Abstract
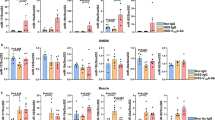
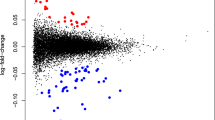
Vascular intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) occurs in about 5% of pregnancies and may reduce the incidence of periventricular leukomalacia in preterm newborns. We evaluated neonatal excitotoxicity in a murine model of vascular IUGR involving unilateral uterine ligation on embryonic day (E)13.5. Birth weight was significantly decreased in the ligation group compared with the sham group (p < 0.001). VEGFs, VEGF receptors (VEGFRs), and NMDA receptor subunit mRNAs in brain extracts were assayed using quantitative RT-PCR. Ligation was associated with increased mRNAs for the vascular marker PECAM-1 on postnatal day (PD)2 and VEGFR-3 on PD2 and PD10, contrasting with decreased VEGFA and VEGFC on PD10. Microvessel density was increased on PD7. Ligated and sham pups received intracerebral ibotenate (NMDA agonist) on PD2 or PD10. Cortical and white matter (WM) lesions after 5 d were reduced in ligated versus sham pups injected on PD2 (p < 0.001 and p < 0.01, respectively); this effect persisted on PD42 (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively). With ibotenate on PD10, lesions were exacerbated after 5 d in the ligated group in the cortex (p < 0.05) and WM (p < 0.05) and on PD42 in the cortex (p < 0.05). In conclusion, vascular IUGR offered only transient protection against neonatal excitotoxic lesions, possibly via angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AUVL:
-
antenatal uterine vessel ligation
- E:
-
embryonic day
- i.c.:
-
intracerebral
- NMDA-R:
-
glutamate receptors of the N-methyl-d-aspartic acid type
- PD:
-
postnatal day
- PECAM-1:
-
platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1, CD-31
- PVL:
-
periventricular leukomalacia
- VEGFR:
-
VEGF receptors (types 1, 2 or 3)
- WM:
-
white matter
References
Mandruzzato G, Antsaklis A, Botet F, Chervenak FA, Figueras F, Grunebaum A, Puerto B, Skupski D, Stanojevic M 2008 Intrauterine restriction (IUGR). J Perinat Med 36: 277–281
Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R 2008 Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet 371: 75–84
Pallotto EK, Kilbride HW 2006 Perinatal outcome and later implications of intrauterine growth restriction. Clin Obstet Gynecol 49: 257–269
Volpe JJ 2009 Brain injury in premature infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol 8: 110–124
Olney JW 1993 Role of excitotoxins in developmental neuropathology. APMIS 40: suppl 103–112
Murphy DJ, Sellers S, MacKenzie IZ, Yudkin PL, Johnson AM 1995 Case-control study of antenatal and intrapartum risk factors for cerebral palsy in very preterm singleton babies. Lancet 346: 1449–1454
Baud O, Zupan V, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Audibert F, Shojaei T, Thebaud B, Ville Y, Frydman R, Dehan M 2000 The relationships between antenatal management, the cause of delivery and neonatal outcome in a large cohort of very preterm singleton infants. BJOG 107: 877–884
Ancel PY, Marret S, Larroque B, Arnaud C, Zupan-Simunek V, Voyer M, Roze JC, Matis J, Burguet A, Ledesert B, Andre M, Pierrat V, Kaminski M 2005 Are maternal hypertension and small-for-gestational age risk factors for severe intraventricular hemorrhage and cystic periventricular leukomalacia? Results of the EPIPAGE cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193: 178–184
Dirnagl U, Becker K, Meisel A 2009 Preconditioning and tolerance against cerebral ischaemia: from experimental strategies to clinical use. Lancet Neurol 8: 398–412
Dirnagl U, Simon RP, Hallenbeck JM 2003 Ischemic tolerance and endogenous neuroprotection. Trends Neurosci 26: 248–254
Olivier P, Baud O, Bouslama M, Evrard P, Gressens P, Verney C 2007 Moderate growth restriction: deleterious and protective effects on white matter damage. Neurobiol Dis 26: 253–263
Wang X, Hagberg H, Nie C, Zhu C, Ikeda T, Mallard C 2007 Dual role of intrauterine immune challenge on neonatal and adult brain vulnerability to hypoxia-ischemia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66: 552–561
Eklind S, Mallard C, Arvidsson P, Hagberg H 2005 Lipopolysaccharide induces both a primary and a secondary phase of sensitization in the developing rat brain. Pediatr Res 58: 112–116
Xi L, Taher M, Yin C, Salloum F, Kukreja RC 2004 Cobalt chloride induces delayed cardiac preconditioning in mice through selective activation of HIF-1alpha and AP-1 and iNOS signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287: H2369–H2375
Sergeev P, da Silva R, Lucchinetti E, Zaugg K, Pasch T, Schaub MC, Zaugg M 2004 Trigger-dependent gene expression profiles in cardiac preconditioning: evidence for distinct genetic programs in ischemic and anesthetic preconditioning. Anesthesiology 100: 474–488
Laudenbach V, Fontaine RH, Medja F, Carmeliet P, Hicklin DJ, Gallego J, Leroux P, Marret S, Gressens P 2007 Neonatal hypoxic preconditioning involves vascular endothelial growth factor. Neurobiol Dis 26: 243–252
