Abstract
Background:
Overweight has its origins largely in early life. We aimed to identify the most important parental, fetal, and infant risk factors of preschool overweight.
Methods:
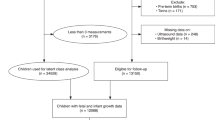
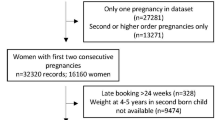
In a prospective cohort study, among 3,610 Caucasian preschool children, we assessed the associations of 34 putative parental, fetal, and infant factors with overweight risk.
Results:
Higher maternal BMI, paternal BMI, and birth weight were associated with higher risk of preschool overweight (odds ratio (OR): 1.23, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.10, 1.39; OR: 1.35, 95% CI: 1.19, 1.53; and OR: 2.71, 95% CI: 2.27, 3.25, respectively, per SD increase). The same model identified low household income (OR: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.24, 2.45), being female (OR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.20, 2.01), and experiencing third-trimester accelerated growth (OR: 1.73, 95% CI: 1.24, 2.40) or postnatal accelerated growth (OR: 6.39, 95% CI: 4.54, 8.99) as risk factors for preschool overweight. Higher polyunsaturated fat intake at 14 mo was associated with a lower risk of preschool overweight (OR: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.62, 0.96 per SD).
Conclusion:
Parental anthropometrics and household income, fetal and infant accelerated growth, and infant dietary fat intake are the major risk factors for the development of preschool overweight. Further studies need to explore whether these risk factors could be potential targets for preventive interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
REFERENCES
James WP . WHO recognition of the global obesity epidemic. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32:Suppl 7:S120–6.
Reilly JJ, Kelly J . Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011;35:891–8.
Bayer O, Krüger H, von Kries R, Toschke AM . Factors associated with tracking of BMI: a meta-regression analysis on BMI tracking. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011;19:1069–76.
Monasta L, Batty GD, Cattaneo A, et al. Early-life determinants of overweight and obesity: a review of systematic reviews. Obes Rev 2010;11:695–708.
Beyerlein A, Toschke AM, von Kries R . Risk factors for childhood overweight: shift of the mean body mass index and shift of the upper percentiles: results from a cross-sectional study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010;34:642–8.
Kitsantas P, Gaffney KF . Risk profiles for overweight/obesity among preschoolers. Early Hum Dev 2010;86:563–8.
Jouret B, Ahluwalia N, Cristini C, et al. Factors associated with overweight in preschool-age children in southwestern France. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;85:1643–9.
Dubois L, Girard M . Early determinants of overweight at 4.5 years in a population-based longitudinal study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006;30:610–7.
Huus K, Ludvigsson JF, Enskär K, Ludvigsson J . Risk factors in childhood obesity-findings from the All Babies In Southeast Sweden (ABIS) cohort. Acta Paediatr 2007;96:1321–5.
Júlíusson PB, Eide GE, Roelants M, Waaler PE, Hauspie R, Bjerknes R . Overweight and obesity in Norwegian children: prevalence and socio-demographic risk factors. Acta Paediatr 2010;99:900–5.
Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR, et al. Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ 2005;330:1357.
Blair NJ, Thompson JM, Black PN, et al. Risk factors for obesity in 7-year-old European children: the Auckland Birthweight Collaborative Study. Arch Dis Child 2007;92:866–71.
Kuhle S, Allen AC, Veugelers PJ . Perinatal and childhood risk factors for overweight in a provincial sample of Canadian Grade 5 students. Int J Pediatr Obes 2010;5:88–96.
Brophy S, Cooksey R, Gravenor MB, et al. Risk factors for childhood obesity at age 5: analysis of the millennium cohort study. BMC Public Health 2009;9:467.
Mook-Kanamori DO, Durmus B, Sovio U, et al. Fetal and infant growth and the risk of obesity during early childhood: the Generation R Study. Eur J Endocrinol 2011;165:623–30.
Ay L, Van Houten VA, Steegers EA, et al. Fetal and postnatal growth and body composition at 6 months of age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:2023–30.
Centrum voor Onderzoek en Statistiek (Centre for Research and Statistics). (http://www.rotterdam.nl/onderzoek). 2005. Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
de Wilde JA, van Dommelen P, Middelkoop BJ, Verkerk PH . Trends in overweight and obesity prevalence in Dutch, Turkish, Moroccan and Surinamese South Asian children in the Netherlands. Arch Dis Child 2009;94:795–800.
Pilgaard K, Hammershaimb Mosbech T, Grunnet L, et al. Differential nongenetic impact of birth weight versus third-trimester growth velocity on glucose metabolism and magnetic resonance imaging abdominal obesity in young healthy twins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:2835–43.
