Abstract
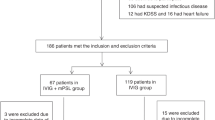
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment-resistant patients are high risk of developing coronary artery lesions with Kawasaki disease. The IVIG-responsive (Group A; n = 6) and IVIG-resistant patients (Group B) were predicted before starting the initial treatment using the Egami scoring system and randomly allocated as a single-IVIG treatment group (group B1; n = 6) or as a IVIG-plus-methylprednisolone (IVMP) combined therapy group (group B2; n = 5). We investigated the transcript abundance in the leukocytes of those patients using a microarray analysis. Five patients in group A and one patient in group B1 responded to initial IVIG treatment. All group B2 patients responded to IVIG-plus-IVMP combined therapy. Before performing these treatments, those transcripts related to IVIG resistance and to the development of coronary artery lesions, such as IL1R, IL18R, oncostatin M, suppressor of cytokine signaling-3, S100A12 protein, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1, matrix metallopeptidase-9, and polycythemia rubra vera-1, were more abundant in group B patients in comparison with group A patients. Moreover, those transcripts in group B2 patients were more profoundly and broadly suppressed than group B1 patients after treatment. This study elucidated the molecular mechanism of the effectiveness of IVIG-plus-IVMP combined therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CALs:
-
coronary artery lesions
- HP:
-
haptoglobin
- IVIG:
-
intravenous immunoglobulin
- IVMP:
-
IVIG-plus-methylprednisolone
- KD:
-
Kawasaki disease
- PRV-1:
-
polycythemia rubra vera-1
References
Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H 1974 A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics 54: 271–276
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode MP, Mason WH, Meissner HC, Rowley AH, Reddy V, Sundel RP, Melish ME, Rosen FS 1991 A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med 324: 1633–1639
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA 2004 Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114: 1708–1733
Durongpisitkul K, Gururaj VJ, Park JM, Martin CF 1995 The prevention of coronary artery aneurysm in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis on the efficacy of aspirin and immunoglobulin treatment. Pediatrics 96: 1057–1061
Burns JC, Capparelli EV, Brown JA, Newburger JW, Glode MP 1998 Intravenous gamma-globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease. US/Canadian Kawasaki Syndrome Study Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17: 1144–1148
Muta H, Ishii M, Egami K, Furui J, Sugahara Y, Akagi T, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa H, Matsuishi T 2004 Early intravenous gamma-globulin treatment for Kawasaki disease: the nationwide surveys in Japan. J Pediatr 144: 496–499
Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, Okada Y, Tamura K, Tomomasa T, Kobayashi T, Morikawa A 2006 Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 113: 2606–2612
Tremoulet AH, Best BM, Song S, Wang S, Corinaldesi E, Eichenfield JR, Martin DD, Newburger JW, Burns JC 2008 Resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 153: 117–121
Egami K, Muta H, Ishii M, Suda K, Sugahara Y, Iemura M, Matsuishi T 2006 Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 149: 237–240
Sano T, Kurotobi S, Matsuzaki K, Yamamoto T, Maki I, Miki K, Kogaki S, Hara J 2007 Prediction of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients with acute Kawasaki disease before starting initial treatment. Eur J Pediatr 166: 131–137
Okada K, Hara J, Maki I, Miki K, Matsuzaki K, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto T, Nishigaki T, Kurotobi S, Sano T 2009 Pulse methylprednisolone with gamma globulin as an initial treatment for acute Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr 168: 181–185
Wright DA, Newburger JW, Baker A, Sundel RP 1996 Treatment of immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease with pulsed doses of corticosteroids. J Pediatr 128: 146–149
Hashino K, Ishii M, Iemura M, Akagi T, Kato H 2001 Re-treatment for immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease: a comparative study of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. Pediatr Int 43: 211–217
Furukawa T, Kishiro M, Akimoto K, Nagata S, Shimizu T, Yamashiro Y 2008 Effects of steroid pulse therapy on immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 93: 142–146
