Abstract
Objectives
Obesity is an important risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This cardiovascular risk remains increased even after substantial weight loss by bariatric surgery. Innate immune cells are important regulators of atherogenesis and can adopt a long-term hyperinflammatory phenotype via epigenetic reprogramming, called “trained immunity”. In this translational observational case-cohort study, we investigated the persistence of innate immune cell hyperresponsiveness following bariatric surgery, and explored the potential contribution of adipose tissue in ex vivo models.
Subjects/methods
In a cohort of 27 patients with obesity blood was drawn before and six months after bariatric surgery, and compared to 20 healthy subjects with normal body weight. We assessed monocytes using flow cytometry, functional assays, and RNA sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation. In an accompanying series of in vitro studies, healthy donor monocytes were exposed for 24 h to adipose tissue obtained from patients with obesity during bariatric surgery. Cytokine production capacity was assessed after one week.
Results
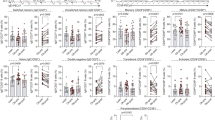
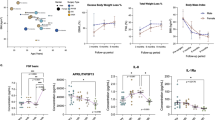
In our case-cohort study, although leukocyte numbers and systemic inflammatory markers such as hs-CRP decreased after bariatric surgery to the level of normal weight control subjects, the hyperresponsive pro-inflammatory monocyte phenotype was only partially reverted six months after bariatric surgery, which aligned with the RNA expression profiles. Exposure of monocytes to adipose tissue obtained from patients with obesity induces a persistent augmented cytokine production capacity.
Conclusions
Although in patients with obesity, six months after bariatric surgery systemic inflammatory markers and leukocyte numbers are decreased to the levels observed in healthy lean subjects, there is still a residual functional and transcriptional hyper-inflammatory monocyte phenotype. This might be caused, at least in part, by the capacity of adipose tissue to induce long-term pro-inflammatory effects in monocytes. These finding help to understand the long-term effects of obesity and bariatric surgery on cardiovascular health.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All RNA sequencing datasets from the patients, and from the ex vivo studies is available in the Radboud Data Repository: https://doi.org/10.34973/f93x-3246 The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request: Niels P. Riksen (niels.riksen@radboudumc.nl).
References
Rohm TV, Meier DT, Olefsky JM, Donath MY. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. 2022;55:31–55.
Nagareddy PR, Kraakman M, Masters SL, Stirzaker RA, Gorman DJ, Grant RW, et al. Adipose tissue macrophages promote myelopoiesis and monocytosis in obesity. Cell Metab. 2014;19:821–35.
Fuster JJ, Ouchi N, Gokce N, Walsh K. Obesity-Induced changes in adipose tissue microenvironment and their impact on cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2016;118:1786–807.
Friedrich K, Sommer M, Strobel S, Thrum S, Bluher M, Wagner U, et al. Perturbation of the monocyte compartment in human obesity. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1874.
Carlsson LMS, Sjoholm K, Jacobson P, Andersson-Assarsson JC, Svensson PA, Taube M, et al. Life Expectancy after Bariatric Surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1535–43.
Cottam MA, Caslin HL, Winn NC, Hasty AH. Multiomics reveals persistence of obesity-associated immune cell phenotypes in adipose tissue during weight loss and weight regain in mice. Nat Commun. 2022;13:2950.
Hinte LC, Castellano-Castillo D, Ghosh A, Melrose K, Gasser E, Noe F, et al. Adipose tissue retains an epigenetic memory of obesity after weight loss. Nature. 2024;636:457–65.
Hata M, Andriessen E, Hata M, Diaz-Marin R, Fournier F, Crespo-Garcia S, et al. Past history of obesity triggers persistent epigenetic changes in innate immunity and exacerbates neuroinflammation. Science. 2023;379:45–62.
Caslin HL, Cottam MA, Pinon JM, Boney LY, Hasty AH. Weight cycling induces innate immune memory in adipose tissue macrophages. Front Immunol. 2022;13:984859.
Riksen NP, Bekkering S, Mulder WJM, Netea MG. Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20:799–811.
Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F, Joosten LA, Ifrim DC, Saeed S, et al. Bacille Calmette-Guerin induces NOD2-dependent nonspecific protection from reinfection via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:17537–42.
Quintin J, Saeed S, Martens JHA, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Ifrim DC, Logie C, et al. Candida albicans infection affords protection against reinfection via functional reprogramming of monocytes. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12:223–32.
Bekkering S, Quintin J, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Netea MG, Riksen NP. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces long-term proinflammatory cytokine production and foam cell formation via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:1731–8.
Crisan TO, Cleophas MC, Oosting M, Lemmers H, Toenhake-Dijkstra H, Netea MG, et al. Soluble uric acid primes TLR-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by human primary cells via inhibition of IL-1Ra. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:755–62.
Seufert AL, Hickman JW, Traxler SK, Peterson RM, Waugh TA, Lashley SJ, et al. Enriched dietary saturated fatty acids induce trained immunity via ceramide production that enhances severity of endotoxemia and clearance of infection. Elife. 2022;11:e76744.
Flores Gomez D, Bekkering S, Horst RT, Cossins B, van den Munckhof ICL, Rutten JHW, et al. The effect of leptin on trained innate immunity and on systemic inflammation in subjects with obesity. J Leukoc Biol. 2024;115:374–84.
Lavillegrand J-R, Al-Rifai R, Thietart S, Guyon T, Vandestienne M, Cohen R, et al. Alternating high-fat diet enhances atherosclerosis by neutrophil reprogramming. Nature. 2024;634:447–56.
Vreeken D, Seidel F, de La Roij G, Vening W, den Hengst WA, Verschuren L, et al. Impact of white adipose tissue on brain structure, perfusion, and cognitive function in patients with severe obesity: The BARICO Study. Neurology. 2023;100:e703–e718.