Morrison JL, Duffield JA, Muhlhausler BS, Gentili S, McMillen IC . Fetal growth restriction, catch-up growth and the early origins of insulin resistance and visceral obesity. Pediatr Nephrol 2010;25:669–77.
Byrne LK, Cook KE, Skouteris H, Do M . Parental status and childhood obesity in Australia. Int J Pediatr Obes 2011;6:415–8.
van Rossem L, Silva LM, Hokken-Koelega A, et al. Socioeconomic status is not inversely associated with overweight in preschool children. J Pediatr 2010;157:929–935.e1.
Moorcroft KE, Marshall JL, McCormick FM . Association between timing of introducing solid foods and obesity in infancy and childhood: a systematic review. Matern Child Nutr 2011;7:3–26.
Seach KA, Dharmage SC, Lowe AJ, Dixon JB . Delayed introduction of solid feeding reduces child overweight and obesity at 10 years. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010;34:1475–9.
Tai CC, Ding ST . N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids regulate lipid metabolism through several inflammation mediators: mechanisms and implications for obesity prevention. J Nutr Biochem 2010;21:357–63.
Jaddoe VW, van Duijn CM, van der Heijden AJ, et al. The Generation R Study: design and cohort update 2010. Eur J Epidemiol 2010;25:823–41.
Durmus B, Kruithof CJ, Gillman MH, et al. Parental smoking during pregnancy, early growth, and risk of obesity in preschool children: the Generation R Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;94:164–71.
Timmermans S, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Steegers-Theunissen RP, Steegers EA . Periconception folic acid supplementation, fetal growth and the risks of low birth weight and preterm birth: the Generation R Study. Br J Nutr 2009;102:777–85.
Klipstein-Grobusch K, den Breeijen JH, Goldbohm RA, et al. Dietary assessment in the elderly: validation of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Eur J Clin Nutr 1998;52:588–96.
Verburg BO, Steegers EA, De Ridder M, et al. New charts for ultrasound dating of pregnancy and assessment of fetal growth: longitudinal data from a population-based cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31:388–96.
Hadlock FP, Harrist RB, Sharman RS, Deter RL, Park SK . Estimation of fetal weight with the use of head, body, and femur measurements–a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:333–7.
Sonnenschein-van der Voort AM, Jaddoe VW, Raat H, et al. Fetal and infant growth and asthma symptoms in preschool children: the Generation R Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2012;185:731–7.
Niklasson A, Ericson A, Fryer JG, Karlberg J, Lawrence C, Karlberg P . An update of the Swedish reference standards for weight, length and head circumference at birth for given gestational age (1977–1981). Acta Paediatr Scand 1991;80:756–62.
Feunekes GI, Van Staveren WA, De Vries JH, Burema J, Hautvast JG . Relative and biomarker-based validity of a food-frequency questionnaire estimating intake of fats and cholesterol. Am J Clin Nutr 1993;58:489–96.
Iglowstein I, Jenni OG, Molinari L, Largo RH . Sleep duration from infancy to adolescence: reference values and generational trends. Pediatrics 2003;111:302–7.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Public Education. American Academy of Pediatrics: Children, adolescents, and television. Pediatrics 2001;107:423–6.
Statistics Netherlands (Centraal Bureau voor Statistiek). Labor force survey ‘09 (Enquête Beroepsbevolking ‘09). Heerlen, the Netherlands: http://www.cbs.nl, 2009.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH . Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 2000;320:1240–3.
Willett WC, Howe GR, Kushi LH . Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am J Clin Nutr 1997;65:Suppl 4:1220S–1228S; discussion 1229S–1231S.
Sterne JA, White IR, Carlin JB, et al. Multiple imputation for missing data in epidemiological and clinical research: potential and pitfalls. BMJ 2009;338:b2393.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of participants and assistance of general practitioners, hospitals, midwives, and pharmacies in Rotterdam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heppe, D., Kiefte-de Jong, J., Durmuş, B. et al. Parental, fetal, and infant risk factors for preschool overweight: the Generation R Study. Pediatr Res 73, 120–127 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.145
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.145
This article is cited by
-
Relationships between intrauterine fetal growth trajectories and markers of adiposity and inflammation in young adults
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
-
Environmental exposure to urinary Bisphenol-A in North Indian children aged between 6 and 16 years and its association with body mass index
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
From conception to infancy — early risk factors for childhood obesity
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2019)
-
Risks of maternal prepregnancy overweight/obesity, excessive gestational weight gain, and bottle-feeding in infancy rapid weight gain: evidence from a cohort study in China
Science China Life Sciences (2019)
-
Early life risk factors and their cumulative effects as predictors of overweight in Spanish children
International Journal of Public Health (2018)