Ogata S, Bando Y, Kimura S, Ando H, Nakahata Y, Ogihara Y, Kaneko T, Minoura K, Kaida M, Yokota Y, Furukawa S, Ishii M 2009 The strategy of immune globulin resistant Kawasaki disease: a comparative study of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. J Cardiol 53: 15–19
Ayusawa M, Sonobe T, Uemura S, Ogawa S, Nakamura Y, Kiyosawa N, Ishii M, Harada K 2005 Revision of diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease (the 5th revised edition). Pediatr Int 47: 232–234
Nomura I, Abe J, Noma S, Saito H, Gao B, Wheeler G, Leung DY 2005 Adrenomedullin is highly expressed in blood monocytes associated with acute Kawasaki disease: a microarray gene expression study. Pediatr Res 57: 49–55
Abe J, Jibiki T, Noma S, Nakajima T, Saito H, Terai M 2005 Gene expression profiling of the effect of high-dose intravenous Ig in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Immunol 174: 5837–5845
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT Method. Methods 25: 402–408
Senzaki H, Masutani S, Kobayashi J, Kobayashi T, Nakano H, Nagasaka H, Sasaki N, Asano H, Kyo S, Yokote Y 2001 Circulating matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 104: 860–863
Foell D, Ichida F, Vogl T, Yu X, Chen R, Miyawaki T, Sorg C, Roth J 2003 S100A12 (EN-RAGE) in monitoring Kawasaki disease. Lancet 361: 1270–1272
Nomura Y, Masuda K, Maeno N, Yoshinaga M, Kawano Y 2004 Serum levels of interleukin-18 are elevated in the subacute phase of Kawasaki syndrome. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 135: 161–165
Popper SJ, Shimizu C, Shike H, Kanegaye JT, Newburger JW, Sundel RP, Brown PO, Burns JC, Relman DA 2007 Gene-expression patterns reveal underlying biological processes in Kawasaki disease. Genome Biol 8: R261
Abe J, Ebata R, Jibiki T, Yasukawa K, Saito H, Terai M 2008 Elevated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels predict treatment failure in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122: 1008–1013. e1008
Takeshita S, Tokutomi T, Kawase H, Nakatani K, Tsujimoto H, Kawamura Y, Sekine I 2001 Elevated serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol 125: 340–344
Makata H, Ichiyama T, Uchi R, Takekawa T, Matsubara T, Furukawa S 2006 Anti-inflammatory effect of intravenous immunoglobulin in comparison with dexamethasone in vitro: implication for treatment of Kawasaki disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 373: 325–332
Suzuki A, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Komatsu K, Nakazawa M, Fukaya T, Baba K, Yutani C 2004 Immunohistochemical study of apparently intact coronary artery in a child after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int 46: 590–596
Onouchi Y, Gunji T, Burns JC, Shimizu C, Newburger JW, Yashiro M, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa H, Wakui K, Fukushima Y, Kishi F, Hamamoto K, Terai M, Sato Y, Ouchi K, Saji T, Nariai A, Kaburagi Y, Yoshikawa T, Suzuki K, Tanaka T, Nagai T, Cho H, Fujino A, Sekine A, Nakamichi R, Tsunoda T, Kawasaki T, Nakamura Y, Hata A 2008 ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms. Nat Genet 40: 35–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (C: 9022950) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology; a Parents' Association Grant at Kitasato University School of Medicine; a Grant-in-aid from the Morinaga Foundation for Health and Nutrition; and a Grant-in-aid from the Kawasaki Disease Research Center in Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogata, S., Ogihara, Y., Nomoto, K. et al. Clinical Score and Transcript Abundance Patterns Identify Kawasaki Disease Patients Who May Benefit From Addition of Methylprednisolone. Pediatr Res 66, 577–584 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181baa3c2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181baa3c2
This article is cited by
-
An Artificial Intelligence-guided signature reveals the shared host immune response in MIS-C and Kawasaki disease
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Kawasaki Disease Patients as Potential Biomarkers for IVIG Sensitivity by Bioinformatics Analysis
Pediatric Cardiology (2016)
-
Global gene expression profiling identifies new therapeutic targets in acute Kawasaki disease
Genome Medicine (2014)
-
Transcriptional regulation by infliximab therapy in kawasaki disease patients with immunoglobulin resistance
Pediatric Research (2014)
-
TARC/CCL17 gene polymorphisms and expression associated with susceptibility and coronary artery aneurysm formation in Kawasaki disease
Pediatric Research (2013)