Abstract
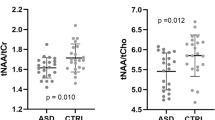
Neurometabolic sequelae of children born at very LBW (VLBW) are not well characterized in early childhood. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) and developmental assessments were acquired from children age 18–22 mo (16 VLBW/7 term) and 3–4 y (12 VLBW/8 term) from the anterior cingulate and left frontal periventricular white matter. Metabolites obtained included combined N-acetylaspartylglutamate and N-acetylaspartate (NAA), total choline-containing compounds (Cho), combined glutamate and glutamine (Glx), combined creatine and phosphocreatine (Cr), myoinositol (mI), and the following ratios: NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, Glx/Cr, mI/Cr, and NAA/Cho. Significant differences were present only in white matter: at 18–22 mo, NAA was decreased in VLBW children (p < 0.04), and at 3–4 y, VLBW children showed lower Cr (p < 0.01), lower NAA/Cho (p < 0.005), higher Glx/Cr (p < 0.02), and higher Cho/Cr (p < 0.005). On developmental testing, VLBW children scored lower on language expression (p < 0.05) and on the A-not-B test of early executive function (p < 0.01) at 18–22 mo and had lower verbal intelligence quotient (IQ) (p < 0.005), performance IQ (p < 0.04), and several measures of early executive function including the bear-dragon test (p < 0.004), gift delay (p < 0.07), and summary categorization score (p < 0.03) at 3–4 y. VLBW children may have neurometabolic and developmental abnormalities that persist at least through early childhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- 1H-MRS:
-
proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- BSID-III:
-
Bayley Scales of Infant Development-III
- Cho:
-
total choline-containing compounds
- Cr:
-
combined creatine and phosphocreatine
- Glx:
-
combined glutamate and glutamine
- mI:
-
myoinositol
- NAA:
-
combined N-acetylaspartylglutamate and N-acetylaspartate
- PIQ:
-
performance intelligence quotient
- TE:
-
echo time
- IQ:
-
intelligence quotient
- VIQ:
-
verbal intelligence quotient
- VLBW:
-
very LBW
- WPPSI-III:
-
Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-III
References
Martin JA, Kung HC, Mathews TJ, Hoyert DL, Strobino DM, Guyer B, Sutton SR 2008 annual summary of vital statistics: 2006. Pediatrics 121: 788–801
Vicari S, Caravale B, Carlesimo GA 2004 Spatial working memory deficits in children at ages 3–4 who were low birth weight, preterm infants. Neuropsychology 18: 673–678
Grunau RE, Whitfield MF, Fay TB 2004 Psychosocial and academic characteristics of extremely low birth weight (< or =800 g) adolescents who are free of major impairment compared with term-born control subjects. Pediatrics 114: e725–e732
Nadeau L, Boivin M, Tessier R, Lefebvre F, Robaey P 2001 Mediators of behavioral problems in 7-year-old children born after 24 to 28 weeks of gestation. J Dev Behav Pediatr 22: 1–10
Rickards AL, Kelly EA, Doyle LW, Callanan C 2001 Cognition, academic progress, behavior and self-concept at 14 years of very low birth weight children. J Dev Behav Pediatr 22: 11–18
Anderson PJ, Doyle LW 2004 Executive functioning in school-aged children who were born very preterm or with extremely low birth weight in the 1990s. Pediatrics 114: 50–57
Edgin JO, Inder TE, Anderson PJ, Hood KM, Clark CA, Woodward LJ 2008 Executive functioning in preschool children born very preterm: relationship with early white matter pathology. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 14: 90–101
Volpe JJ 2009 Brain injury in premature infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol 8: 110–124
Khong PL, Tse C, Wong I, Lam BC, Cheung PT, Goh WH, Kwong NS, Ooi GC 2004 Diffusion-weighted imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: association with neuromotor outcome at 18 months of age. J Child Neurol 19: 872–881
Kadri M, Shu S, Holshouser B, Deming D, Hopper A, Peverini R, Ashwal S 2003 Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy improves outcome prediction in perinatal CNS insults. J Perinatol 23: 181–185