Schutte MH, Kleemann R, Nota NM, Wiepjes CM, Snabel JM, T’Sjoen G, et al. The effect of transdermal gender-affirming hormone therapy on markers of inflammation and hemostasis. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0261312.
Gart E, Salic K, Morrison MC, Caspers M, van Duyvenvoorde W, Heijnk M, et al. Krill oil treatment increases distinct pufas and oxylipins in adipose tissue and liver and attenuates obesity-associated inflammation via direct and indirect mechanisms. Nutrients. Nutrients. 2021;13:2836
Bekkering S, Blok BA, Joosten LA, Riksen NP, van Crevel R, Netea MG. In vitro experimental model of trained innate immunity in human primary monocytes. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016;23:926–33.
Dominguez-Andres J, Arts RJW, Bekkering S, Bahrar H, Blok BA, de Bree LCJ, et al. In vitro induction of trained immunity in adherent human monocytes. STAR Protoc. 2021;2:100365.
Teufel LU, Arts RJW, Netea MG, Dinarello CA, Joosten LAB. IL-1 family cytokines as drivers and inhibitors of trained immunity. Cytokine. 2022;150:155773.
Cossins BC, van den Munckhof I, Rutten JHW, van der Graaf M, Stienstra R, Joosten LAB, et al. Sex-specific Association Between Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Vascular and Metabolic Complications of Obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108:2537–49.
Poitou C, Dalmas E, Renovato M, Benhamo V, Hajduch F, Abdennour M, et al. CD14dimCD16+ and CD14+CD16+ monocytes in obesity and during weight loss: relationships with fat mass and subclinical atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:2322–30.
Devevre EF, Renovato-Martins M, Clement K, Sautes-Fridman C, Cremer I, Poitou C. Profiling of the three circulating monocyte subpopulations in human obesity. J Immunol. 2015;194:3917–23.
van der Valk ES, Mulder DS, Kouwenhoven T, Nagtzaam NMA, van Rossum EFC, Dik WA, et al. Monocyte adaptations in patients with obesity during a 1.5 year lifestyle intervention. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1022361.
Fanucchi S, Dominguez-Andres J, Joosten LAB, Netea MG, Mhlanga MM. The intersection of epigenetics and metabolism in trained immunity. Immunity. 2021;54:32–43.
Ling C, Ronn T. Epigenetics in human obesity and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019;29:1028–44.
Bannister S, Kim B, Dominguez-Andres J, Kilic G, Ansell BRE, Neeland MR, et al. Neonatal BCG vaccination is associated with a long-term DNA methylation signature in circulating monocytes. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabn4002.
Verma D, Parasa VR, Raffetseder J, Martis M, Mehta RB, Netea M, et al. Anti-mycobacterial activity correlates with altered DNA methylation pattern in immune cells from BCG-vaccinated subjects. Sci Rep. 2017;7:12305.
Ter Horst R, van den Munckhof ICL, Schraa K, Aguirre-Gamboa R, Jaeger M, Smeekens SP, et al. Sex-Specific Regulation of Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome in Obesity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:1787–1800.
Earhart AP, Karasseva NG, Storey KM, Olthoff B, Sarker MB, Laffey KG, et al. Lower female survival from an opportunistic infection reveals progesterone-driven sex bias in trained immunity. Cell Rep. 2023;42:113007.
Groh LA, Verel DE LA, van der Heijden C, Matzaraki V, Moorlag S, de Bree LC, et al. Immune modulatory effects of progesterone on oxLDL-induced trained immunity in monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;112:279–88.
Balza E, Piccioli P, Carta S, Lavieri R, Gattorno M, Semino C, et al. Proton pump inhibitors protect mice from acute systemic inflammation and induce long-term cross-tolerance. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2304.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jessica Snabel for technical assistance with the plasma analyses. NPR, MGN, and LABJ received a CVON grant from the Dutch Cardiovascular Alliance (DCVA) and Dutch Heart Foundation (CVON2018-27; IN CONTROL II). NPR was recipient of a grant of the ERA-CVD Joint Transnational Call 2018 supported by the Dutch Heart Foundation (JTC2018, project MEMORY; 2018T093) SB is supported by the Dutch Heart Foundation (2018T028). MGN was supported by an ERC Advanced Grant (#833247) and a Spinoza grant of the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research. YL was supported by an ERC starting Grant (948207) and a Radboud University Medical Center Hypatia Grant. AJK was supported by a grant of the Rijnstate-Radboudumc Promotion Fund. RK and FS received support from TNO’s Research programs Biomedical Health (PMC13) and seed-ERP Brain-Power. This study was performed in collaboration with the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (TNO) Metabolisch Health Research (Leiden, the Netherlands) with support from the Shared Research Program GLoBAL, an initiative of the Radboudumc, Rijnstate Hospital and TNO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Julia van Tuijl: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualisation, Writing – original draft. Debby Vreeken: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualisation, Writing – original draft. Wieteke Broeders: Investigation, Writing – original draft. Benjamin Cossins: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualisation, Writing – review and editing. Liesbeth van Emst: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. Florine Seidel: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. Rinke Stienstra: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Yang Li: Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Leo A. B. Joosten: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Mihai G. Netea: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Eric J. Hazebroek: Conceptualisation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Robert Kleemann: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Amanda J. Kiliaan: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Siroon Bekkering: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Visualisation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Niels P. Riksen: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
LABJ is scientific founder of TTxD and Lemba TX. MGN is scientific founder of TTxD, Lemba and Biotrip.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
van Tuijl, J., Vreeken, D., Broeders, W. et al. The long-term effect of metabolic bariatric surgery on innate immune cell phenotype and function. Int J Obes 49, 2473–2483 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01886-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01886-3