Abstract
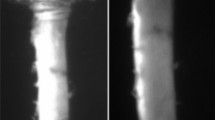
Low birth weight for gestational age has been epidemiologically linked to cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in adult life. This study aimed to determine whether in utero growth restriction influences an early feature of atherosclerotic pathology; disruption of the aortic internal elastic lamina (IEL) in the adult Brown Norway (BN) rat. In utero growth restriction was induced by bilateral uterine artery ligation on day 18 of gestation, thereby decreasing newborn BN pup weight by approximately 14%. Restriction surgery significantly increased aortic IEL defect number at 8 wk of age in both sexes compared with no surgery animals (p < 0.002). At 16 wk of age placental restriction surgery significantly increased the number of defects in males compared with both no surgery and sham surgery control groups (p < 0.001). The total number of IEL defects was significantly correlated with several postnatal growth rate parameters, including 72-h postpartum weight. Neither blood pressure was significantly different between treatment groups, nor was it correlated with body weight or IEL defect numbers. The findings of this study seem to support the fetal origins of adult disease hypothesis, by demonstrating that a moderate growth restricting insult dramatically increases aortic elastic tissue defect formation via an apparently blood pressure-independent mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BN:
-
Brown Norway
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- GD:
-
gestational day
- IEL:
-
internal elastic lamina
- PN:
-
postnatal
References
Forsdahl A 1977 Are poor living conditions in childhood and adolescence an important risk factor for arteriosclerotic heart disease?. Br J Prev Soc Med 31: 91–95
Barker DJ, Osmond C 1986 Infant mortality, childhood nutrition, and ischaemic heart disease in England and Wales. Lancet 1: 1077–1081
Leon DA, Lithell HO, Vagero D, Koupilova I, Mohsen R, Berglund L, Lithell UB, McKeigue PM 1998 Reduced fetal growth rate and increased risk of death from ischaemic heart disease: cohort study of 15 000 Swedish men and women born 1915–29. BMJ 317: 241–245
Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Tuomilehto J, Osmond C, Barker DJ 2001 Early growth and coronary heart disease in later life: longitudinal study. BMJ 322: 949–953
Ikari Y, McManus BM, Kenyon J, Schwartz SM 1999 Neonatal intima formation in the human coronary artery. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 2036–2040
Meyer WW, Kauffman SL, Hardy-Stashin J 1980 Studies on human aortic bifurcation. Part 1: Histo-architecture of the bifurcation. Atherosclerosis 37: 377–388
Davies H 1990 Atherogenesis and the coronary arteries of childhood. Int J Cardiol 28: 283–291
Meyer WW, Lind J, Yao AC, Kauffman SL 1982 Early arterial lesions in infancy and childhood and ways of prevention. Paediatrician 11: 136–156
Sims FH 1985 Discontinuities in the internal elastic lamina: a comparison of coronary and internal mammary arteries. Artery 13: 127–143
Capdeville M, Coutard M, Osborne-Pellegrin MJ 1989 Spontaneous rupture of the internal elastic lamina in the rat: the manifestation of a genetically determined factor which may be linked to vascular fragility. Blood Vessels 26: 197–212
Jones GT, Harris EL, Jacob HJ, van Rij AM 2000 Spontaneous elastic tissue lesions in the rat abdominal aorta, a genetically determined phenotype. J Vasc Res 37: 73–81
Jones GT, Jiang F, McCormick SP, Dusting GJ 2005 Elastic lamina defects are an early feature of aortic lesions in the apolipoprotein e knockout mouse. J Vasc Res 42: 237–246
Wlodek ME, Westcott KT, O'Dowd R, Serruto A, Wassef L, Moritz KM, Moseley JM 2005 Uteroplacental restriction in the rat impairs fetal growth in association with alterations in placental growth factors including PTHrP. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288: R1620–R1627
Briscoe TA, Rehn AE, Dieni S, Duncan JR, Wlodek ME, Owens JA, Rees SM 2004 Cardiovascular and renal disease in the adolescent guinea pig after chronic placental insufficiency. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191: 847–855
Jones GT, van Rij AM 1996 Localisation of endothelin-1 in rat aortae, the relationship to flow and elastic tissue tears. J Vasc Res 33: 425–431