Barkovich AJ, Miller SP, Bartha A, Newton N, Hamrick SE, Mukherjee P, Glenn OA, Xu D, Partridge JC, Ferriero DM, Vigneron DB 2006 MR imaging, MR spectroscopy, and diffusion tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27: 533–547
Miller SP, Newton N, Ferriero DM, Partridge JC, Glidden DV, Barnwell A, Chuang NA, Vigneron DB, Barkovich AJ 2002 Predictors of 30-month outcome after perinatal depression: role of proton MRS and socioeconomic factors. Pediatr Res 52: 71–77
Shu SK, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, Nystrom G, Hinshaw DB 1997 Prognostic value of 1H-MRS in perinatal CNS insults. Pediatr Neurol 17: 309–318
Groenendaal F, Grond J, Eken P, Haastert C, Rademaker KJ, Toet MC, deVries LS 1997 Early cerebral proton MRS and neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with cystic leukomalacia. Dev Med Child Neurol 39: 373–379
Cheong JL, Cady EB, Penrice J, Wyatt JS, Cox IJ, Robertson NJ 2006 Proton MR spectroscopy in neonates with perinatal cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury: metabolite peak-area ratios, relaxation times, and absolute concentrations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27: 1546–1554
Robertson NJ, Kuint J, Counsell TJ, Ruterford TA, Coutts A, Cox IJ, Edwards AD 2000 Characterization of cerebral white matter damage in preterm infants using 1H and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20: 1446–1456
Augustine EM, Spielman DM, Barnes PD, Sutcliffe TL, Dermon JD, Mirmiran M, Clayton DB, Ariagno RL 2008 Can magnetic resonance spectroscopy predict neurodevelopmental outcome in very low birth weight preterm infants?. J Perinatol 28: 611–618
Gimenez M, Soria-Pastor SS, Junque C, Caldu X, Narberhaus A, Botet F, Bargello N, Falcon C, Mercader J 2008 Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals medial temporal metabolic abnormalities in adolescents with history of preterm birth. Pediatr Res 64: 572–577
Bathen TF, Sjobakk T, Skranes J, Brubakk A, Vik T, Martinussen M, Myhr GE, Gribbestad IS, Axelson D 2006 Cerebral metabolite differences in adolescents with low birth weight: assessment with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Pediatr Radiol 36: 802–809
Bayley N 2005 Bayley Scales of Infant Development Manual. 3rd ed. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Diamond A 1985 Development of the ability to use recall to guide action, as indicated by infants' performance on AB. Child Dev 56: 868–883
Espy KA, Kaufmann PM, McDiarmid MD, Glisky ML 1999 Executive functioning in preschool children: performance on A-not-B and other delayed response format tasks. Brain Cogn 41: 178–199
Wechsler D 2002 Manual for Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-Third Edition (WPPSI-III). The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Reed MA, Pien DL, Rothbart MK 1984 Inhibitory self-control in preschool children. Merrill Palmer Q 30: 131–147
Kochanska G, Murray KT, Jacques TY, Koenig AL, Vandegeest KA 1996 Inhibitory control in young children and its role in emerging internalization. Child Dev 67: 490–507
Frye D, Zelazo PD, Palfai T 1995 Theory of mind and rule-based reasoning. Cogn Dev 10: 483–527
Zelazo PD, Reznick JS, Pinon DE 1995 Response control and the execution of verbal rules. Dev Psychol 31: 508–517
Mullins PG, Chen H, Xu J, Caprihan A, Gasparovic C 2008 Comparative reliability of proton spectroscopy techniques designed to improved detection of J-coupled metabolites. Magn Reson Med 60: 964–969
Provencher SW 2001 Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed 14: 260–264
Gasparovic C, Song T, Devier D, Bockholt HJ, Caprihan A, Mullins PG, Posse S, Jung R, Morrison L 2006 Use of tissue water as a concentration reference for proton spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 55: 1219–1226
Vangberg TR, Skranes J, Dale AM, Martinussen M, Brubakk AM, Haraldseth O 2006 Changes in white matter diffusion anisotropy in adolescents born prematurely. Neuroimage 32: 1538–1548
