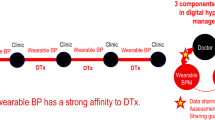
Abstract
Out-of-office blood pressure (BP) measurement is considered an integral component of the diagnostic algorithm and management of hypertension. In the era of digitalization, a great deal of wearable BP measuring devices has been developed. These digital blood pressure monitors allow frequent BP measurements with minimal annoyance to the patient while they do promise radical changes regarding the diagnostic accuracy, as the importance of making an accurate diagnosis of hypertension has become evident. By increasing the number of BP measurements in different conditions, these monitors allow accurate identification of different clinical phenotypes, such as masked hypertension and pathological BP variability, that seem to have a negative impact on cardiovascular prognosis. Frequent measurements of BP and the incorporation of new features in BP variability, both enable well-rounded interpretation of BP data in the context of real-life settings. This article is a review of all different technologies and wearable BP monitoring devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analysed during this study can be found within the published article and its supplementary.
References
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–50.
COVID-19 Surveillance Group Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients dying in Italy Report Based on Available Data on 24 March 2020; The Italian National Health Service: Rome, Italy, 27 March 2020.
World Health Organization (WHO) -China Joint Mission. Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19); World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 28 February 2020.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Rosei EA, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;2018:3021–104.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Himmelfarb CD, et al. ACC / AHA / AAPA / ABC / ACPM / AGS /APhA/ ASH / ASPC / NMA / PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology / American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2017;00:e000–e000.
Kaplan NM. Commentary on the sixth report of the Joint National Committee (JNC-6). Am J Hypertens. 1998;11:134–6.
Choi YM, Leopold D, Campbell K, Mulligan J, Grudic GZ, Moulton SL. Noninvasive monitoring of physiologic compromise in acute appendicitis: New insight into an old disease. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53:241–6.
Ding XR, Zhao N, Yang GZ, Pettigrew RI, Lo B, Miao F, et al. Continuous blood pressure measurement from invasive to unobtrusive: celebration of 200th birth anniversary of carl ludwig. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. 2016;20:1455–65.
Kario K. Management of hypertension in the digital era: small wearable monitoring devices for remote blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension 2020;76:640–50.
Kario K. New insight of morning blood pressure surge into the triggers of cardiovascular disease-synergistic resonance of blood pressure variability. Am J Hypertens. 2016;29:14–16.
Kario K, Chirinos JA, Townsend RR, Weber MA, Scuteri A, Avolio A, et al. Systemic hemodynamic atherothrombotic syndrome (SHATS) - coupling vascular disease and blood pressure variability: proposed concept from pulse of Asia. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63:22–32.
Kario K, Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Yasui N, Nishizawa M, Fujiwara T, et al. Development of a new ICT-based multisensory blood pressure monitoring system for use in hemodynamic biomarker-initiated anticipation medicine for cardiovascular disease: the National IMPACT Program Project. ProgCardiovascDis. 2017;60:435–49.
Kuwajima I, Mitani K, Miyao M, Suzuki Y, Kuramoto K, Ozawa T. Cardiac implications of the morning surge in blood pressure in elderly hypertensive patients: relation to arising time. Am J Hypertens. 1995;8:29–33.
Yano Y, Hoshide S, Inokuchi T, Kanemaru Y, Shimada K, Kario K. Association between morning blood pressure surge and cardiovascular remodeling in treated elderly hypertensive subjects. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22:1177–82.
Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, Yamaguchi J, Kikuya M, Ohmori K, Michimata M, et al. Prognostic significance of the nocturnal decline in blood pressure in individuals with and without high 24-h blood pressure: the Ohasama study. J Hypertens. 2002;20:2183–9.
Mauck GW, Smith CR, Geddes LA, Bourland JD. The meaning of the point of maximum oscillations in cuff pressure in the indirect measurement of blood pressure - part ii. J Biomech Eng. 1980;102:28–33.
Arakawa T. Recent research and developing trends of wearable sensors for detecting blood pressure. Sensors. 2018;18:2772. 23
Kuwabara M, Harada K, Hishiki Y, Kario K. Validation of two watch-type wearable blood pressure monitors according to the ANSI / AAMI / ISO81060-2: 2013 guidelines: Omron HEM-6410T-ZM and HEM-6410T-ZL. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21:853–8.
Kikuya M, Chonan K, Imai Y, Goto E, Ishii M. Research group to assess the validity of automated blood pressure measurement devices in Japan. Accuracy and reliability of wrist ‐ cuff devices for self ‐ measurement of blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2002;20:629–38.
Kario K, Shimbo D, Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Schwartz JE, Williams B. The first study comparing a wearable watch-type blood pressure monitor with a conventional ambulatory blood pressure monitor on in-office and out-of-office settings. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22:135–41.
Penaz J Photo-electric measurement of blood pressure, volume and flow in the finger. In Proceedings of the Digest of the Tenth International Conference on Medical Biological Engineering, Dresden, Germany, 13–17 August 1973.
Parati G, Casadei R, Groppelli A, Di Rienzo M, Mancia G. Comparison of finger and intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring at rest and during laboratory testing. Hypertension. 1989;13:647–55. 6 Pt 1.
Van Egmond J, Hasenbos M, Crul JF. Invasive v. non-invasive measurement of blood pressure. Comparison of two automatic methods and simultaneously measured direct intra-arterial pressure. Br J Anaesth. 1985;57:434–44.
