were negatively related to aIMT (β = –0.750, p < 0.001). Neonates with IUGR have significant aIMT with decreased IGF-I. IGF-I levels determine aIMT not only in neonates with IUGR but also in healthy controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AGA:
-
appropriate for gestational age
- aIMT:
-
aortic intima-media thickness
- cIMT:
-
carotid intima-media thickness
- CVD:
-
cardiovascular disease
- IGFBP-3:
-
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3
- IMT:
-
intima-media thickness
- IUGR:
-
intrauterine growth restricted
- SGA:
-
small for gestational age
References
Barker DJ, Winter PD, Osmond C, Margetts B, Simmonds SJ 1989 Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet 2: 577–580
Mi J, Law C, Zhang KL, Osmond C, Stein C, Barker D 2000 Effects of infant birth weight and maternal body mass index in pregnancy on components of the insulin resistance syndrome in China. Ann Intern Med 132: 253–260
Molina M, Casanueva V, Cid X, Ferrada MC, Perez R, Dios G, Reyes M, Venegas H, Cid L 2000 Lipid profile in newborns with intrauterine growth retardation. Rev Med Chil 128: 741–748
Gordon T, Kannel WB 1971 Premature mortality from coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. JAMA 215: 1617–1625
Koklu E, Kurtoglu S, Akcakus M, Koklu S, Buyukkayhan D, Gumus H, Yikilmaz A 2006 Increased aortic intima-media thickness is related to lipid profile in newborns with intrauterine growth restriction. Horm Res 65: 269–275
Christou H, Connors JM, Ziotopoulou M, Hatzidakis V, Papathanassoglou E, Ringer SA, Mantzoros CS 2001 Cord blood leptin and insulin-like growth factor levels are independent predictors of fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 935–938
Randhawa R, Cohen P 2005 The role of the insulin-like growth factor system in prenatal growth. Mol Genet Metab 86: 84–90
Lombardi G, Colao A, Marzullo P, Ferone D, Longobardi S, Esposito V, Merola B 1997 Is growth hormone bad for your heart? Cardiovascular impact of GH deficiency and of acromegaly. J Endocrinol 155: S33–S37
Johansson AG, Forslund A, Hambraeus L, Blum WF, Ljunghall S 1994 Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein is a major determinant of bone mineral density in healthy men. J Bone Miner Res 9: 915–921
Skilton MR, Evans N, Griffiths KA, Harmer JA, Celermajer DS 2005 Aortic wall thickness in newborns with intrauterine growth restriction. Lancet 365: 1484–1486
Bajoria R, Sooranna SR, Ward BS, Chatterjee R 2002 Prospective function of placental leptin at maternal-fetal interface. Placenta 23: 103–115
Varvarigou A, Mantzoros CS, Beratis NG 1999 Cord blood leptin concentrations in relation to intrauterine growth. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 50: 177–183
Beltowski J 2006 Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 189: 47–60
Lembo G, Vecchione C, Fratta L, Marino G, Trimarco V, d'Amati G, Trimarco B 2000 Leptin induces direct vasodilation through distinct endothelial mechanisms. Diabetes 49: 293–297
Vecchione C, Maffei A, Colella S, Aretini A, Poulet R, Frati G, Gentile MT, Fratta L, Trimarco V, Trimarco B, Lembo G 2002 Leptin effect on endothelial nitric oxide is mediated through Akt-endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation pathway. Diabetes 51: 168–173
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Wolk R, Svatikova A, Phillips BG, Davison DE, Berger PB, Somers VK 2004 Independent association between plasma leptin and C-reactive protein in healthy humans. Circulation 109: 2181–2185
Watson AM, Poloyac SM, Howard G, Blouin RA 1999 Effect of leptin on cytochrome P-450, conjugation, and antioxidant enzymes in the ob/ob mouse. Drug Metab Dispos 27: 695–700
Be€towski J, Wojcicka G, Jamroz A 2003 Leptin decreases plasma paraoxonase 1 (PON1) activity and induces oxidative stress: the possible novel mechanism for proatherogenic effect of chronic hyperleptinemia. Atherosclerosis 170: 21–29
Konstantinides S, Schafer K, Koschnick S, Loskutoff DJ 2001 Leptin dependent platelet aggregation and arterial thrombosis suggests a mechanism for atherothrombotic disease in obesity. J Clin Invest 108: 1533–1540
Shin HJ, Oh J, Kang SM, Lee JH, Shin MJ, Hwang KC, Jang Y, Chung JH 2005 Leptin induces hypertrophy via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329: 18–24
Jarvisalo MJ, Jartti L, Nanto-Salonen K, Irjala K, Ronnemaa T, Hartiala JJ, Celermajer DS, Raitakari OT 2001 Increased aortic intima-media thickness: a marker of preclinical atherosclerosis in high-risk children. Circulation 104: 2943–2947
Irving RJ, Belton NR, Elton RA, Walker BR 2000 Adult cardiovascular risk factors in premature babies. Lancet 355: 2135–2136
Lubchenco LO, Hansman C, Boyd E 1966 Intrauterine growth in length and head circumference as estimated from live births at gestational ages from 26 to 42 weeks. Pediatrics 37: 403–408
McGill HC Jr, McMahan CA, Herderick EE, Tracy RE, Malcom GT, Zieske AW, Strong JP 2000 Effects of coronary heart disease risk factors on atherosclerosis of selected regions of the aorta and right coronary artery. PDAY Research Group. Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 836–845
SAS/STAT User's Guide. 1998 SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC,
Yang SW, Yu JS 2000 Relationship of insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, insulin, growth hormone in cord blood and maternal factors with birth height and birth weight. Pediatr Int 42: 31–36
Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Hands SJ, Adcock CJ, Holly JM, Matthews DR, Mohamed-Ali V, Yudkin JS, Wilkinson AR, Dunger DB 1998 Insulin, insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein-1, growth hormone, and feeding in the newborn. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 3550–3557
Wang HS, Lim J, English J, Irvine L, Chard T 1991 The concentration of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in human umbilical cord serum at delivery: relation to fetal weight. J Endocrinol 129: 459–464
Davidson S, Shtaif B, Gil-Ad I 2001 Insulin, insulin-like growth factors-I and -II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in newborn serum: association with normal fetal head growth and head circumference. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 14: 151–158
Cinaz P, Sen E, Bideci A, Ezgu FS, Atalay Y, Koca E 1999 Plasma leptin levels of large for gestational age and small for gestational age infants. Acta Paediatr 88: 753–756
Shekhawat PS, Garland JS, Shivpuri C, Mick GJ, Sasidharan P, Pelz CJ, McCormick KL 1998 Neonatal cord blood leptin: its relationship to birth weight, body mass index, maternal diabetes, and steroids. Pediatr Res 43: 338–343
Raitakari OT 1999 Imaging of subclinical atherosclerosis in children and young adults. Ann Med 31: 33–40
Tonstad S, Joakimsen O, Stensland-Bugge E, Leren TP, Ose L, Russell D, Bonaa KH 1996 Risk factors related to carotid intima-media thickness and plaque in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and control subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16: 984–991
Bayes-Genis A, Conover CA, Schwartz RS 2000 The insulin-like growth factor axis: a review of atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circ Res 86: 125–130
Ruotolo G, Bavenholm P, Brismar K, Efendic S, Ericsson CG, de Faire U, Nilsson J, Hamsten A 2000 Serum insulin-like growth factor-I level is independently associated with coronary artery disease progression in young male survivors of myocardial infarction: beneficial effects of bezafibrate treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol 35: 647–654
Colao A, Spiezia S, Cerbone G, Pivonello R, Marzullo P, Ferone D, Di Somma C, Assanti AP, Lombardi G 2001 Increased arterial intima-media thickness by B-M mode echodoppler ultrasonography in acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 54: 515–524
Brevetti G, Marzullo P, Silvestro A, Pivonello R, Oliva G, di Somma C, Lombardi G, Colao A 2002 Early vascular alterations in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 3174–3179
Koklu E, Akcakus M, Kurtoglu S, Koklu S, Yikilmaz A, Coskun A, Gunes T 2007 Aortic intima-media thickness and lipid profile in macrosomic newborns. Eur J Pediatr 166: 333–338
Koklu E, Kurtoglu S, Akcakus M, Yikilmaz A, Gunes T 2007 Serum insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and leptin levels are related to abdominal aortic intima-media thickness in macrosomic newborns. Growth Horm IGF Res 17: 26–32
Eidelman AI, Samueloff A 2002 The pathophysiology of the fetus of the diabetic mother. Semin Perinatol 26: 232–236
Colao A, Di Somma C, Filippella M, Rota F, Pivonello R, Orio F, Vitale G, Lombardi G 2004 Insulin-like growth factor–1 deficiency determines increased intima-media thickness at common carotid arteries in adult patients with growth hormone deficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 61: 360–366
Walsh MF, Barazi M, Pete G, Muniyappa R, Dunbar JC, Sowers JR 1996 Insulin-like growth factor-I diminishes in vivo and in vitro vascular contractility: role of vascular nitric oxide. Endocrinology 137: 1798–1803
Gryglewski RJ, Palmer RM, Moncada S 1986 Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature 320: 454–456
Ikari Y, McManus BM, Kenyon J, Schwartz SM 1999 Neonatal intima formation in the human coronary artery. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 2036–2040
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Ahmet Ozturk (Department of Biostatistics, Erciyes University) and Associate Professor Abdulhakim Coskun (Department of Radiology, Division of Pediatric Radiology, Erciyes University) for help with statistical evaluation and selection of the images for reading, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Erciyes University Research Fund supported this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koklu, E., Ozturk, M., Kurtoglu, S. et al. Aortic Intima-Media Thickness, Serum IGF-I, IGFBP-3, and Leptin Levels in Intrauterine Growth-Restricted Newborns of Healthy Mothers. Pediatr Res 62, 704–709 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318157caaa
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318157caaa
This article is cited by
-
Maternal cholesterol levels during gestation: boon or bane for the offspring?
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
-
The relationship between serum vitamin D levels and intima-media thickness in term infants
European Journal of Pediatrics (2019)
-
Intrauterine growth restriction: impact on cardiovascular development and function throughout infancy
Pediatric Research (2016)
-
Systemic arterial stiffness in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: potential cause of systemic hypertension
Journal of Perinatology (2016)
-
Abdominal Aortic Intima-Media Thickness in Preschool Children Born Preterm
Pediatric Cardiology (2014)