Abstract
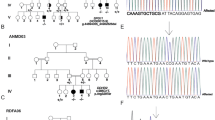
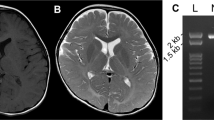
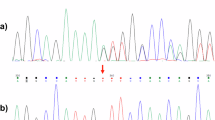
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by abnormalities in the gene PLP1. Most females harboring heterozygous PLP1 abnormalities are basically asymptomatic. However, as a result of abnormal patterns of X-chromosome inactivation, it is possible for some female carriers to be symptomatic. Whole-exome sequencing of a female patient with unknown spastic paraplegia was performed to obtain a molecular diagnosis. As a result, a de novo heterozygous single-nucleotide deletion in PLP1 [NM_000533.5(PLP1_v001):c.783del; p.Thr262Leufs*20] was identified. RNA sequencing was performed in a patient-derived lymphoblastoid cell line, confirming mono-allelic expression of the mutated allele and abnormal inactivation of the wild-type allele. The patient-derived lymphoblastoid cell line was then treated with VX680 or 5azadC, which resulted in restored expression of the wild-type allele. These two agents thus have the potential to reverse inappropriately-skewed inactivation of the X-chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Charzewska A, Wierzba J, Izycka-Swieszewska E, Bekiesinska-Figatowska M, Jurek M, Gintowt A, et al. Hypomyelinating leukodystrophies-a molecular insight into the white matter pathology. Clin Genet. 2016;90:293–304.
Yamamoto T, Shimojima K. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease as a chromosomal disorder. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2013;53:3–8.
Shimojima K, Tanaka R, Shimada S, Sangu N, Nakayama J, Iwasaki N, et al. A novel homozygous mutation of GJC2 derived from maternal uniparental disomy in a female patient with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease. J Neurol Sci. 2013;330:123–6.
Shimojima K, Okumura A, Ikeno M, Nishimura A, Saito A, Saitsu H, et al. A de novo TUBB4A mutation in a patient with hypomyelination mimicking Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Dev. 2015;37:281–5.
Sasaki H, Yanagi K, Ugi S, Kobayashi K, Ohkubo K, Tajiri Y, et al. Definitive diagnosis of mandibular hypoplasia, deafness, progeroid features and lipodystrophy (MDPL) syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo mutation in the POLD1 gene. Endocr J. 2018;65:227–38.
Bertelsen B, Tumer Z, Ravn K. Three new loci for determining x chromosome inactivation patterns. J Mol Diagn. 2011;13:537–40.
Shimada S, Okamoto N, Ito M, Arai Y, Momosaki K, Togawa M, et al. MECP2 duplication syndrome in both genders. Brain Dev. 2013;35:411–9.
Yu D, Sakurai F, Corey DR. Clonal Rett Syndrome cell lines to test compounds for activation of wild-type MeCP2 expression. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:5202–5.
Shimojima K, Inoue T, Imai Y, Arai Y, Komoike Y, Sugawara M, et al. Reduced PLP1 expression in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from a Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease patient with a partial PLP1 duplication. J Hum Genet. 2012;57:580–6.
Omata T, Nagai J, Shimbo H, Koizume S, Miyagi Y, Kurosawa K, et al. A splicing mutation of proteolipid protein 1 in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Dev. 2016;38:581–4.
Hodes ME, DeMyer WE, Pratt VM, Edwards MK, Dlouhy SR. Girl with signs of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease heterozygous for a mutation in exon 2 of the proteolipid protein gene. Am J Med Genet. 1995;55:397–401.
Woodward K, Kirtland K, Dlouhy S, Raskind W, Bird T, Malcolm S, et al. X inactivation phenotype in carriers of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: skewed in carriers of a duplication and random in carriers of point mutations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2000;8:449–54.
Inoue K, Tanaka H, Scaglia F, Araki A, Shaffer LG, Lupski JR. Compensating for central nervous system dysmyelination: females with a proteolipid protein gene duplication and sustained clinical improvement. Ann Neurol. 2001;50:747–54.
Fattal-Valevski A, DiMaio MS, Hisama FM, Hobson GM, Davis-Williams A, Garbern JY, et al. Variable expression of a novel PLP1 mutation in members of a family with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Child Neurol. 2009;24:618–24.
