Abstract
Background and aim
Obesity is an already identified risk factor for various noncommunicable diseases. Berberine is an alkaloid that has manifested a significant effect in the treatment of obesity and its complications. The aim of this systematic review and meta analysis is to evaluate the effect of berberine on obesity indices.
Methods
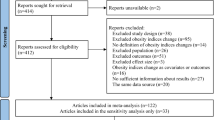
We conducted a comprehensive search of Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating berberine’s impact on obesity indices in adults. Eligible studies included human trials with quantitative outcomes for weight, BMI, WC, or WHR. Animal studies, reviews, and non-RCTs were excluded. Two reviewers independently screened studies, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias using the Cochrane RoB 2 tool. A random-effects meta-analysis was performed to calculate mean differences (MDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was evaluated using I² statistics.
Results
A total of 23 articles were included. Berberine significantly reduced body weight (MD of -0.88 kg, 95% CI: -1.36 to -0.39, p = 0.0003), BMI (MD of -0.48 kg/m², 95% CI: -0.89 to -0.07, p < 0.0216), and WC (MD of -1.32 kg/m², 95% CI: -2.24 to -0.41, p < 0.0046). However, berberine did not significantly reduce WHR compared to control groups (MD of -0.01, 95% CI: -0.03 to 0.01). Meta-regression revealed no association between berberine use and age.
Conclusion
Berberine use significantly reduces body weight, BMI, and WC but does not significantly reduce WHR. Future trials should focus on improving reporting standards for biochemical characterization (such as purity, potency and gram amounts) and address common biases such as lack of blinding and randomization to enhance the reliability of the evidence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data of this study are available upon a reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
World Health Organization. Draft recommendations for the prevention and management of obesity over the life course, including potential targets. World Health Organization. 2021.
Organization, W.H. Obesity and overweight. 2024. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Carmienke S, Freitag M, Pischon T, Schlattmann P, Fankhaenel T, Goebel H, et al. General and abdominal obesity parameters and their combination in relation to mortality: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67:573–85.
Murray CJ, Aravkin AY, Zheng P, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396:1223–49.
Naghavi M, Ong KL, Aali A, Ababneh HS, Abate YH, Abbafati C, et al. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403:2100–32.
World Health Organization. Guideline: sugars intake for adults and children. World Health Organization. 2015.
Organization, W.H. WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. World Health Organization; 2020.
Haber R, Zarzour F, Ghezzawi M, Saadeh N, Bacha DS, Al Jebbawi L, et al. The impact of metformin on weight and metabolic parameters in patients with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diab Obes Metab. 2024;26:1850–67.
Melson E, Ashraf U, Papamargaritis D, Davies MJ. What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity?. International Journal of Obesity. 2025;49:433–51.
Karri S, Sharma S, Hatware K, Patil K. Natural anti-obesity agents and their therapeutic role in management of obesity: a future trend perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:224–38.
Pengelly A. The constituents of medicinal plants: an introduction to the chemistry and therapeutics of herbal medicine. Routledge, 2020.
Bandala C, Carro-Rodríguez J, Cárdenas-Rodríguez N, Peña-Montero I, Gómez-López M, Hernández-Roldán AP, et al. Comparative effects of gymnema sylvestre and berberine on adipokines, body composition, and metabolic parameters in obese patients: a randomized study. Nutrients. 2024;16:2284.
Cesarone MR, Hu S, Belcaro G, Cornelli U, Feragalli B, Corsi M, et al. Borderline hyperlipidemia preventive management with Berberine PL in asymptomatic prevention of early atherosclerosis. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2024;70:10–15.
D’Assante R, De Luca M, Ferraro S, Ferraro A, Ruvolo A, Natale F, et al. Beneficial metabolic effect of a nutraceuticals combination (monacolin k, yeasted red rice, polyphenolic extract of annurca apple and berberine) on acquired hypercholesterolemia: a prospective analysis. Metabolites. 2021;11:223.
Ilyas Z, Perna S, Al-thawadi S, Alalwan TA, Riva A, Petrangolini G, et al. The effect of Berberine on weight loss in order to prevent obesity: a systematic review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110137.
Yu M, Jin X, Liang C, Bu F, Pan D, He Q, et al. Berberine for diarrhea in children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020;13:1756284820961299.
Nie Q, Li M, Huang C, Yuan Y, Liang Q, Ma X, et al. The clinical efficacy and safety of berberine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Transl Med. 2024;22:225.
Guo J, Chen H, Zhang X, Lou W, Zhang P, Qiu Y, et al. The effect of berberine on metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:2074610.
