Abstract
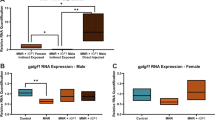
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with an increased risk for short stature and diseases in adulthood thought to be inflicted by fetal programming. We hypothesized that placental endocrine systems involved in perinatal growth might also play a role in postnatal growth after IUGR. In a prospective controlled multicenter study, placental gene expression of IGF-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), leptin and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11β-HSD2) were measured in 14 IUGR infants and 15 children born appropriate for gestational age (AGA) proven by serial ultrasound examinations. Postnatally, IUGR infants experienced a significantly higher growth velocity than AGA neonates (at 1 y: p = 0.001). Gene expression of 11β-HSD2 at birth correlated positively with birth length (r = 0.55, p = 0.04) and inversely with growth velocity in the first year of life (r = −0.69, p = 0.01) in the IUGR, but not in the AGA group. There was no correlation between gene expression of placental IGFBP-1, leptin and birth weight, length and growth velocity during the first year of life. AGA infants showed significantly higher concentrations of cortisone in venous cord blood after birth (p = 0.02) as a surrogate of a higher 11β-HSD2 activity in the fetoplacental unit. In conclusion, placental 11β-HSD2 gene expression might predict postnatal growth in IUGR.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AGA:
-
appropriate for gestational age
- 11β-HSD2:
-
11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2
- IGFBP-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1
- SGA:
-
small for gestational age
References
Ibanez L, Potau N, Francois I, de Zegher F 1998 Precocious pubarche, hyperinsulinism, and ovarian hyperandrogenism in girls: relation to reduced fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 3558–3562
Levy-Marchal C, Czernichow P 2006 Small for gestational age and the metabolic syndrome: which mechanism is suggested by epidemiological and clinical studies?. Horm Res 65: 123–130
Plank C, Östreicher I, Dittrich K, Waldherr R, Voigt M, Amann K, Rascher W, Dötsch J 2007 Low birth weight, but not postnatal weight gain, aggravates the course of nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 22: 1881–1889
Plagemann A 2006 Perinatal nutrition and hormone-dependent programming of food intake. Horm Res 65: 83–89
Dötsch J, Nusken KD, Knerr I, Kirschbaum M, Repp R, Rascher W 1999 Leptin and neuropeptide Y gene expression in human placenta: ontogeny and evidence for similarities to hypothalamic regulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84: 2755–2758
Abuzzahab MJ, Schneider A, Goddard A, Grigorescu F, Lautier C, Keller E, Kiess W, Klammt J, Kratzsch J, Osgood D, Pfaffle R, Raile K, Seidel B, Smith RJ, Chernausek SD 2003 IGF-I receptor mutations resulting in intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation. N Engl J Med 349: 2211–2222
Struwe E, Berzl GM, Schild RL, Beckmann MW, Dörr HG, Rascher W, Dötsch J 2007 Simultaneously reduced gene expression of cortisol-activating and cortisol-inactivating enzymes in placentas of small-for-gestational-age neonates. Am J Obstet Gynecol 197: 43.e1–43.e6
Lapillonne A, Peretti N, Ho PS, Claris O, Salle BL 1997 Aetiology, morphology and body composition of infants born small for gestational age. Acta Paediatr Suppl 423: 173–176, discussion 177
Ibanez L, Lopez-Bermejo A, Suarez L, Marcos MV, Diaz M, de Zegher F 2008 Visceral adiposity without overweight in children born small for gestational age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 2079–2083
Jaquet D, Gaboriau A, Czernichow P, Levy-Marchal C 2001 Relatively low serum leptin levels in adults born with intra-uterine growth retardation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25: 491–495
Bouret SG, Draper SJ, Simerly RB 2004 Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 304: 108–110
Seckl JR 2004 Prenatal glucocorticoids and long-term programming. Eur J Endocrinol 151: U49–U62
Benediktsson R, Calder AA, Edwards CR, Seckl JR 1997 Placental 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: a key regulator of fetal glucocorticoid exposure. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 46: 161–166
Lindsay RS, Lindsay RM, Edwards CR, Seckl JR 1996 Inhibition of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in pregnant rats and the programming of blood pressure in the offspring. Hypertension 27: 1200–1204
Mune T, White PC 1996 Apparent mineralocorticoid excess: genotype is correlated with biochemical phenotype. Hypertension 27: 1193–1199
Barbazanges A, Piazza PV, Le Moal M, Maccari S 1996 Maternal glucocorticoid secretion mediates long-term effects of prenatal stress. J Neurosci 16: 3943–3949
Murphy VE, Clifton VL 2003 Alterations in human placental 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and 2 with gestational age and labour. Placenta 24: 739–744
Giudice LC, de Zegher F, Gargosky SE, Dsupin BA, de las Fuentes L, Crystal RA, Hintz RL, Rosenfeld RG 1995 Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the term and preterm human fetus and neonate with normal and extremes of intrauterine growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80: 1548–1555
