Abstract
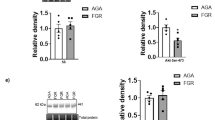
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with reduced activity of placental amino acid transport systems β and A. Whether this phenotype is maintained in fetal cells outside the placenta is unknown. In IUGR, cord blood tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α concentrations are raised, potentially influencing amino acid transport in fetal cells. We used fetal T lymphocytes as a model to study systems β and A amino acid transporters in IUGR compared with normal pregnancy. We also studied the effect of TNF-α on amino acid transporter activity. In fetal lymphocytes from IUGR pregnancies, taurine transporter mRNA expression encoding system β transporter was reduced, but there was no change in system β activity. No significant differences were observed in system A mRNA expression (encoding SNAT1 and SNAT2) or system A activity between the two groups. After 24 or 48 h TNF-α treatment, fetal T lymphocytes from normal pregnancies showed no significant change in system A or system β activity, although cell viability was compromised. This study represents the first characterization of amino acid transport in a fetal cell outside the placenta in IUGR. We conclude that the reduced amino acid transporter activity found in placenta in IUGR is not a feature of all fetal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AGA:
-
appropriate for gestational age
- BM:
-
basal plasma membrane
- MeAIB:
-
α-(methylamino)isobutyric acid
- MVM:
-
microvillous plasma membrane
- SNAT:
-
sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter
- TAUT:
-
taurine transporter
References
Chiswick ML 1985 Intrauterine growth retardation. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 291: 845–848
Pryor J 1997 The identification and long term effects of fetal growth restriction. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104: 1116–1122
Economides DL, Nicoliades KH, Gahl WA, Bernardini I, Evans MI 1989 Plasma amino acids in appropriate- and small-for-gestational-age fetuses. Am J Obstet Gynecol 161: 1219–1227
Cetin I, Ronzoni S, Marconi AM, Perugino G, Corbetta C, Battaglia FC, Pardi G 1996 Maternal concentrations and fetal-maternal concentration differences of plasma amino acids in normal and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 174: 1575–1583
Jansson T, Powell TL 2007 Role of the placenta in fetal programming: underlying mechanisms and potential interventional approaches. Clin Sci 113: 1–13
Jansson T 2001 Amino acid transporters in human placenta. Pediatr Res 49: 141–147
Mahendran D, Donnai P, Glazier JD, D'Souza SW, Boyd RD, Sibley CP 1993 Amino acid (system A) transporter activity in microvillous membrane vesicles from placentas of appropriate and small for gestational age babies. Pediatr Res 34: 661–665
Glazier JD, Cetin I, Perugino G, Ronzoni S, Grey AM, Mahendran D, Pardi G, Sibley CP 1997 Association between the activity of the system A amino acid transporter in the microvillous plasma membrane of the human placenta and the severity of fetal compromise in intrauterine growth restriction. Pediatr Res 42: 514–519
Jansson T, Ylvén K, Wennergren M, Powell TL 2002 Glucose transport and system A activity in syncytiotrophoblast microvillous and basal membranes in intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta 23: 386–391
Jansson T, Scholtbach V, Powell TL 1998 Placental transport of leucine and lysine are reduced in intrauterine growth restriction. Pediatr Res 44: 532–537
Norberg S, Powell TL, Jansson T 1998 Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with reduced activity of placental taurine transporters. Pediatr Res 44: 233–238
Chien PF, Smith K, Watt PW, Scrimgeour CM, Taylor DJ, Rennie MJ 1993 Protein turnover in the human fetus studied at term using stable isotope tracer amino acids. Am J Physiol 265: E31–E35
Sibley CP, Turner MA, Cetin I, Ayuk P, Boyd CA, D'Souza SW, Glazier JD, Greenwood SL, Jansson T, Powell T 2005 Placental phenotypes of intrauterine growth. Pediatr Res 58: 827–832
Christie GR, Hyde R, Hundal HS 2001 Regulation of amino acid transporters by amino acid availability. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 4: 425–431
Bartha JL, Romero-Carmona R, Comino-Delgado R 2003 Inflammatory cytokines in intrauterine growth retardation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 82: 1099–1102
Kang YS, Ohtsuki S, Takanaga H, Toni M, Hosoya K, Terasaki T 2002 Regulation of taurine transport at the blood–brain barrier by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, taurine and hypertonicity. J Neurochem 83: 1188–1195
