Abstract
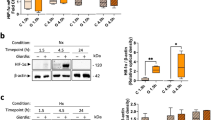
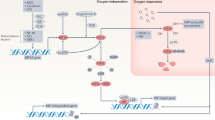
Previously, it has been suggested that hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) 1 signaling may play determinative role in the maintenance of the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Our aim was to depict the alteration of HIF-1α and related genes in celiac disease (CD) where the importance of the barrier function is well known. Duodenal biopsy specimens were collected from 16 children with untreated CD, 9 children with treated CD and 10 controls. HIF-1α, trefoil factor 1 (TFF1), ecto-5-prime nucleotidase (CD73), and multi drug resistance gene 1 (MDR1) mRNA and HIF-1α protein expression were determined by real-time PCR and Western blot, respectively. Localization of HIF-1α was determined by immunofluorescent staining. We found increased HIF-1α and TFF1 mRNA and HIF-1α protein expression in the duodenal mucosa of children with untreated CD compared with controls or children with treated CD (p < 0.05). In untreated CD children, HIF-1α staining was present in cytoplasmic and nuclear region of the villous enterocytes. In treated CD mRNA expression of CD73 and MDR1 were increased compared with controls (p < 0.01 and 0.05, respectively). Our results of increased mucosal HIF-1α expression in CD children suggest the contribution of this signaling pathway in the pathomechanism of CD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
coeliac disease
- CD73:
-
ecto-5-prime nucleotidase
- HIF:
-
hypoxia inducible factor
- IBD:
-
inflammatory bowel disease
- MDR1:
-
multi drug resistance gene 1
- TFF1:
-
trefoil factor 1
References
Johnston SD, Watson RG, McMillan SA, Sloan J, Love AH 1997 Prevalence of coeliac disease in Northern Ireland. Lancet 350: 1370
Sanders DS, Patel D, Stephenson TJ, Ward AM, McCloskey EV, Hadjivassiliou M, Lobo AJ 2003 A primary care cross-sectional study of undiagnosed adult coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15: 407–413
West J, Logan RF, Hill PG, Lloyd A, Lewis S, Hubbard R, Reader R, Holmes GK, Khaw KT 2003 Seroprevalence, correlates, and characteristics of undetected coeliac disease in England. Gut 52: 960–965
Fasano A, Berti I, Geraduzzi T, Not T, Colletti RB, Drago S, Elitsur Y, Green PH, Guandalini S, Hill ID, Pietzak M, Ventura A, Thorpe M, Kryszak D, Fornaroli F, Wasserman SS, Murray JA, Horvath K 2003 Prevalence of coeliac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States. Arch Intern Med 163: 286–292
Stepniak D, Koning F 2006 Celiac disease–sandwiched between innate and adaptive immunity. Hum Immunol 67: 460–468
Koning F 2005 Celiac disease: caught between a rock and a hard place. Gastroenterology 129: 1294–1301
Furuta GT, Turner JR, Taylor CT, Hershberg RM, Comerford K, Narravula S, Podolsky DK, Colgan SP 2001 Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent induction of intestinal trefoil factor protects barrier function during hypoxia. J Exp Med 193: 1027–1034
Synnestvedt K, Furuta GT, Comerford KM, Louis N, Karhausen J, Eltzschig HK, Hansen KR, Thompson LF, Colgan SP 2002 Ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates permeability changes in intestinal epithelia. J Clin Invest 110: 993–1002
Adams JM, Difazio LT, Rolandelli RH, Luján JJ, Haskó G, Csóka B, Selmeczy Z, Németh ZH 2009 HIF-1: a key mediator in hypoxia. Acta Physiol Hung 96: 19–28
Salceda S, Caro J 1997 Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem 272: 22642–22647
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP, Camenisch G 2005 Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE 2005: re12
Hoffmann W 2005 Trefoil factors TFF (trefoil factor family) peptide-triggered signals promoting mucosal restitution. Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 2932–2938
Colgan SP, Eltzschig HK, Eckle T, Thompson LF 2006 Physiological roles for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Purinergic Signal 2: 351–360
Annese V, Valvano MR, Palmieri O, Latiano A, Bossa F, Andriulli A 2006 Multidrug resistance 1 gene in inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 12: 3636–3644
Karhausen J, Furuta GT, Tomaszewski JE, Johnson RS, Colgan SP, Haase VH 2004 Epithelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is protective in murine experimental colitis. J Clin Invest 114: 1098–1106
Hirota SA, Beck PL, MacDonald JA 2009 Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) signaling in therapeutics: implications for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 3: 1–16
Walker-Smith JA, Guandalini S, Schmitz J, Shmerling DH, Visakorpi JK 1990 Revised criteria for diagnosis of coeliac disease. Report of Working Group of European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Arch Dis Child 65: 909–911