Xie W, Su F, Wang G, Peng Z, Xu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Glucose-lowering effect of berberine on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1015045.
Ye Y, Liu X, Wu N, Han Y, Wang J, Yu Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of berberine alone for several metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:653887.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Sterne JA, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.
Zhang Y, Li X, Zou D, Liu W, Yang J, Zhu N, et al. Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2559–65.
Gu Y, Zhang Y, Shi X, Li X, Hong J, Chen J, et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine berberine on type 2 diabetes based on comprehensive metabonomics. Talanta. 2010;81:766–72.
Wei W, Zhao H, Wang A, Sui M, Liang K, Deng H, et al. A clinical study on the short-term effect of berberine in comparison to metformin on the metabolic characteristics of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;166:99–105.
Shidfar F, Ebrahimi SS, Hosseini S, Heydari I, Shidfar S, Hajhassani G. The effects of berberis vulgaris fruit extract on serum lipoproteins, apoB, apoA-I, homocysteine, glycemic control and total antioxidant capacity in type 2 diabetic patients. Iran J Pharm Res. 2012;11:643–52.
Derosa G, D’Angelo A, Bonaventura A, Bianchi L, Romano D, Maffioli P. Effects of berberine on lipid profile in subjects with low cardiovascular risk. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13:475–82.
An Y, Sun Z, Zhang Y, Liu B, Guan Y, Lu M. The use of berberine for women with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing IVF treatment. Clin Endocrinol. 2014;80:425–31.
Pérez-Rubio KG, González-Ortiz M, Martínez-Abundis E, Robles-Cervantes JA, Espinel-Bermúdez MC. Effect of berberine administration on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2013;11:366–9.
Afsharinasab M, Mohammad-Sadeghipour M, Reza Hajizadeh M, Khoshdel A, Mirzaiey V, Mahmoodi M. The effect of hydroalcoholic Berberis integerrima fruits extract on the lipid profile, antioxidant parameters and liver and kidney function tests in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27:2031–7.
Aryaeian N, Sedehi SK, Khorshidi M, Zarezadeh M, Hosseini A, Shahram F. Effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Berberis Integerrima on the anthropometric indices and metabolic profile in active rheumatoid arthritis patients. Complement Ther Med. 2020;50:102331.
Harrison SA, Gunn N, Neff GW, Kohli A, Liu L, Flyer A, et al. A phase 2, proof of concept, randomised controlled trial of berberine ursodeoxycholate in patients with presumed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5503.
Ming J, Yu X, Xu X, Wang L, Ding C, Wang Z, et al. Effectiveness and safety of Bifidobacterium and berberine in human hyperglycemia and their regulatory effect on the gut microbiota: a multi-center, double-blind, randomized, parallel-controlled study. Genome Med. 2021;13:125.
Soltani R, Ghanadian SM, Iraj B, Homayouni A, Esfahani TS, Akbari M. The effects of Berberis integerrima fruit extract on glycemic control parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2021;2021:5583691.
Zhao JV, Yeung WF, Chan YH, Vackova D, Leung JY, Ip DK, et al. Effect of berberine on cardiovascular disease risk factors: a mechanistic randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021;13:2550.
Chan M, Qin Z, Man SC, Lam M, Lai WH, Ng RMK, et al. Adjunctive berberine reduces antipsychotic-associated weight gain and metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized controlled trial. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022;76:77–85.
Di Pierro F, Sultana R, Eusaph AZ, Abrar S, Bugti M, Afridi F, et al. Effect of berberine phytosome on reproductive, dermatologic, and metabolic characteristics in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a controlled, randomized, multi-centric, open-label clinical trial. Front Pharm. 2023;14:1269605.
Rondanelli M, Gasparri C, Petrangolini G, Allegrini P, Avenoso D, Fazia T, et al. Berberine phospholipid exerts a positive effect on the glycemic profile of overweight subjects with impaired fasting blood glucose (IFG): a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2023;27:6718–27.
Emamat H, Zahedmehr A, Asadian S, Nasrollahzadeh J. The effect of purple-black barberry (Berberis integerrima) on blood pressure in subjects with cardiovascular risk factors: a randomized controlled trial. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;289:115097.
Ruiz-Herrera VV, Navarro-Lara SA, Andrade-Villanueva JF, Alvarez-Zavala M, Sánchez-Reyes K, Toscano-Piña M, et al. Pilot study on the efficacy and safety of berberine in people with metabolic syndrome and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Int J STD AIDS. 2023;34:1042–52.
Koperska A, Moszak M, Seraszek-Jaros A, Bogdanski P, Szulinska M. Does berberine impact anthropometric, hepatic, and metabolic parameters in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease? Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024;75.
