Abstract
Background:
Tandem mass spectrometry has been proposed as a method of diagnosing or predicting the development of common complex neonatal diseases. Our objective was to identify metabolites associated with common complications of prematurity.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective analysis of medical data and metabolite measurements from routine neonatal screening on 689 preterm (<37 wk of gestational age) neonates.
Results:
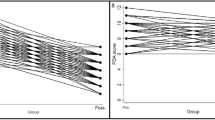
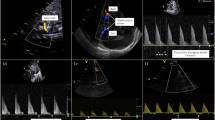
We observed higher levels of phenylalanine (PHE) in infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS; P = 1.7 × 10−5), the only association that was significant after correction for multiple testing. We found suggestive significance (P < 0.001) of higher essential amino acids in infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Functionality of these findings was explored in the ductus arteriosus (DA) isolated from term and preterm mouse pups. None of the amino acids had a direct vasodilatory effect on the isolated DA.
Conclusion:
We found that newborns with RDS had higher levels of PHE that may be a result of impaired PHE hydroxylase activity. We also detected marginally higher levels of all measured essential amino acids in infants with PDA. We did not find dilation of the mouse ductus for these metabolites, indicating that instead of potentially causing PDA, they are probably serving as markers of catabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Atzori L, Antonucci R, Barberini L, Griffin JL, Fanos V . Metabolomics: a new tool for the neonatologist. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009;22:Suppl 3:50–3.
Antonucci R, Atzori L, Barberini L, Fanos V . Metabolomics: the “new clinical chemistry” for personalized neonatal medicine. Minerva Pediatr 2010;62:3 Suppl 1:145–8.
Fanos V, Barberini L, Antonucci R, Atzori L . Metabolomics in neonatology and pediatrics. Clin Biochem 2011;44:452–4.
Atzori L, Antonucci R, Barberini L, et al. 1H NMR-based metabolomic analysis of urine from preterm and term neonates. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2011;3:1005–12.
Oladipo OO, Weindel AL, Saunders AN, Dietzen DJ . Impact of premature birth and critical illness on neonatal range of plasma amino acid concentrations determined by LC-MS/MS. Mol Genet Metab 2011;104:476–9.
Chu CY, Xiao X, Zhou XG, et al. Metabolomic and bioinformatic analyses in asphyxiated neonates. Clin Biochem 2006;39:203–9.
Favretto D, Cosmi E, Ragazzi E, et al. Cord blood metabolomic profiling in intrauterine growth restriction. Anal Bioanal Chem 2012;402:1109–21.
Dessì A, Atzori L, Noto A, et al. Metabolomics in newborns with intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR): urine reveals markers of metabolic syndrome. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;24:Suppl 2:35–9.
Fanos V, Antonucci R, Barberini L, Noto A, Atzori L . Clinical application of metabolomics in neonatology. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:Suppl 1:104–9.
Siegel JH . Cardiorespiratory manifestations of metabolic failure in sepsis and the multiple organ failure syndrome. Surg Clin North Am 1983;63:379–99.
Kuo CD, Wu WG, Wang JH, Chen SM, Chiang BN . Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of plasma to determine metabolic status of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Chem 1989;35:667–70.
Ploder M, Neurauter G, Spittler A, Schroecksnadel K, Roth E, Fuchs D . Serum phenylalanine in patients post trauma and with sepsis correlate to neopterin concentrations. Amino Acids 2008;35:303–7.
Harper AE, Miller RH, Block KP . Branched-chain amino acid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 1984;4:409–54.
Illsinger S, Schmidt KH, Lücke T, Vaske B, Bohnhorst B, Das AM . Plasma and urine amino acid pattern in preterm infants on enteral nutrition: impact of gestational age. Amino Acids 2010;38:959–72.
Borum PR . Plasma carnitine compartment and red blood cell carnitine compartment of healthy adults. Am J Clin Nutr 1987;46:437–41.
Harper P, Wadström C, Cederblad G . Carnitine measurements in liver, muscle tissue, and blood in normal subjects. Clin Chem 1993;39:592–9.
Reuter SE, Evans AM, Chace DH, Fornasini G . Determination of the reference range of endogenous plasma carnitines in healthy adults. Ann Clin Biochem 2008;45(Pt 6):585–92.
Borum PR . Regulation of the carnitine deficiency syndromes. In: Frenkel RA, McGarry JD, eds. Carnitine Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Functions. New York: Academic Press, 1980:115–26.
Steffen KM, Cooper ME, Shi M, et al. Maternal and fetal variation in genes of cholesterol metabolism is associated with preterm delivery. J Perinatol 2007;27:672–80.
Ehn NL, Cooper ME, Orr K, et al. Evaluation of fetal and maternal genetic variation in the progesterone receptor gene for contributions to preterm birth. Pediatr Res 2007;62:630–5.
Walsh MC, Kliegman RM . Necrotizing enterocolitis: treatment based on staging criteria. Pediatr Clin North Am 1986;33:179–201.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Newborn screening for preterm, low birth weight, and sick newborns; approved guideline. CLSI Document I/LA31-A 2004;29:1–29. Wayne, PA: CLSI.
Turgeon C, Magera MJ, Allard P, et al. Combined newborn screening for succinylacetone, amino acids, and acylcarnitines in dried blood spots. Clin Chem 2008;54:657–64.
Chace DH, Lim T, Hansen CR, De Jesus VR, Hannon WH . Improved MS/MS analysis of succinylacetone extracted from dried blood spots when combined with amino acids and acylcarnitine butyl esters. Clin Chim Acta 2009;407:6–9.
Chace DH, DiPerna JC, Mitchell BL, Sgroi B, Hofman LF, Naylor EW . Electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of acylcarnitines in dried postmortem blood specimens collected at autopsy from infants with unexplained cause of death. Clin Chem 2001;47:1166–82.
Reese J, Waleh N, Poole SD, Brown N, Roman C, Clyman RI . Chronic in utero cyclooxygenase inhibition alters PGE2-regulated ductus arteriosus contractile pathways and prevents postnatal closure. Pediatr Res 2009;66:155–61.
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the coordinating medical and research staff at the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics in Iowa City, Iowa, including a special thanks to research coordinators Laura Knosp and Susan Berends. We thank the Congenital and Inherited Disorders Advisory Committee, particularly Kim Piper for her enthusiastic support and management. We thank Sara Copeland at the Health Resources Services Administration for her guidance and support on this project. We thank Franklin Delin and Dariush Shirazi from the State Hygienic Laboratory for their assistance in the acquisition of the newborn screening data. We also thank Susie McConnell, Nancy Davin, and Erin Brothers-Smith for administrative support.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryckman, K., Dagle, J., Shchelochkov, O. et al. Association of amino acids with common complications of prematurity. Pediatr Res 73, 700–705 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.43
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.43
This article is cited by
-
Newborn screen metabolic panels reflect the impact of common disorders of pregnancy
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Newborn metabolic vulnerability profile identifies preterm infants at risk for mortality and morbidity
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Polymorphisms in urea cycle enzyme genes are associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
Pediatric Research (2018)
-
Analysis and interpretation of acylcarnitine profiles in dried blood spot and plasma of preterm and full-term newborns
Pediatric Research (2015)