Abstract
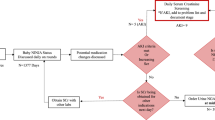
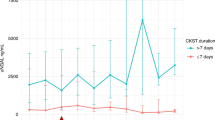
In very low birth weight (VLBW) infants, acute renal impairment (ARI) is common, but there is no consensus about criteria for its diagnosis. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is an early and sensitive indicator of renal impairment in experimental animals, children, and adults. Urinary NGAL (UNGAL) is detectable in VLBW infants; however, there is no reference range in this population. The objective of this study is to define the reference range for UNGAL in VLBW infants with no risk factors for acute renal impairment. UNGAL concentration was determined in urine samples collected from day of life (DOL) 4 through DOL 30 in 50 newborns with uncomplicated clinical courses, selected from a total of 145 prospectively enrolled appropriate for gestational age inborn VLBW premature infants. The birth weight and gestational age ranges were 790-1490 g and 26–33 wk, respectively. The median, 95th and 99th percentiles, and range of pooled UNGAL values were 5 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, 120 ng/mL, and 2–150 ng/mL, respectively. Greater variability and higher quantile levels of UNGAL were observed in females versus males. In conclusion, a reference range for UNGAL in VLBW infants, similar to that in children and adults, has been established.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ARI:
-
acute renal impairment
- DOL:
-
day of life
- GFR:
-
glomerular filtration rate
- NGAL:
-
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- [SCreat]:
-
serum creatinine concentration
- UNGAL:
-
urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- VLBW:
-
very low birth weight
References
Choker G, Gouyon JB 2004 Diagnosis of acute renal failure in very preterm infants. Biol Neonate 86: 212–216
Miall LS, Henderson MJ, Turner AJ, Brownlee KG, Brocklebank JT, Newell SJ, Allgar VL 1999 Plasma creatinine rises dramatically in the first 48 hours of life in preterm infants. Pediatrics 104: e76
Guignard JP, Drukker A 1999 Why do newborn infants have a high plasma creatinine?. Pediatrics 103: e49
Gallini F, Maggio L, Romagnoli C, Marrocco G, Tortorolo G 2000 Progression of renal function in preterm neonates with gestational age < or = 32 weeks. Pediatr Nephrol 15: 119–124
Toth-Heyn P, Drukker A, Guignard JP 2000 The stressed neonatal kidney: from pathophysiology to clinical management of neonatal vasomotor nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 14: 227–239
Gouyon JB, Guignard JP 2000 Management of acute renal failure in newborns. Pediatr Nephrol 14: 1037–1044
Coulthard MG, Vernon B 1995 Managing acute renal failure in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 73: F187–F192
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Li JY, Paragas N, Nicholas T, Devarajan P, Barasch J 2006 Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-mediated iron traffic in kidney epithelia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15: 442–449
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Li JY, Kalandadze A, Cohen DJ, Devarajan P, Barasch J 2007 Dual action of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 407–413
Goetz DH, Holmes MA, Borregaard N, Bluhm ME, Raymond KN, Strong RK 2002 The neutrophil lipocalin NGAL is a bacteriostatic agent that interferes with siderophore-mediated iron acquisition. Mol Cell 10: 1033–1043
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P 2003 Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 2534–2543
Devarajan P, Mishra J, Supavekin S, Patterson LT, Steven Potter S 2003 Gene expression in early ischemic renal injury: clues towards pathogenesis, biomarker discovery, and novel therapeutics. Mol Genet Metab 80: 365–376
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Devarajan P 2004 Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol 24: 307–315
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J, Mitsnefes M, Barasch J, Devarajan P 2004 Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 3073–3082
Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Mitsnefes M, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P 2006 Kidney NGAL is a novel early marker of acute injury following transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol 21: 856–863
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P 2005 Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365: 1231–1238
Wagener G, Jan M, Kim M, Mori K, Barasch JM, Sladen RN, Lee HT 2006 Association between increases in urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and acute renal dysfunction after adult cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 105: 485–491
Parikh CR, Jani A, Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P 2006 Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 6: 1639–1645
Trachtman H, Christen E, Cnaan A, Patrick J, Mai V, Mishra J, Jain A, Bullington N, Devarajan P, Investigators of the HUS-SYNSORB Pk Multicenter Clinical Trial 2006 Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalcin in D+HUS: a novel marker of renal injury. Pediatr Nephrol 21: 989–994
Brunner HI, Mueller M, Rutherford C, Passo MH, Witte D, Grom A, Mishra J, Devarajan P 2006 Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54: 2577–2584
Hirsch R, Dent C, Pfriem H, Allen J, Beekman RH 3rd, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes M, Devarajan P 2007 NGAL is an early predictive biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol 22: 2089–2095
Yang J, Mori K, Li JY, Barasch J 2003 Iron, lipocalin, and kidney epithelia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285: F9–F18
Gwira JA, Wei F, Ishibe S, Ueland JM, Barasch J, Cantley LG 2005 Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin regulates epithelial morphogenesis in vitro. J Biol Chem 280: 7875–7882
Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, Wang W, Mori K, Setlik D, Du T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Strong R, Barasch J 2002 An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell 10: 1045–1056
Parravicini E, Lorenz JM, Nemerofsky SL, O'Rourke M, Barasch J, Bateman D 2009 Reference range of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in very low-birth-weight infants: preliminary data. Am J Perinatol 26: 437–440
Wilcox RR 1997 Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing. Academic Press, San Diego, CA 296 pp
Cole TJ 2000 Sympercents: symmetric percentage differences on the 100 log (e) scale simplify the presentation of log transformed data. Stat Med 19: 3109–3125
Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Schibler KR 2008 Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 64: 423–428
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR, Foster K, Yang J, Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Li JY, Weiss S, Mishra J, Cheema FH, Markowitz G, Suganami T, Sawai K, Mukoyama M, Kunis C, D'Agati V, Devarajan P, Barasch J 2005 Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 115: 610–621
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL 2007 Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11: R84
Acknowledgements
Assistance in collecting daily urine samples was provided by Allison R. Polland, BS, Kristin M. Capone, BS, and Patrick L. Scarborough, BS. Shlomo Kuperman, BS, and Matthew O'Rourke, MD, provided technical help and assisted in data entry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Grant UL1 RR024156 from the National Center for Research Resources; Grants DK-55388 and DK-58872 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (J.B.); and grants from the Emerald Foundation and the March of Dimes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, T., Bateman, D., Parravicini, E. et al. Reference Values of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatr Res 66, 528–532 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181baa3dd
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181baa3dd
This article is cited by
-
Impact of nephrotoxic drugs on urinary biomarkers of renal function in very preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Gestational age, sex, and time affect urine biomarker concentrations in extremely low gestational age neonates
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Serial urinary neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin in pediatric diabetic ketoacidosis with acute kidney injury
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology (2021)
-
Urinary acute kidney injury biomarkers in very low-birth-weight infants on indomethacin for patent ductus arteriosus
Pediatric Research (2019)
-
Urinary Biomarkers of Aminoglycoside-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Cystic Fibrosis: Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin
Scientific Reports (2018)