Firth SM, Baxter RC 2002 Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23: 824–854
Crossey PA, Pillai CC, Miell JP 2002 Altered placental development and intrauterine growth restriction in IGF binding protein-1 transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 110: 411–418
Popovici RM, Lu M, Bhatia S, Faessen GH, Giaccia AJ, Giudice LC 2001 Hypoxia regulates insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 in human fetal hepatocytes in primary culture: suggestive molecular mechanisms for in utero fetal growth restriction caused by uteroplacental insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 2653–2659
Kajimura S, Aida K, Duan C 2005 Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) mediates hypoxia-induced embryonic growth and developmental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 1240–1245
Voigt M, Schneider KT, Jahrig K 1996 [Analysis of a 1992 birth sample in Germany. 1: New percentile values of the body weight of newborn infants]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 56: 550–558
Prader A, Largo RH, Molinari L, Issler C 1989 Physical growth of Swiss children from birth to 20 years of age. First Zurich longitudinal study of growth and development. Helv Paediatr Acta Suppl 52: 1–125
Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Wabitsch M, Kunze D, Geller F, Geib HC, Hesse V, von Hippel A, Jaeger U, Johnsen D, Korte W, Menner K, Muller G, Muller JM, Niemann-Pilatus A, Remer T, Schaefer F, Wittchen HU, Zabransky S, Zellner K, Ziegler A, Hebebrand J 2001 [Percentiles for the body mass index for the child and young adult under consulting different German samples]. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 149: 807–818
Vogeser M, Briegel J, Jacob K 2001 Determination of serum cortisol by isotope-dilution liquid-chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry with on-line extraction. Clin Chem Lab Med 39: 944–947
Trollmann R, Klingmuller K, Schild RL, Rascher W, Dötsch J 2007 Differential gene expression of somatotrophic and growth factors in response to in vivo hypoxia in human placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol 197: 601.e601–601.e606
Gudmundsson S, Korszun P, Olofsson P, Dubiel M 2003 New score indicating placental vascular resistance. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 82: 807–812
Ong KK, Ahmed ML, Emmett PM, Preece MA, Dunger DB 2000 Association between postnatal catch-up growth and obesity in childhood: prospective cohort study. BMJ 320: 967–971
Barker DJ 2006 Adult consequences of fetal growth restriction. Clin Obstet Gynecol 49: 270–283
Fuqua JS 2006 Growth after organ transplantation. Semin Pediatr Surg 15: 162–169
Ulinski T, Cochat P 2006 Longitudinal growth in children following kidney transplantation: from conservative to pharmacological strategies. Pediatr Nephrol 21: 903–909
McTernan CL, Draper N, Nicholson H, Chalder SM, Driver P, Hewison M, Kilby MD, Stewart PM 2001 Reduced placental 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 mRNA levels in human pregnancies complicated by intrauterine growth restriction: an analysis of possible mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 4979–4983
Homan A, Guan H, Hardy DB, Gratton RJ, Yang K 2006 Hypoxia blocks 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 induction in human trophoblast cells during differentiation by a time-dependent mechanism that involves both translation and transcription. Placenta 27: 832–840
Plank C, Meissner U, Rauh M, Wollmann H, Dörr HG, Rascher W, Dötsch J 2007 Cortisol-cortisone ratios in small for gestational age (SGA) children without postnatal catch-up growth. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 67: 304–309
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the members of the FIPS-study group protocol committee, namely H. Böhles, M.D. (Frankfurt), E. Landmann, M.D. (Giessen), U. Lang, M.D. (Graz), L. Gortner, M.D., S. Zabransky, M.D., K. Ertan, M.D. (Homburg/Saar), M. Kirschbaum, M.D., J. Möller, M.D. (Saarbrücken). We also thank Mrs. Bitterer, Mrs. Allabauer, and Mrs. Birkner for measurements of placental gene expression and technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Pfizer and Novo Nordisk (Educational Grant).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzschoppe, A., Struwe, E., Blessing, H. et al. Placental 11β-HSD2 Gene Expression at Birth Is Inversely Correlated With Growth Velocity in the First Year of Life After Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Pediatr Res 65, 647–653 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819e7337
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819e7337
This article is cited by
-
Influence of labor on direct and indirect determinants of placental 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2021)
-
Mechanisms for establishment of the placental glucocorticoid barrier, a guard for life
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)
-
Fetale Programmierung und spätere Nierenfunktionsstörungen nach intrauteriner Wachstumsrestriktion
Der Nephrologe (2009)