Iruloh CG, D'Souza SW, Speake PF, Crocker I, Fergusson W, Baker PN, Sibley CP, Glazier JD 2007 Taurine transporter in fetal T lymphocytes and platelets: differential expression and functional activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292: C332–C341
Mackenzie B, Erickson JD 2004 Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid (System N/A) transporters of the SLC38 gene family. Pflugers Arch 447: 784–785
Wilcox MA, Johnson IR, Maynard PV, Smith SJ, Chilvers CE 1993 The individualised birthweight ratio: a more logical outcome measure of pregnancy than birthweight alone. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 100: 342–347
Desforges M, Lacey HA, Glazier JD, Greenwood SL, Mynett KJ, Speake PF, Sibley CP 2006 SNAT4 isoform of system A amino acid transporter is expressed in human placenta. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290: C305–C312
Vatansever U, Acunas B, Demir M, Karasalihoglu S, Ekuklu G, Ener S, Pala O 2002 Nucleated red blood cell counts and erythropoietin levels in high-risk neonates. Pediatr Int 44: 590–595
Roos S, Powell TL, Jansson T 2004 Human placental taurine transporter in uncomplicated and IUGR pregnancies: cellular localisation, protein expression and regulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287: R886–R893
Hatanaka T, Huang W, Wang H, Sugawara M, Prasad PD, Leibach FH, Ganapathy V 2000 Primary structure, functional characteristics and tissue expression pattern of human ATA2, a subtype of amino acid transport system A. Biochim Biophys Acta 1467: 1–6
Wang H, Huang W, Sugawara M, Devoe LD, Leibach FH, Prasad PD, Ganapathy V 2000 Cloning and functional expression of ATA1, a subtype of amino acid transporter A, from human placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273: 1175–1179
Novak D, Lehman M, Bernstein H, Beveridge M, Cramer S 2006 SNAT expression in rat placenta. Placenta 27: 510–516
Cramer S, Beveridge M, Kilberg M, Novak D 2002 Physiological importance of system A-mediated amino acid transport to fetal rat development. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282: C153–C160
Jansson N, Pettersson J, Haafiz A, Ericsson A, Palmberg I, Tranberg M, Ganapathy V, Powell TL, Jansson T 2006 Down regulation of placental transport of amino acids precedes the development of intrauterine growth restriction. J Physiol 576: 935–946
Constância M, Hemberger M, Hughes J, Dean W, Ferguson-Smith A, Fundele R, Stewart F, Kelsey G, Fowden A, Sibley C, Reik W 2002 Placental-specific IGF-II is a major modulator of placental and fetal growth. Nature 417: 945–948
Xanthou M 1985 Immunological deficiencies in small-for-dates neonates. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 319: 143–149
Rangamani P, Sirovich L 2007 Survival and apoptotic pathways initiated by TNF-alpha: modeling and predictions. Biotechnol Bioeng 97: 1216–1229
Mochizuki T, Satsu H, Shimizu M 2002 Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates taurine uptake and transporter gene expression in human intestinal CaCo-2 cells. FEBS Lett 517: 92–96
Acknowledgements
We thank the midwives and medical staff at St. Mary's Hospital, Manchester, for their help in obtaining placentas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported, in part, by a Wellcome Trust project grant (071224/Z/03/Z).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iruloh, C., D'Souza, S., Fergusson, W. et al. Amino Acid Transport Systems β and A in Fetal T Lymphocytes in Intrauterine Growth Restriction and With Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Treatment. Pediatr Res 65, 51–56 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31818a0793
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31818a0793
This article is cited by
-
Taurine supplementation improves hippocampal metabolism in immature rats with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) through protecting neurons and reducing gliosis
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Amino-acid transporters in T-cell activation and differentiation
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
The SLC38 family of sodium–amino acid co-transporters
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2014)
-
Differences in Transport Mechanisms of trans-1-Amino-3-[18F]Fluorocyclobutanecarboxylic Acid in Inflammation, Prostate Cancer, and Glioma Cells: Comparison with l-[Methyl-11C]Methionine and 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]Fluoro-d-Glucose
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2014)