Yiu EM, Farrell SA, Soman T. Classic Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease in a girl with an unbalanced chromosomal translocation and functional duplication of PLP1. Mov Disord. 2009;24:2171–2.
Carvalho CM, Bartnik M, Pehlivan D, Fang P, Shen J, Lupski JR. Evidence for disease penetrance relating to CNV size: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and manifesting carriers with a familial 11 Mb duplication at Xq22. Clin Genet. 2012;81:532–41.
Fonseca AC, Bonaldi A, Costa SS, Freitas MR, Kok F, Vianna-Morgante AM. PLP1 duplication at the breakpoint regions of an apparently balanced t(X;22) translocation causes Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease in a girl. Clin Genet. 2013;83:169–74.
Matsufuji M, Osaka H, Gotoh L, Shimbo H, Takashima S, Inoue K. Partial PLP1 deletion causing X-linked dominant spastic paraplegia type 2. Pedia Neurol. 2013;49:477–81.
Lassuthova P, Zaliova M, Inoue K, Haberlova J, Sixtova K, Sakmaryova I, et al. Three new PLP1 splicing mutations demonstrate pathogenic and phenotypic diversity of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Child Neurol. 2014;29:924–31.
Brender T, Wallerstein D, Sum J, Wallerstein R. Unusual presentation of pelizaeus-merzbacher disease: female patient with deletion of the proteolipid protein 1 gene. Case Rep Genet. 2015;2015:453105.
Masliah-Planchon J, Dupont C, Vartzelis G, Trimouille A, Eymard-Pierre E, Gay-Bellile M, et al. Insertion of an extra copy of Xq22.2 into 1p36 results in functional duplication of the PLP1 gene in a girl with classical Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:77.
Inoue K. PLP1-related inherited dysmyelinating disorders: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2. Neurogenetics. 2005;6:1–16.
Inoue K, Khajavi M, Ohyama T, Hirabayashi S, Wilson J, Reggin JD, et al. Molecular mechanism for distinct neurological phenotypes conveyed by allelic truncating mutations. Nat Genet. 2004;36:361–9.
Bhatnagar S, Zhu X, Ou J, Lin L, Chamberlain L, Zhu LJ, et al. Genetic and pharmacological reactivation of the mammalian inactive X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:12591–8.
Minkovsky A, Sahakyan A, Bonora G, Damoiseaux R, Dimitrova E, Rubbi L, et al. A high-throughput screen of inactive X chromosome reactivation identifies the enhancement of DNA demethylation by 5-aza-2’-dC upon inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2015;8:42.
Lessing D, Dial TO, Wei C, Payer B, Carrette LL, Kesner B, et al. A high-throughput small molecule screen identifies synergism between DNA methylation and Aurora kinase pathways for X reactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:14366–71.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the patient and her family for their cooperation. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (17K18133) and a Restart Postdoctoral Fellowship (17J40108) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) for KY. This study was also funded by the Practical Research Project for Rare/Intractable Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED 18ek0109270, TY, KI) and JSPS KAKENHI JP18K07803 (TY). We are also thankful for the support from the Initiative on Rare and Undiagnosed Diseases (IRUD) via the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto-Shimojima, K., Imaizumi, T., Aoki, Y. et al. Elucidation of the pathogenic mechanism and potential treatment strategy for a female patient with spastic paraplegia derived from a single-nucleotide deletion in PLP1. J Hum Genet 64, 665–671 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0600-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0600-x
This article is cited by
-
Reciprocal chromosome translocation t(3;4)(q27;q31.2) with deletion of 3q27 and reduced FBXW7 expression in a patient with developmental delay, hypotonia, and seizures
Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Novel BCL11B truncation variant in a patient with developmental delay, distinctive features, and early craniosynostosis
Human Genome Variation (2022)
-
Whole-exome analysis of 177 pediatric patients with undiagnosed diseases
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Deep intronic deletion in intron 3 of PLP1 is associated with a severe phenotype of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease
Human Genome Variation (2021)
-
A recurrent de novo ZSWIM6 variant in a Japanese patient with severe neurodevelopmental delay and frequent vomiting
Human Genome Variation (2021)