Abstract
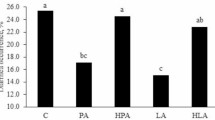
Our study aimed at investigating the impact of the level of protein in milk formula on intestinal structure, barrier function, and its nervous regulation in normal and LBW neonates using a porcine model. Normal birth weight (NBW) or LBW piglets were fed from d7 to d28 of age either with a high protein (HP) or with an adequate protein (AP) formula or stayed with their mother [mother fed (MF)]. The proximal jejunum and distal ileum were sampled at d28 for morphometry analysis and ex vivo permeability measurement in Ussing chambers. Formula feeding induced a trophic effect on the jejunum and ileum of both NBW and LBW piglets, which exhibited longer villi than MF animals, irrespective of the type of formula. In NBW piglets, intestinal permeability was not altered by formula feeding. On the contrary, LBW piglets fed with HP formula, but not AP, exhibited a greater ileal permeability than MF piglets. Feeding the HP formula also disturbed jejunal and ileal regulation of permeability by acetylcholine and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in LBW compared with MF LBW piglets. In conclusion, the level of protein in formulas did not modify intestinal structure and function in NBW individuals but dramatically modified intestinal barrier function physiology in LBW individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AChE:
-
acetylcholine esterase
- AP:
-
adequate protein
- CGN:
-
cingulin
- ChAT:
-
choline acetyl transferase
- FD-4:
-
FITC-dextran 4000
- HP:
-
high protein
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- MF:
-
mother fed
- NBW:
-
normal birth weight
- TJ:
-
tight junction
- VIP:
-
vasoactive intestinal peptide
References
Jost R, Maire JC, Maynard F, Secretin MC 1999 Aspects of whey protein usage in infant nutrition, a brief review. Int J Food Sci Technol 34: 533–542
Baird J, Fisher D, Lucas P, Kleijnen J, Roberts H, Law C 2005 Being big or growing fast: systematic review of size and growth in infancy and later obesity. BMJ 331: 929–931
Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Akrout M, Bellisle F 1995 Influence of macronutrients on adiposity development: a follow up study of nutrition and growth from 10 months to 8 years of age. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 19: 573–578
Turck D, Grillon C, Lachambre E, Robiliard P, Beck L, Maurin JL, Kempf C, Bernet JP, Marx J, Lebrun F, Van Egroo LD 2006 Adequacy and safety of an infant formula with a protein/energy ratio of 1.8 g/100 kcal and enhanced protein efficiency for term infants during the first 4 months of life. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 43: 364–371
Thureen P, Heird WC 2005 Protein and energy requirements of the preterm/low birthweight (LBW) infant. Pediatr Res 57: 95R–98R
Thompson FM, Catto-Smith AG, Moore D, Davidson G, Cummins AG 1998 Epithelial growth of the small intestine in human infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26: 506–512
Yeh KY 1983 Small intestine of artificially reared pups: weight gain and changes in alkaline phosphatase, lactase and sucrase activities during development. J Nutr 113: 1489–1495
Dvorak B, McWilliam DL, Williams CS, Dominguez JA, Machen NW, McCuskey RS, Philipps AF 2000 Artificial formula induces precocious maturation of the small intestine of artificially reared suckling rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 31: 162–169
Cameron HL, Perdue MH 2007 Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation increases transcellular transport of macromolecules across mouse and human intestinal epithelium in vitro. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19: 47–56
Neunlist M, Toumi F, Oreschkova T, Denis M, Leborgne J, Laboisse CL, Galmiche JP, Jarry A 2003 Human ENS regulates the intestinal epithelial barrier permeability and a tight junction-associated protein ZO-1 via VIPergic pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285: G1028–G1036
Catassi C, Bonucci A, Coppa GV, Carlucci A, Giorgi PL 1995 Intestinal permeability changes during the first month: effect of natural versus artificial feeding. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 21: 383–386
Weaver LT, Laker MF, Nelson R, Lucas A 1987 Milk feeding and changes in intestinal permeability and morphology in the new born. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 6: 351–358
Udall JN, Colony P, Fritze L, Pang K, Trier JS, Walker WA 1981 Development of gastrointestinal mucosal barrier. II. The effect of natural versis artificial feeding on intestinal permeability to macromolecules. Pediatr Res 15: 245–249
Teichberg S, Isolauri E, Wapnir RA, Roberts B, Lifshitz F 1990 Development of the neonatal rat small intestinal barrier to nonspecific macromolecular absorption: effect of early weaing to artificial diets. Pediatr Res 28: 31–37
Gebbers JO, Laissue JA 2004 Bacterial translocation in the normal human appendix parallels the development of the local immune system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1029: 337–343