Setty M, Hormaza L, Guandalini S 2008 Celiac disease: risk assessment, diagnosis, and monitoring. Mol Diagn Ther 12: 289–298
Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Sanders DS 2008 Coeliac disease. Br Med Bull 88: 157–170
Koning F, Gilissen L, Wijmenga C 2005 Gluten: a two-edged sword. Immunopathogenesis of celiac disease. Springer Semin Immunopathol 27: 217–232
Szebeni B, Veres G, Dezsofi A, Rusai K, Vannay A, Bokodi G, Vásárhelyi B, Korponay-Szabó IR, Tulassay T, Arató A 2007 Increased mucosal expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 in coeliac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 45: 187–193
Groschwitz KR, Hogan SP 2009 Intestinal barrier function: molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124: 3–20
Weidemann A, Johnson RS 2008 Biology of HIF-1alpha. Cell Death Differ 15: 621–627
Yee Koh M, Spivak-Kroizman TR, Powis G 2008 HIF-1 regulation: not so easy come, easy go. Trends Biochem Sci 33: 526–534
Dehne N, Brüne B 2009 HIF-1 in the inflammatory microenvironment. Exp Cell Res 315: 1791–1797
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL 1995 Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92: 5510–5514
Ziello JE, Jovin IS, Huang Y 2007 Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia. Yale J Biol Med 80: 51–60
Taylor CT, Colgan SP 2007 Hypoxia and gastrointestinal disease. J Mol Med 85: 1295–1300
Cummins EP, Seeballuck F, Keely SJ, Mangan NE, Callanan JJ, Fallon PG, Taylor CT 2008 The hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine is protective in a murine model of colitis. Gastroenterology 134: 156–165
Shah YM, Ito S, Morimura K, Chen C, Yim SH, Haase VH, Gonzalez FJ 2008 Hypoxia inducible factor augments experimental colitis through an MIF-dependent inflammatory signaling cascade. Gastroenterology 134: 2036–2048, 2048.e1-2048.e3
Robinson A, Keely S, Karhausen J, Gerich ME, Furuta GT, Colgan SP 2008 Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. Gastroenterology 134: 145–155
Noyer CM, Brandt LJ 1999 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for perineal Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol 94: 318–321
Buchman AL, Fife C, Torres C, Smith L, Aristizibal J 2001 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for severe ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 33: 337–339
Agarwal S, Mayer L 2010 Gastrointestinal manifestations in primary immune disorders. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16: 703–711
Wong WM, Playford RJ, Wright NA 2000 Peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration: ordered sequence or redundancy?. Gut 46: 286–292
Tarnawski A, Szabo IL, Husain SS, Soreghan B 2001 Regeneration of gastric mucosa during ulcer healing is triggered by growth factors and signal transduction pathways. J Physiol (Paris) 95: 337–344
Hoffmann W 2004 Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides: regulators of mucosal regeneration and repair, and more. Peptides 25: 727–730
Linden J 2001 Molecular approach to adenosine receptors: receptor-mediated mechanisms of tissue protection. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41: 775–787
Weissmuller T, Eltzschig HK, Colgan SP 2005 Dynamic purine signaling and metabolism during neutrophil-endothelial interactions. Purinergic Signal 1: 229–239
Schinkel AH 1997 The physiological function of drug-transporting P-glycoproteins. Semin Cancer Biol 8: 161–170
Marzolini C, Paus E, Buclin T, Kim RB 2004 Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75: 13–33
Acknowledgements
We thank Maria Bernáth for her excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by funds from the Hungarian National Scientific Research Foundation Grant (OTKA 71730, T046082, OTKA-K81117), and Grant of the Ministry of Health (ETT 435/2006, ETT- 028-02) and TÁMOP-4.2.2-08/1/KMR-2008-0004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vannay, Á., Sziksz, E., Prókai, Á. et al. Increased Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in Coeliac Disease. Pediatr Res 68, 118–122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181e5bc96
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181e5bc96
This article is cited by
-
Intestinal drug transporters in pathological states: an overview
Pharmacological Reports (2020)
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and thymic stromal lymphopoietin are involved in the pathophysiology of childhood coeliac disease
Virchows Archiv (2014)
-
Hydroxylases as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease
Laboratory Investigation (2013)
-
Expression of PARK7 is increased in celiac disease
Virchows Archiv (2013)