Abstract
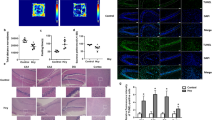
Using various animal models, studies have greatly expanded our understanding of perinatal hypoxia-induced neuronal injury in the newborn at the cellular/molecular levels. However, the synapse-basis pathogenesis and therapeutic strategy for such detrimental alterations in the neonatal brain remain to be addressed. We investigated whether the damaged synaptic efficacy and neurogenesis within hippocampal CA1 region (an essential integration area for mammalian learning and memory) of the neonatal rat brain after perinatal hypoxia were restored by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) therapy. Ten-day-old (P10) rat pups were subjected to experimentally perinatal hypoxia. G-CSF (10, 30, or 50 μg/kg, single injection/d, P11–16) was s.c. administered to neonatal rats which were analyzed on P17. Perinatal hypoxia reduced the expression in pRaf-pERK1/2-pCREBSer-133 signaling, the synaptic complex of postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) with N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunits (NR1, NR2A, and NR2B), synaptic efficacy, and neurogenesis. A representatively effective dosage of G-CSF (30 μg/kg) alleviated the perinatal hypoxia-induced detrimental changes and improved the performance in long-term cognitive function. In summary, our results suggest a novel concept that synaptic efficacy defects exist in the neonatal brain previously exposed to perinatal hypoxia and that G-CSF could be a clinical potential for the synapse-basis recovery in the perinatal hypoxia suffers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BrdU:
-
bromodeoxyuridine
- G-CSF:
-
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor
- LTP:
-
long-term potentiation
- NeuN:
-
neuronal nuclei
- NMDAR:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor
- pCREBSer-133:
-
phosphorylated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein at serine 133
- pERK1/2:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase ½
- pRaf:
-
phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein-kinase-kinase-kinase
- PSD-95:
-
postsynaptic density 95.
References
du Plessis AJ, Volpe JJ 2002 Perinatal brain injury in the preterm and term newborn. Curr Opin Neurol 15: 151–157
Oler JA, Markus EJ 1998 Age-related deficits on the radial maze and in fear conditioning: hippocampal processing and consolidation. Hippocampus 8: 402–415
Mizuno M, Yamada K, Olariu A, Nawa H, Nabeshima T 2000 Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats. J Neurosci 20: 7116–7121
Lin CS, Tao PL, Jong YJ, Chen WF, Yang CH, Huang LT, Chao CF, Yang SN 2009 Prenatal morphine alters the synaptic complex of PSD-95 with NMDA receptor subunit in hippocampal CA1 subregion of rat offspring leading to long-term cognitive deficits. Neuroscience 158: 1326–1337
Yamada Y, Chochi Y, Takamiya K, Sobue K, Inui M 1999 Modulation of the channel activity of the ε2/ζ1-subtype N-methyl-D-asparate receptor by PSD-95. J Biol Chem 274: 6647–6652
Kennedy MB 2000 Signal-processing machines at the postsynaptic density. Science 290: 750–754
Takagi N, Logan R, Teves L 2000 Altered interaction between PSD-95 and the NMDA receptor following transient global ischemia. J Neurochem 74: 169–178
Köhr G 2006 NMDA receptor function: subunit composition versus spatial distribution. Cell Tissue Res 326: 439–446
Chen WF, Chang H, Wong CS, Huang LT, Yang CH, Yang SN 2007 Impaired expression of postsynaptic density proteins in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats following perinatal hypoxia. Exp Neurol 204: 400–410
Bender RA, Luterborn JC, Gall CM, Cariage W, Baram TZ 2001 Enhanced phosphorylation in immature dentate gyrus cells precedes neutrophin expression and indicates a specific role of CREB in granule cells differentiation. Eur J Neurosci 13: 679–686
Kandel ER 2001 The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294: 1030–1038
Mayr B, Montminy M 2001 Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 599–609
Chen WF, Chang H, Huang LT, Yang CH, Lai MC, Wan TH, Yang SN 2006 Alterations in long-term seizure susceptibility and the complex of PSD-95 with NMDA receptor from animals previously exposed to perinatal hypoxia. Epilepsia 47: 288–296
Frampton JE, Lee CR, Faulds D 1994 Filgrastim. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in neutropenia. Drugs 48: 731–760
Heard SO, Fink MP 1999 Counterregulatory control of the acute inflammatory response: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor has anti-inflammatory properties. Crit Care Med 27: 1019–1021
Schäbitz WR, Kollmar R, Schwaninger M, Juettler E, Bardutzky J, Schölzke MN, Sommer C, Schwab S 2003 Neuroprotective effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 34: 745–751