Olivier P, Baud O, Evrard P, Gressens P, Verney C 2005 Prenatal ischemia and white matter damage in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64: 998–1006
Husson I, Mesples B, Bac P, Vamecq J, Evrard P, Gressens P 2002 Melatoninergic neuroprotection of the murine periventricular white matter against neonatal excitotoxic challenge. Ann Neurol 51: 82–92
Laudenbach V, Mantz J, Lagercrantz H, Desmonts JM, Evrard P, Gressens P 2002 Effects of alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists on perinatal excitotoxic brain injury: comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine. Anesthesiology 96: 134–141
Gressens P, Marret S, Hill JM, Brenneman DE, Gozes I, Fridkin M, Evrard P 1997 Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents excitotoxic cell death in the murine developing brain. J Clin Invest 100: 390–397
Marret S, Mukendi R, Gadisseux JF, Gressens P, Evrard P 1995 Effect of ibotenate on brain development: an excitotoxic mouse model of microgyria and posthypoxic-like lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54: 358–370
Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K 2009 VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 154–165
Sentilhes L, Marret S, Leroux P, Gonzalez BJ, Laquerrière A 2011 Vascular-endothelial growth factor and its high affinity receptor VEGFR-2 in the normal versus destructive lesions in human forebrain during development: an immuno-histochemical comparative study. Brain Res 1385: 77–86
Rangon CM, Fortes S, Lelievre V, Leroux P, Plaisant F, Joubert C, Lanfumey L, Cohen-Salmon C, Gressens P 2007 Chronic mild stress during gestation worsens neonatal brain lesions in mice. J Neurosci 27: 7532–7540
Bernaudin M, Nedelec AS, Divoux D, MacKenzie ET, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P 2002 Normobaric hypoxia induces tolerance to focal permanent cerebral ischemia in association with an increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and its target genes, erythropoietin and VEGF, in the adult mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22: 393–403
Bernaudin M, Tang Y, Reilly M, Petit E, Sharp FR 2002 Brain genomic response following hypoxia and re-oxygenation in the neonatal rat. Identification of genes that might contribute to hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance. J Biol Chem 277: 39728–39738
Hennebert O, Laudenbach V, Laquerrière A, Verney C, Carmeliet P, Marret S, Leroux P 2005 Ontogenic study of the influence of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) in neonatal excitotoxic brain insult and the subsequent microglia/macrophage activation. Neuroscience 130: 697–712
Tsatsaris V, Goffin F, Munaut C, Brichant JF, Pignon MR, Noel A, Schaaps JP, Cabrol D, Frankenne F, Foidart JM 2003 Overexpression of the soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor in preeclamptic patients: pathophysiological consequences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 5555–5563
Savvidou MD, Yu CK, Harland LC, Hingorani AD, Nicolaides KH 2006 Maternal serum concentration of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in women with abnormal uterine artery Doppler and in those with fetal growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195: 1668–1673
Boutsikou T, Malamitsi-Puchner A, Economou E, Boutsikou M, Puchner KP, Hassiakos D 2006 Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in intrauterine growth restricted fetuses and neonates. Early Hum Dev 82: 235–239
Leonard H, Nassar N, Bourke J, Blair E, Mulroy S, de Klerk N, Bower C 2008 Relation between intrauterine growth and subsequent intellectual disability in a ten-year population cohort of children in Western Australia. Am J Epidemiol 167: 103–111
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. S. Jegou-Colleter, Dr. B.J. Gonzalez, and Dr. P. Mulder for technical help and critical discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by University of Rouen, the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), the Société Française d'Anesthésie Réanimation (SFAR), ELA Foundation, the European Found for Regional Development (FEDER), the Regional Council of Haute-Normandie, and the National Research Agency (ANR).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catteau, J., Gernet, JI., Marret, S. et al. Effects of Antenatal Uteroplacental Hypoperfusion on Neonatal Microvascularisation and Excitotoxin Sensitivity in Mice. Pediatr Res 70, 229–235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318224285f
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318224285f
This article is cited by
-
MIUH Inhibits the Hippocampal Neuron Growth in Fetal Rat by Affecting the PTEN Pathway
Neurochemical Research (2021)
-
Placental pathology and outcome after perinatal asphyxia and therapeutic hypothermia
Journal of Perinatology (2016)
-
Anhedonic behavior in cryptochrome 2-deficient mice is paralleled by altered diurnal patterns of amygdala gene expression
Amino Acids (2015)