Abstract
Background:
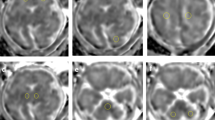
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of axonal degenerative changes in the cerebral peduncle of the corticospinal tract following cerebral hypoxic–ischemic damage might distinguish infants most appropriate for receiving prompt treatment. The optimal MRI sequence for very early diagnosis of axonal degenerative changes is unknown. We hypothesized that magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) imaging would be more sensitive than traditional MRI, e.g., T2 or diffusion weighted imaging.
Methods:
Transient unilateral cerebral hypoxia–ischemia was produced in the neonatal rat followed by MRI of changes in T2, the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of water, and MTR, with a focus on the parietal cortex (an ischemic damaged region) and the cerebral peduncle (remote within the corticospinal tract). Rats were imaged at 2 h, 1 d, or 1 wk postinsult.
Results:
In the cerebral peduncle, MTR and T2 responded similarly, with alterations occurring ipsilaterally at 1 d postinsult. ADC was most sensitive for detecting changes as early as 2 h postinsult, and this corresponded to a reduced staining of axonal filaments ipsilaterally.
Conclusion:
MTR and T2 imaging have comparable sensitivity for distinguishing early axonal damage in the cerebral peduncle. ADC imaging is highly sensitive for detecting early disruption of corticospinal axons, supporting its potential hyperacute diagnostic use clinically.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Volpe JJ . Perinatal brain injury: from pathogenesis to neuroprotection. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2001;7:56–64.
Folkerth RD . The neuropathology of acquired pre- and perinatal brain injuries. Semin Diagn Pathol 2007;24:48–57.
Kirton A, deVeber G . Advances in perinatal ischemic stroke. Pediatr Neurol 2009;40:205–14.
Bennet L, Booth L, Gunn AJ . Potential biomarkers for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;15:253–60.
Perlman M, Shah PS . Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: challenges in outcome and prediction. J Pediatr 2011;158:Suppl 2:e51–4.
Lawrence RK, Inder TE . Anatomic changes and imaging in assessing brain injury in the term infant. Clin Perinatol 2008;35:679–93, vi.
Counsell SJ, Tranter SL, Rutherford MA . Magnetic resonance imaging of brain injury in the high-risk term infant. Semin Perinatol 2010;34:67–78.
Ferriero DM, Miller SP . Imaging selective vulnerability in the developing nervous system. J Anat 2010;217:429–35.
Ment LR, Hirtz D, Hüppi PS . Imaging biomarkers of outcome in the developing preterm brain. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:1042–55.
Boardman JP, Ganesan V, Rutherford MA, Saunders DE, Mercuri E, Cowan F . Magnetic resonance image correlates of hemiparesis after neonatal and childhood middle cerebral artery stroke. Pediatrics 2005;115:321–6.
Lee J, Croen LA, Lindan C, et al. Predictors of outcome in perinatal arterial stroke: a population-based study. Ann Neurol 2005;58:303–8.
Domi T, deVeber G, Shroff M, Kouzmitcheva E, MacGregor DL, Kirton A . Corticospinal tract pre-wallerian degeneration: a novel outcome predictor for pediatric stroke on acute MRI. Stroke 2009;40:780–7.
Kirton A, Shroff M, Visvanathan T, deVeber G . Quantified corticospinal tract diffusion restriction predicts neonatal stroke outcome. Stroke 2007;38:974–80.
Lama S, Qiao M, Kirton A, et al. Imaging corticospinal degeneration in neonatal rats with unilateral cerebral infarction. Exp Neurol 2011;228:192–9.
Tofts PS . MT: magnetization transfer. In: Tofts PS, ed. Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Measuring Changes Caused by Disease. Chichester, UK: Wiley, 2003:257–98.
Henkelman RM, Stanisz GJ, Graham SJ . Magnetization transfer in MRI: a review. NMR Biomed 2001;14:57–64.
Jiang Q, Ewing JR, Zhang ZG, et al. Magnetization transfer MRI: application to treatment of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001;13:178–84.
Tuor UI, Meng S, Qiao M, et al. Differential progression of magnetization transfer imaging changes depending on severity of cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008;28:1613–23.
Kato Y, Matsumura K, Kinosada Y, Narita Y, Kuzuhara S, Nakagawa T . Detection of pyramidal tract lesions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with magnetization-transfer measurements. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18:1541–7.
Tanabe JL, Vermathen M, Miller R, Gelinas D, Weiner MW, Rooney WD . Reduced MTR in the corticospinal tract and normal T2 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging 1998;16:1163–9.
da Rocha AJ, Oliveira AS, Fonseca RB, Maia AC Jr, Buainain RP, Lederman HM . Detection of corticospinal tract compromise in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with brain MR imaging: relevance of the T1-weighted spin-echo magnetization transfer contrast sequence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:1509–15.
Lexa FJ, Grossman RI, Rosenquist AC . Dyke Award paper. MR of wallerian degeneration in the feline visual system: characterization by magnetization transfer rate with histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1994;15:201–12.
Vannucci RC, Lyons DT, Vasta F . Regional cerebral blood flow during hypoxia-ischemia in immature rats. Stroke 1988;19:245–50.
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ . Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 2005;27:81–6.
Qiao M, Malisza KL, Del Bigio MR, Tuor UI . Correlation of cerebral hypoxic-ischemic T2 changes with tissue alterations in water content and protein extravasation. Stroke 2001;32:958–63.
Qiao M, Malisza KL, Del Bigio MR, Tuor UI . Transient hypoxia-ischemia in rats: changes in diffusion-sensitive MR imaging findings, extracellular space, and Na+-K+ -adenosine triphosphatase and cytochrome oxidase activity. Radiology 2002;223:65–75.
Meng S, Qiao M, Foniok T, Tuor UI . White matter damage precedes that in gray matter despite similar magnetic resonance imaging changes following cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats. Exp Brain Res 2005;166:56–60.
Kerschensteiner M, Schwab ME, Lichtman JW, Misgeld T . In vivo imaging of axonal degeneration and regeneration in the injured spinal cord. Nat Med 2005;11:572–7.
Nikic I, Merkler D, Sorbara C, et al. A reversible form of axon damage in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 2011;17:495–9.
da Rocha AJ, Maia AC Jr, da Silva CJ, et al. Pyramidal tract degeneration in multiple system atrophy: the relevance of magnetization transfer imaging. Mov Disord 2007;22:238–44.
Haynes RL, Borenstein NS, Desilva TM, et al. Axonal development in the cerebral white matter of the human fetus and infant. J Comp Neurol 2005;484:156–67.
Sun SW, Liang HF, Cross AH, Song SK . Evolving Wallerian degeneration after transient retinal ischemia in mice characterized by diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2008;40:1–10.
Paxinos G, Watson C . The Rat Brain in Sterotaxic Coordinates, 4th edn. New York: Academic Press, 1998.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank C. Smith and I. Jalal for contributing to preliminary image analysis and histology; M. Sule for helping with editing of the figures; and D. Kirk for providing animal anesthesia and monitoring during acquisition of magnetic resonance images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuor, U., Qiao, M., Morgunov, M. et al. Magnetization transfer and diffusion imaging of acute axonal damage in the cerebral peduncle following hypoxia–ischemia in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res 73, 325–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.178
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.178