Abstract
Background
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Network Neurobehavioral Scale (NNNS) is a standardized method for infant neurobehavioral assessment. Normative values are available for newborns, but the NNNS is not always feasible at birth. Unfortunately, 1-month NNNS normative data are lacking.
Aims
To provide normative data for the NNNS examination at 1 month and to assess birth-to-one-month changes in NNNS summary scores.
Study design
The NNNS was administered at birth and at 1 month within a longitudinal prospective study design.
Subjects
A cohort of 99 clinically healthy full-term infants were recruited from a well-child nursery.
Outcome measures
Birth-to-1-month NNNS variations were evaluated and the association of neonatal and sociodemographic variables with the rate of change of NNNS summary scores were investigated.
Results and conclusions
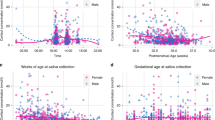
NNNS scores from the 10th to the 90th percentile represent a range of normative performance at 1 month. A complex pattern of stability and change emerged comparing NNNS summary scores from birth to 1 month. Orienting, Regulation, and Quality of movements significantly increased, whereas Lethargy and Hypotonicity significantly decreased. Birth-to-1-month changes in NNNS performance suggest improvements in neurobehavioral organization. These data are useful for research purposes and for clinical evaluation of neurobehavioral performance in both healthy and at-risk 1-month-old infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lester BM, Tronick EZ . History and description of the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Network Neurobehavioral Scale. Pediatrics 2004;113 (3, Part 2): 634–640.
Lester BM, Tronick EZ, LaGasse L et al. Summary statistics of neonatal intensive care unit network neurobehavioral scale scores from the maternal lifestyle study: a quasinormative sample. Pediatrics 2004;113:668–675.
Lester BM, Tronick EZ, Brazelton TB . The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Network Neurobehavioral Scale procedures. Pediatrics 2004;113 (3): 641–667.
Lester BM, Tronick EZ, LaGasse L et al. The maternal lifestyle study: effects of substance exposure during pregnancy on neurodevelopmental outcome in 1-month-old infants. Pediatrics 2002;110 (6): 1182–1192.
Salisbury AL, Lester BM, Seifer R et al. Prenatal cocaine use and maternal depression: effects on infant neurobehavior. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007;29 (3): 331–340.
Coyle MG, Salisbury AL, Lester BM et al. Neonatal neurobehavior effects following buprenorphine versus methadone exposure. Addiction 2012;107 (Suppl 1): 63–73.
Montirosso R, Del Prete A., Bellu R, Tronick E, Borgatti R, Group NAC for Q of L (NEO-AS. Level of NICU quality of developmental care and neurobehavioral performance in very preterm infants. Pediatrics 2012;129 (5): e1129–e1137.
Liu J, Bann C, Lester B et al. Neonatal neurobehavior predicts medical and behavioral outcome. Pediatrics 2010;125 (1): e90–e98.
Sucharew H, Khoury JC, Xu Y, Succop P, Yolton K . NICU Network Neurobehavioral Scale Profiles Predict Developmental Outcomes in a LOW-RISK SAMPLE. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2012;26 (4): 344–352.
Tronick E, Lester BM . Grandchild of the NBAS: The NICU Network Neurobehavioral Scale (NNNS): a review of the research using the NNNS. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs 2013;26 (3): 193–203.
Fink NS, Tronick E, Olson K, Lester B . Healthy newborns’ neurobehavior: norms and relations to medical and demographic factors. J Pediatr. 2012;161 (6): 1073–1079.e3.
Spittle AJ, Walsh J, Olsen JE et al. Neurobehaviour and neurological development in the first month after birth for infants born between 32–42 weeks’ gestation. Early Hum Dev 2016;96:7–14.
Lester BM, Miller RJ, Hawes K et al. Infant neurobehavioral development. Semin Perinatol 2011;35 (1): 8–19.
Noble Y, Boyd R . Neonatal assessments for the preterm infant up to 4 months corrected age: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 2012;54 (2): 129–139.
Hobel CJ, Youkeles L, Forsythe A . Prenatal and intrapartum high-risk screening: II. Risk factors reassessed. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1979;135 (8): 1051–1056.
Maloni JA, Kane JH, Suen L, Wang KK . Dysphoria among high-risk pregnant hospitalized women on bed rest: a longitudinal study. Nurs Res 2002;51 (2): 92–99.
Hollingshead AB . Four Factor Index of Social Status. New Haven, CT: Yale University, 1968.
DeSantis A, Harkins D, Tronick E, Kaplan E, Beeghly M . Exploring an integrative model of infant behavior: What is the relationship among temperament, sensory processing, and neurobehavioral measures? Infant Behav Dev 2011;34 (2): 280–292.
Tronick EZ, Olson K, Rosenberg R, Bohne L, Lu J, Lester BM . Normative neurobehavioral performance of healthy infants on the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Network Neurobehavioral Scale. Pediatrics 2004;113 (3, Part 2): 676–678.
Hadders-Algra M, Prechtl HF . Developmental course of general movements in early infancy. I. Descriptive analysis of change in form. Early Hum Dev 28 (3): 201–213.
Mirmiran M, Lunshof S . Perinatal development of human circadian rhythms. Prog Brain Res 1996;111:217–226.
Brown N, Spittle A . Neurobehavioral evaluation in the preterm and term infant. Curr Pediatr Rev 2014;10 (1): 65–72.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Standardization of the NRN-Neurobehavioral Scale, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (R01Hd37138 to E.T.). The supporting agency has no role in study design, collection, analysis and interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript, and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Provenzi, L., Olson, K., Giusti, L. et al. NICU Network Neurobehavioral Scale: 1-month normative data and variation from birth to 1 month. Pediatr Res 83, 1104–1109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2018.25
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2018.25
This article is cited by
-
Impaired in vivo feto-placental development is associated with neonatal neurobehavioral outcomes
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
Randomized clinical trial investigating the effect of consistent, developmentally-appropriate, and evidence-based multisensory exposures in the NICU
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Development of an abbreviated symptom score for the neonatal abstinence syndrome
Journal of Perinatology (2020)
-
Psychosocial and medical adversity associated with neonatal neurobehavior in infants born before 30 weeks gestation
Pediatric Research (2020)