Imholz BP, Langewouters GJ, van Montfrans GA, Parati G, van Goudoever J, Wesseling KH, et al. Feasibility of ambulatory, continuous 24-hour finger arterial pressure recording. Hypertension. 1993;21:65–73.
Pressman GL, Newgard PM. A transducer for the external measurement of arterial blood pressure. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1963;10:73–81.
Sato T, Nishinaga M, Kawamoto A, Ozawa T, Takatsuji H. Accuracy of a continuous blood pressure monitor based on arterial tonometry. Hypertension. 1993;21:866–74.
Nair D, Tan SY, Gan HW, Lim SF, Tan J, Zhu M, et al. The use of ambulatory tonometric radial arterial wave capture to measure ambulatory blood pressure: the validation of a novel wrist-bound device in adults. J Hum Hypertens. 2008;22:220–2.
Komori T, Eguchi K, Hoshide S, Williams B, Kario K. Comparison of wrist-type and arm-type 24-h blood pressure monitoring devices for ambulatory use. Blood Press Monit. 2013;18:57–62.
Hornstrup BG, Rosenbæk JB, Bech JN. Comparison of ambulatory tonometric and oscillometric blood pressure monitoring in hypertensive patients. Integr Blood Press Control. 2020;13:41–47.
Kario K. Evidence and perspectives on the 24-hour management of hypertension: hemodynamic biomarker-initiated ‘anticipation medicine’ for zero cardiovascular event. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;59:262–81.
Kokubo A, Kuwabara M, Nakajima H, Tomitani N, Yamashita S, Shiga T, et al. Automatic detection algorithm for establishing standard to identify “surge blood pressure”. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020;58:1393–404.
Van Velzen MHN, Loeve AJ, Niehof SP, Mik EG. Increasing accuracy of pulse transit time measurements by automated elimination of distorted photoplethysmography waves. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017;55:1989–2000.
Wang R, Jia W, Mao ZH, Sclabassi RJ, Sun M. Cuff-free blood pressure estimation using pulse transit time and heart rate. Int Conf Signal Process Proc. 2014;2014:115–8.
Lazazzera R, Belhaj Y, Carrault G. A new wearable device for blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmogram. Sensors. 2019;19:2557.
Chan G, Cooper R, Hosanee M, Welykholowa K, Kyriacou PA, Zheng D, et al. Multi-site photoplethysmography technology for blood pressure assessment: challenges and recommendations. J Clin Med. 2019;8:1827.
Dey J, Gaurav A, Tiwari VN. InstaBP: cuff-less blood pressure monitoring on smartphone using single PPG sensor. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2018;2018:5002–5.
Chandrasekhar A, Kim CS, Naji M, Natarajan K, Hahn JO, Mukkamala R. Smartphone-based blood pressure monitoring via the oscillometric finger-pressing method. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10:eaap8674.
Luo H, Yang D, Barszczyk A, Vempala N, Wei J, Wu SJ, et al. Smartphone-based blood pressure measurement using transdermal optical imaging technology. CircCardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:e008857.
IEEE 1708-2014 - IEEE Standard for Wearable Cuffless Blood Pressure Measuring Devices. Available online at: https://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1708-2014.html.
Michalakeas C, Katsi V, Soulaidopoulos S, Dilaveris P, Vrachatis D, Lekakis I, et al. Mobile phones and applications in the management of patients with arterial hypertension. Am J CardiovascDis. 2020;10:419–31.
Omboni S, Gazzola T, Carabelli G, Parati G. Clinical usefulness and cost effectiveness of home blood pressure telemonitoring: meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. J Hypertens. 2013;31:455–67.
Pellaton C, Vybornova A, Fallet S, Marques L, Grossenbacher O, De Marco B, et al. Accuracy testing of a new optical device for noninvasive estimation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to intra-arterial measurements. Blood Press Monit. 2020;25:105–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBP.0000000000000421.
Vybornova A, Polychronopoulou E, Wurzner-Ghajarzadeh A, Fallet S, Sola J, Wuerzner G. Blood pressure from the optical Aktiia Bracelet: a 1-month validation study using an extended ISO81060-2 protocol adapted for a cuffless wrist device. Blood Press Monit. 2021;26:305–11.
Dörr M, Weber S, Birkemeyer R, Leonardi L, Winterhalder C, Raichle CJ, et al. iPhone App compared with standard blood pressure measurement -The iPARR trial. Am Heart J. 2021;233:102–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KT (K Tsioufis) was responsible for designing the rationale of the article. FT, KT (K Thomopoulos), KD, DT were responsible for conducting the search, screening potentially eligible studies, extracting and analysing data, interpreting results, and updating reference lists. DK and PI were responsible for collecting all above data according to the article rationale and write the main article as well as designing the table and figure of the article
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantinidis, D., Iliakis, P., Tatakis, F. et al. Wearable blood pressure measurement devices and new approaches in hypertension management: the digital era. J Hum Hypertens 36, 945–951 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-022-00675-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-022-00675-z
This article is cited by
-
Integration of wearable technology and artificial intelligence in digital health for remote patient care
Journal of Cloud Computing (2025)
-
Wearable blood pressure sensors for cardiovascular monitoring and machine learning algorithms for blood pressure estimation
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2025)
-
Effectiveness of biofeedback on blood pressure in patients with hypertension: systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Human Hypertension (2024)
-
Blood pressure management to prevent recurrent stroke: current evidence and perspectives
npj Cardiovascular Health (2024)
-
Noninvasive biometric monitoring technologies for patients with heart failure
Heart Failure Reviews (2024)