Moffett JR, Ross B, Arun P, Madhavarao CN, Namboodiri AM 2007 N-acteylaspartate in the CNS; from neurodiagnostics to neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol 81: 89–131
Brooks WM, Stidley CA, Petropoulos H, Jung RE, Weers DC, Friedman SD, Barlow MA, Sibbitt WL Jr Yeo RA 2000 Metabolic and cognitive response to human traumatic brain injury: a quantitative proton magnetic resonance study. J Neurotrauma 17: 629–640
Khan O, Shen Y, Bao F, Caon C, Tselis A, Latif Z, Zak I 2008 Long-term study of brain 1H-MRS study in multiple sclerosis: effect of glatiramer acetate therapy on axonal metabolic function and feasibility of long-term H-MRS monitoring in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 18: 314–319
Bitsch A, Bruhn H, Vougioukas V, Stringaris A, Lassman H, Frahm J, Bruck W 1999 Inflammatory CNS demyelination: histopathologic correlation with in vivo quantitative proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20: 1619–1627
Gasparovic C, Yeo R, Mannell M, Ling J, Elgie R, Phillips JP, Doezema D, Mayer A 2009 Neurometabolite concentrations in gray and white matter in mild traumatic brain injury: a H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Neurotrauma 26: 1635–1643
Brockmann K, Dechent P, Wilken B, Rusch O, Frahm J, Hanefeld F 2003 Proton MRS profile of cerebral metabolic abnormalities in Krabbe disease. Neurology 60: 819–825
Panigrahy A, Borzage M, Bluml S 2010 Basic principles and concepts underlying recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging of the developing brain. Semin Perinatol 34: 3–19
Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R 2000 Creatine and creatine metabolism. Physiol Rev 80: 1107–1213
Deleted in proof
Deleted in proof
Bhutta AT, Cleves MA, Casey PH, Cradock MM, Anand KJ 2002 Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: a meta-analysis. JAMA 288: 728–737
Luciana M 2003 Cognitive development in children born preterm: implications for theories of brain plasticity following early injury. Dev Psychopathol 15: 1017–1047
Sun J, Mohay H, O'Callaghan M 2009 A comparison of executive function in very preterm and term infants at 8 months corrected age. Early Hum Dev 85: 225–230
Espy KA, Stalets MM, McDiarmid MM, Senn TE, Cwik MF, Hamby A 2002 Executive functions in preschool children born preterm: application of cognitive neuroscience paradigms. Child Neuropsychol 8: 83–92
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the critical role played by the following people: Susanne Duvall, Lynette Silva, Diana South, Cathy Smith, Judith Segall, Joy Van Meter, Becky Montman, Carol Hartenberger, Mashid Rhoohi, Conra Backstrom-Lacy, and Dr. Joyce Phillips.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by grants from University of New Mexico Clinical and Translational Science Center 1ULRR031977-01, and The Mind Research Network (Department of Energy grant #DE-FG02-08ER64581) [to J.P.P.].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, J., Ruhl, D., Montague, E. et al. Anterior Cingulate and Frontal Lobe White Matter Spectroscopy in Early Childhood of Former Very LBW Premature Infants. Pediatr Res 69, 224–229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182091d52
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182091d52
This article is cited by
-
Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and neurodevelopment after preterm birth: a systematic review
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Altered brain metabolism contributes to executive function deficits in school-aged children born very preterm
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
The long-term effect of erythropoiesis stimulating agents given to preterm infants: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study on neurometabolites in early childhood
Pediatric Radiology (2018)
-
Neuroimaging in former preterm children who received erythropoiesis stimulating agents
Pediatric Research (2017)