Skilton MR, Gosby AK, Wu BJ, Ho LM, Stocker R, Caterson ID, Celermajer DS 2006 Maternal undernutrition reduces aortic wall thickness and elastin content in offspring rats without altering endothelial function. Clin Sci 111: 281–287
Ogata ES, Bussey ME, Finley S 1986 Altered gas exchange, limited glucose and branched chain amino acids, and hypoinsulinism retard fetal growth in the rat. Metabolism 35: 970–977
Levitsky LL, Kimber A, Marchichow JA, Uehara J 1977 Metabolic response to fasting in experimental intrauterine growth retardation induced by surgical and nonsurgical maternal stress. Biol Neonate 31: 311–315
Leon DA, Koupilova I, Lithell HO, Berglund L, Mohsen R, Vagero D, Lithell UB, McKeigue PM 1996 Failure to realise growth potential in utero and adult obesity in relation to blood pressure in 50 year old Swedish men. BMJ 312: 401–406
Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Tuomilehto J, Winter PD, Osmond C, Barker DJ 1999 Catch-up growth in childhood and death from coronary heart disease: longitudinal study. BMJ 318: 427–431
Wigglesworth JS 1964 Experimental growth retardation in the foetal rat. J Pathol Bacteriol 88: 1–13
Nitzan M, Orloff S, Schulman JD 1979 Placental transfer of analogs of glucose and amino acids in experimental intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res 13: 100–103
Ogata ES, Bussey ME, LaBarbera A, Finley S 1985 Altered growth, hypoglycemia, hypoalaninemia, and ketonemia in the young rat: postnatal consequences of intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res 19: 32–37
Jansson T, Lambert GW 1999 Effect of intrauterine growth restriction on blood pressure, glucose tolerance and sympathetic nervous system activity in the rat at 3–4 months of age. J Hypertens 17: 1239–1248
Alexander BT 2003 Placental insufficiency leads to development of hypertension in growth-restricted offspring. Hypertension 41: 457–462
Petry CJ, Ozanne SE, Wang CL, Hales CN 1997 Early protein restriction and obesity independently induce hypertension in 1-year-old rats. Clin Sci 93: 147–152
Langley SC, Jackson AA 1994 Increased systolic blood pressure in adult rats induced by fetal exposure to maternal low protein diets. Clin Sci 86: 217–222
Ozaki T, Nishina H, Hanson MA, Poston L 2001 Dietary restriction in pregnant rats causes gender-related hypertension and vascular dysfunction in offspring. J Physiol 530: 141–152
Battista MC, Oligny LL, St-Louis J, Brochu M 2002 Intrauterine growth restriction in rats is associated with hypertension and renal dysfunction in adulthood. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283: E124–E131
Huang W, Alhenc Gelas F, Osborne-Pellegrin MJ 1998 Protection of the arterial internal elastic lamina by inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system in the rat. Circ Res 82: 879–890
Skilton MR, Evans N, Griffiths KA, Harmer JA, Celermajer DS 2005 Aortic wall thickness in newborns with intrauterine growth restriction. Lancet 365: 1484–1486
Jarvisalo MJ, Jartti L, Nanto-Salonen K, Irjala K, Ronnemaa T, Hartiala JJ, Celermajer DS, Raitakari OT 2001 Increased aortic intima-media thickness: a marker of preclinical atherosclerosis in high-risk children. Circulation 104: 2943–2947
Berry CL, Looker T, Germain J 1972 The growth and development of the rat aorta. I. Morphological aspects. J Anat 113: 1–16
Ibrahim J, Miyashiro JK, Berk BC 2003 Shear stress is differentially regulated among inbred rat strains. Circ Res 92: 1001–1009
Jones GT, Stehbens WE 1995 The ultrastructure of arteries proximal to chronic experimental carotid-jugular fistulae in rabbits. Pathology 27: 36–42
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Janet Ledingham for guidance with BP measurements and critical appraisal of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was Supported by a Health Research Council of New Zealand project grant 00/354.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascoe, K., Wlodek, M. & Jones, G. Increased Elastic Tissue Defect Formation in the Growth Restricted Brown Norway Rat: A Potential Link Between In Utero Condition and Cardiovascular Disease. Pediatr Res 64, 125–130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181761859
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181761859