Sheibani N, Grabowski EF, Schoenfeld DA, Whalen MJ 2004 Effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on functional and histopathologic outcome after traumatic brain injury in mice. Crit Care Med 32: 2274–2278
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Yang HI, Tzeng YS, Pang CY, Yen PS, Li H 2004 Functional recovery of stroke rats induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-stimulated stem cells. Circulation 110: 1847–1854
Gibson CL, Jones NC, Prior MJ, Bath PM, Murphy SP 2005 G-CSF suppresses edema formation and reduces interleukin-1beta expression after cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64: 763–769
Schneider A, Kruger C, Steigleder T, Weber D, Pitzer C, Laage R, Arononwski J, Maurer MH, Gassler N, Mier W, Hasselblatt M, Kollmar R, Schwab S, Sommer C, Bach A, Kuhn HG, Schabitz WR 2005 The hematopoietic factor G-CSF is a neuronal ligand that counteracts programmed cell death and drives neurogenesis. J Clin Invest 115: 2083–2098
Ohki Y, Heissig P, Sato Y, Akiyama H, Zhu Z, Hicklin DJ, Shimada K, Ogawa H, Daida H, Hattori K, Ohsaka A 2005 Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor promotes neovascularization by releasing vascular endothelial growth factor from neutrophils. FASEB J 19: 2005–2007
Solaroglu I, Jadhav V, Zhang JH 2007 Neuroprotective effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Front Biosci 12: 712–724
Yata K, Matchett GA, Tsubokawa T, Tang J, Kanamaru K, Zhang JH 2007 Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor inhibits apoptotic neuron loss after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1145: 227–238
Minnerup J, Heidrich J, Wellmann J, Rogalweski A, Schneider A, Schäbitz WR 2008 Meta-analysis of the efficacy of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in animal models of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 39: 1855–1861
Yang SN, Huang LT, Wang CL, Chen WF, Yang CH, Lin SZ, Lai MC, Chen SJ, Tao PL 2003 Prenatal administration of morphine decreases CREBSerine-133 phosphorylation and synaptic plasticity range mediated by glutamatergic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 area of cognitive-deficient rat offspring. Hippocampus 13: 915–921
Romijn HJ, Hofman MA, Gramsbergen A 1991 At what age is the developing cerebral cortex of the rat comparable to that of the full-term newborn human baby?. Early Hum Dev 26: 61–67
Impey S, Obrietan K, Wong ST, Poser S, Yano S, Wayman G, Deloulme JC, Chan G, Storm DR 1998 Cross talk between ERK and PKA required for Ca2+ stimulation of CREB-dependent transcription and ERK nuclear translocation. Neuron 21: 869–883
Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR 1999 Making new connections: role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron 23: 11–14
Bito H, Takemoto-Kimura S 2003 Ca(2+)/CREB/CBP-dependent gene regulation: a shared mechanism critical in long-term synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. Cell Calcium 34: 425–430
Tojima T, Ito E 2004 Signal transduction cascades underlying de novo protein synthesis required for neuronal morphogenesis in differentiating neurons. Prog Neurobiol 72: 183–193
Garoflos E, Stamatakis A, Mantelas A, Philippidis H, Stylianopoulou F 2005 Cellular mechanisms underlying an effect of “early handling” on pCREB and BDNF in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1052: 187–195
Hughes PE, Alexi T, Walton M, Williams CE, Dragunow M, Clark RG, Gluckman PD 1999 Activity and injury-dependent expression of inducible transcription factors, growth factors and apoptosis-related genes within the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 57: 421–450
Lie DC, Song H, Colamarino SA, Ming GL, Gage FH 2004 Neurogenesis in the adult brain: new strategies for central nervous system diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44: 399–421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 98-2320-B-037-022-MY3) and Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUH-97-7R06, KMUH99-9R-38 and KMUH-6R-23), Taiwan.
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WF., Hsu, JH., Lin, CS. et al. Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Alleviates Perinatal Hypoxia-Induced Decreases in Hippocampal Synaptic Efficacy and Neurogenesis in the Neonatal Rat Brain. Pediatr Res 70, 589–595 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182324424
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182324424
This article is cited by
-
The role of G-CSF neuroprotective effects in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE): current status
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)