Rashidi H, Namjoyan F, Mehraban Z, Zakerkish M, Ghaderian SB, Latifi SM. The effects of active ingredients of barberry root (berberine) on glycemic control and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod. 2018;13:e64180.
Nejati L, Movahedi A, Salari G, Moeineddin R, Nejati P. The effect of berberine on lipid profile, liver enzymes, and fasting blood glucose in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a randomized controlled trial. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2022;36:39.
吕霄, 陈烨, 翁慧男, and 夏建红, 盐酸小檗碱对多囊卵巢综合征伴胰岛素抵抗的疗效及对血浆颗粒蛋白前体水平的影响. 2020.
Yan HM, Xia MF, Wang Y, Chang XX, Yao XZ, Rao SX, et al. Efficacy of berberine in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0134172.
Affuso F, Mercurio V, Ruvolo A, Pirozzi C, Micillo F, Carlomagno G, et al. A nutraceutical combination improves insulin sensitivity in patients with metabolic syndrome. World J Cardiol. 2012;4:77.
Vuddanda PR, Chakraborty S, Singh S. Berberine: a potential phytochemical with multispectrum therapeutic activities. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;19:1297–307.
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut. 2009;58:1091–103.
Yin J, Xing H, Ye J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2008;57:712–7.
Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ, Shen Y, et al. Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes. 2006;55:2256–64.
Dhar D, Packer J, Michalopoulou S, Cruz J, Stansfield C, Viner RM, et al. Assessing the evidence for health benefits of low-level weight loss: a systematic review. Int J Obes. 2025;49:254–68.
Yan HM, Xia MF, Wang Y, Chang XX, Yao XZ, Rao SX, et al. Efficacy of berberine in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 2015.
Kavyani Z, shahhosseini E, Moridpour AH, Falahatzadeh M, Vajdi M, Musazadeh V, et al. The effect of berberine supplementation on lipid profile and obesity indices: an umbrella review of meta-analysis. PharmaNutrition. 2023;26:100364.
Mishra N, Verma R, Jadaun P. Study on the effect of berberine, myoinositol, and metformin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a prospective randomised study. Cureus. 2022;14:e21781.
Amini MR, Sheikhhossein F, Naghshi S, Djafari F, Askari M, Shahinfar H, et al. Effects of berberine and barberry on anthropometric measures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med. 2020;49:102337.
Wei X, Wang C, Hao S, Song H, Yang L. The therapeutic effect of berberine in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:3593951.
Zhao L, Cang Z, Sun H, Nie X, Wang N, Lu Y. Berberine improves glucogenesis and lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017;17:1–8.
Li M-F, Zhou X-M, Li X-L. The effect of berberine on polycystic ovary syndrome patients with insulin resistance (PCOS-IR): a meta-analysis and systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:2532935.
Ionescu O-M, Frincu F, Mehedintu A, Plotogea M, Cirstoiu M, Petca A, et al. Berberine—a promising therapeutic approach to polycystic ovary syndrome in infertile/pregnant women. Life. 2023;13:125.
Xie L, Zhang D, Ma H, He H, Xia Q, Shen W, et al. The effect of berberine on reproduction and metabolism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:7918631.
Asbaghi O, Ghanbari N, Shekari M, Reiner Ž, Amirani E, Hallajzadeh J, et al. The effect of berberine supplementation on obesity parameters, inflammation and liver function enzymes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020;38:43–9.
Xiong P, Niu L, Talaei S, Kord-Varkaneh H, Clark CCT, Găman MA, et al. The effect of berberine supplementation on obesity indices: a dose-response meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Clin Pr. 2020;39:101113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: MR; Methodology: IE; Validation: MR, MM, MJ, AB, MMS, and HS; Investigation: SN, FS, MMS, MR, and ES; Formal analysis: IE; Data curation: IE, MR, NS, MM, SG, and SN; Writing—original draft preparation: ES, SN, and SG; Writing—review and editing: MR, HS, MMS, SN, NS, AB, MM, IE, FS, and MJ; Supervision: MR; Project administration: MR and HS; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Declaration of AI-assisted technologies
For final language editing during the writing of this paper, the authors used Microsoft Copilot and QuillBot. Following these tools, the authors checked and edited the content based on the requirements, and take full responsibility for the publication’s content.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This systematic review was based solely on the analysis of previously published studies and publicly available data. No new data were collected from human or animal participants; therefore, ethical approval and informed consent were not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Elahi Vahed, I., Shahir-Roudi, E., Nojumi, S. et al. The effect of berberine on obesity indices: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes 50, 53–73 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01943-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01943-x