Urao M, Teitelbaum DH, Drongowski RA, Coran AG 1996 The association of gut-associated lymphoid tissue and bacterial translocation in the newborn rabbit. J Pediatr Surg 31: 1482–1487
Söderholm JD, Yates DA, Gareau MG, Yang PC, MacQueen G, Perdue MH 2002 Neonatal maternal separation predisposes adult rats to colonic barrier dysfunction in response to mild stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283: G1257–G1263
Barreau F, Ferrier L, Fioramonti J, Bueno L 2004 Neonatal maternal deprivation triggers long-term alterations in colonic epithelial barrier and mucosal immunity in rats. Gut 53: 501–506
Morise A, Sève B, Macé K, Magliola C, Le Huërou-Luron I, Louveau I 2009 Impact of intra-uterine growth retardation and early protein intake on growth, adipose tissue, and the insulin-like growth factor system in piglets. Pediatr Res 65: 45–50
Marion J, Biernat M, Thomas F, Savary G, Le Breton Y, Zabielski R, Le Huerou-Luron I, Le Dividich J 2002 Small intestine growth and morphometry in piglets weaned at 7 days of age. Effects of energy intake. Reprod Nutr Dev 42: 339–354
Guggi D, Bernkop-Schnürch A 2005 Improved paracellular uptake by the combination of different types of permeation enhancers. Int J Pharm 288: 141–150
Heyman M, Ducroc R, Desjeux JF, Morgat JL 1982 Horseradish peroxidase transport across adult rabbit jejunum in vitro. Am J Physiol 242: G558–G564
Yajima T, Kanno T, Katoku Y, Kuwata T 1998 Gut hypertrophy in response to the ratios of casein and whey protein in milk formulas in artificially reared rat pups. Biol Neonate 74: 314–322
Pluske JR, Williams IH, Aherne FX 1996 Villous height and crypt depth in piglets in response to increases in the intake of cow's milk after weaning. Anim Sci 62: 145–158
van Beers-Schreurs HM, Nabuurs MJ, Vellenga L, Kalsbeek-van der Valk HJ, Wensing T, Breukink HJ 1998 Weaning and the weanling diet influence the villous height and crypt depth in the small intestine of pigs and alter the concentrations of short-chain fatty acids in the large intestine and blood. J Nutr 128: 947–953
Colomé G, Sierra C, Blasco J, Garcia MV, Valverde E, Sanchez E 2007 Intestinal permeability in different feedings in infancy. Acta Paediatr 96: 69–72
Barrat E, Michel C, Poupeau G, David-Sochard A, Rival M, Pagniez A, Champ M, Darmaun D 2008 Supplementation with galacto-oligosaccharides and inulin increases bacterial translocation in artificially-reared newborn rats. Pediatr Res 64: 34–39
Hamard A, Mazurais D, Boudry G, Le Huërou-Luron I, Sève B, Le Floc'h N 2009 A moderate threonine deficiency affects gene expression profile, paracellular permeability and glucose absorption capacity in the ileum of piglets. J Nutr Biochem 2010; 21: 914–921
Guillemot L, Citi S 2006 Cingulin regulates claudin-2 expression and cell proliferation through the small GTPase RhoA. Mol Biol Cell 17: 3569–3577
Paschoud S, Citi S 2008 Inducible overexpression of cingulin in stably transfected MDCK cells does not affect tight junction organization and gene expression. Mol Membr Biol 25: 1–13
Hirota CL, McKay DM 2006 Cholinergic regulation of epithelial ion transport in the mammalian intestine. Br J Pharmacol 149: 463–479
Aulí M, Nasser Y, Ho W, Burgueno JF, Keenan CM, Romero C, Sharkey KA, Fernandez E 2008 Neuromuscular changes in a rat model of colitis. Auton Neurosci 141: 10–21
Sigge W, Wedel T, Kühnel W, Krammer HJ 1998 Morphologic alterations of the enteric nervous system and deficiency of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic inhibitory innervation in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur J Pediatr Surg 8: 87–94
Acknowledgements
We thank our technical staff for technical assistance and also thank Dr. Katherine Macé and Dr. Clara Garcia-Rodenas for fruitful discussion of the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA) and Nestec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boudry, G., Morise, A., Seve, B. et al. Effect of Milk Formula Protein Content on Intestinal Barrier Function in a Porcine Model of LBW Neonates. Pediatr Res 69, 5–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181fc9d13
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181fc9d13
This article is cited by
-
Changes of the glutathione redox system during the weaning transition in piglets, in relation to small intestinal morphology and barrier function
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2020)
-
A mixture of milk and vegetable lipids in infant formula changes gut digestion, mucosal immunity and microbiota composition in neonatal piglets
European Journal of Nutrition (2018)
-
Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation in Formula Modulates the Neonatal Gut Microbiome and Normalizes Intestinal Development
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Early maternal separation induces alterations of colonic epithelial permeability and morphology
Pediatric Surgery International (2014)
-
The digestive neuronal–glial–epithelial unit: a new actor in gut health and disease
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2013)