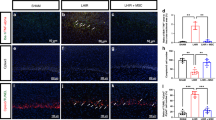
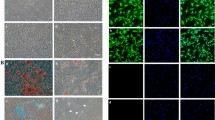
Abstract
Background:
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy may prevent neonatal hyperoxia-induced lung injury (HILI). There are, however, no clear data on the therapeutic efficacy of MSC therapy in established HILI, the duration of the reparative effects, and the exact mechanisms of repair. The main objective of this study was to evaluate whether the long-term reparative effects of a single intratracheal (IT) dose of MSCs or MSC-conditioned medium (CM) are comparable in established HILI.
Methods:
Newborn rats exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia from postnatal day (P)2)–P16 were randomized to receive IT MSCs, IT CM, or IT placebo (PL) on P9. Alveolarization and angiogenesis were evaluated at P16, P30, and P100.
Results:
At all time periods, there were marked improvements in alveolar and vascular development in hyperoxic pups treated with MSCs or CM as compared with PL. This was associated with decreased expression of inflammatory mediators and an upregulation of angiogenic factors. Of note, at P100, the improvements were more substantial with MSCs as compared with CM.
Conclusion:
These data suggest that acute effects of MSC therapy in HILI are mainly paracrine mediated; however, optimum long-term improvement following HILI requires treatment with the MSCs themselves or potentially repetitive administration of CM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jobe AH, Bancalari E . Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163:1723–9.
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2010;126:443–56.
Jobe AJ . The new BPD: an arrest of lung development. Pediatr Res 1999;46:641–3.
Weiss DJ, Kolls JK, Ortiz LA, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Prockop DJ . Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and lung diseases. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008;5:637–67.
Krause DS, Theise ND, Collector MI, et al. Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone marrow-derived stem cell. Cell 2001;105:369–77.
Krasnodembskaya A, Song Y, Fang X, et al. Antibacterial effect of human mesenchymal stem cells is mediated in part from secretion of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Stem Cells 2010;28:2229–38.
Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, Lee JW, Serikov V, Matthay MA . Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol 2007;179:1855–63.
van Haaften T, Byrne R, Bonnet S, et al. Airway delivery of mesenchymal stem cells prevents arrested alveolar growth in neonatal lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;180:1131–42.
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ . Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair–current views. Stem Cells 2007;25:2896–902.
Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;180:1122–30.
Roberts RJ, Weesner KM, Bucher JR . Oxygen-induced alterations in lung vascular development in the newborn rat. Pediatr Res 1983;17:368–75.
Wilson WL, Mullen M, Olley PM, Rabinovitch M . Hyperoxia-induced pulmonary vascular and lung abnormalities in young rats and potential for recovery. Pediatr Res 1985;19:1059–67.
Stahlman MT, Gray ME, Whitsett JA . Expression of thyroid transcription factor-1(TTF-1) in fetal and neonatal human lung. J Histochem Cytochem 1996;44:673–8.
Lee JW, Fang X, Krasnodembskaya A, Howard JP, Matthay MA . Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors. Stem Cells 2011;29:913–9.
Thébaud B . Angiogenesis in lung development, injury and repair: implications for chronic lung disease of prematurity. Neonatology 2007;91:291–7.
Kotecha S, Wilson L, Wangoo A, Silverman M, Shaw RJ . Increase in interleukin (IL)-1 beta and IL-6 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid obtained from infants with chronic lung disease of prematurity. Pediatr Res 1996;40:250–6.
Ray P, Tang W, Wang P, et al. Regulated overexpression of interleukin 11 in the lung. Use to dissociate development-dependent and -independent phenotypes. J Clin Invest 1997;100:2501–11.
Maeda Y, Davé V, Whitsett JA . Transcriptional control of lung morphogenesis. Physiol Rev 2007;87:219–44.
Kimura S, Hara Y, Pineau T, et al. The T/ebp null mouse: thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein is essential for the organogenesis of the thyroid, lung, ventral forebrain, and pituitary. Genes Dev 1996;10:60–9.
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006;8:315–7.
Yet SF, Perrella MA, Layne MD, et al. Hypoxia induces severe right ventricular dilatation and infarction in heme oxygenase-1 null mice. J Clin Invest 1999;103:R23–9.
Fulton RM, Hutchinson EC, Jones AM . Ventricular weight in cardiac hypertrophy. Br Heart J 1952;14:413–20.
Young KC, Torres E, Hatzistergos KE, Hehre D, Suguihara C, Hare JM . Inhibition of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis attenuates neonatal hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 2009;104:1293–301.
McGrath-Morrow SA, Cho C, Soutiere S, Mitzner W, Tuder R . The effect of neonatal hyperoxia on the lung of p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1-deficient mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2004;30:635–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Methods online
(PDF 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sutsko, R., Young, K., Ribeiro, A. et al. Long-term reparative effects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy following neonatal hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Pediatr Res 73, 46–53 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.152
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.152
This article is cited by
-
Perinatal origins of bronchopulmonary dysplasia—deciphering normal and impaired lung development cell by cell
Molecular and Cellular Pediatrics (2023)
-
Consecutive daily administration of intratracheal surfactant and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2021)
-
Paracrine stimulation of perinatal lung functional and structural maturation by mesenchymal stem cells
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Intra-tracheal administration of a naked plasmid expressing stromal derived factor-1 improves lung structure in rodents with experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Respiratory Research (2019)
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell conditioned media for lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies
Respiratory Research (2019)