Abstract
Objective
Determine whether hematological and transfusion patterns following, the onset of NEC can identify infants likely to develop fulminant, fatal necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
Design
Determine hematological predictors of fulminant NEC.
Results
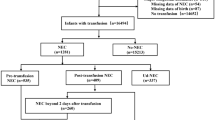
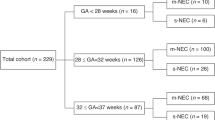
Of 336 neonates with NEC, 35 (10%) who developed fulminant NEC were born with higher birth weights and more frequently developed radiologically evident pneumoperitoneumand/or portal venous gas. Following the diagnosis of NEC, these infants were more likely to rapidly develop thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, and lower total white blood cell counts compared to medical/surgical non-fulminant type. They were also more likely to have received a red blood cell (RBC) transfusion (76.7% vs. 53.1%, p = 0.001) within 48 h after disease onset and platelet transfusion (24.2% vs. 11.7%; p = 0.03) before the onset of NEC.
Conclusion
Neonates with fulminant NEC frequently developed thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, and leukopenia, received RBC transfusions after or platelet transfusions before the onset of NEC developed the fulminant disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neu J, Walker WA. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:255–64.
Sankaran K, Puckett B, Lee DS, Seshia M, Boulton J, Qiu Z, et al. Variations in incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in Canadian neonatal intensive care units. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39:366–72.
Sjoberg Bexelius T, Ahle M, Elfvin A, Bjorling O, Ludvigsson JF, Andersson RE. Intestinal failure after necrotising enterocolitis: incidence and risk factors in a Swedish population-based longitudinal study. BMJ Paediatrics Open. 2018;2:e000316.
Allin BSR, Long AM, Gupta A, Lakhoo K, Knight M. One-year outcomes following surgery for necrotising enterocolitis: a UK-wide cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018;103:F461–6.
Knell J, Han SM, Jaksic T, Modi BP. Current status of necrotizing enterocolitis. Curr Probl Surg. 2019;56:11–38.
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Walsh MC, Carlo WA, Shankaran S, et al. Trends in care practices, morbidity, and mortality of extremely preterm neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA. 2015;314:1039–1051.
Santulli TV, Schullinger JN, Heird WC, Gongaware RD, Wigger J, Barlow B, et al. Acute necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy: a review of 64 cases. Pediatrics. 1975;55:376–87.
Mowitz ME, Dukhovny D, Zupancic JAF. The cost of necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. Semin fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;23:416–9.
Ganapathy V, Hay JW, Kim JH, Lee ML, Rechtman DJ. Long term healthcare costs of infants who survived neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a retrospective longitudinal study among infants enrolled in Texas Medicaid. BMC Pediatr. 2013;13:127.
Kurscheid T, Holschneider AM. Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)-mortality and long-term results. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1993;3:139–43.
Thakkar HS, Lakhoo K. The surgical management of necrotising enterocolitis (NEC). Early Hum Dev. 2016;97:25–8.
Raval MV, Moss RL. Current concepts in the surgical approach to necrotizing enterocolitis. Pathophysiol: Off J Int Soc Pathophysiol. 2014;21:105–10.
Rees CM, Hall NJ, Eaton S, Pierro A. Surgical strategies for necrotising enterocolitis: a survey of practice in the United Kingdom. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90:F152–5.
Maheshwari A. Immunologic and hematological abnormalities in necrotizing enterocolitis. Clin Perinatol. 2015;42:567–85.
Hutter JJ Jr., Hathaway WE, Wayne ER. Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1976;88:1026–31.
Ragazzi S, Pierro A, Peters M, Fasoli L, Eaton S. Early full blood count and severity of disease in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2003;19:376–9.
Patel CC. Hematologic abnormalities in acute necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1977;24:579–84.
Kenton AB, O’Donovan D, Cass DL, Helmrath MA, Smith EO, Fernandes CJ, et al. Severe thrombocytopenia predicts outcome in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol. 2005;25:14–20.
Ververidis M, Kiely EM, Spitz L, Drake DP, Eaton S, Pierro A. The clinical significance of thrombocytopenia in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2001;36:799–803.
Lambert DK, Christensen RD, Baer VL, Henry E, Gordon PV, Besner GE, et al. Fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis in a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol. 2012;32:194–8.
MohanKumar K, Namachivayam K, Song T, Jake Cha B, Slate A, Hendrickson JE, et al. A murine neonatal model of necrotizing enterocolitis caused by anemia and red blood cell transfusions. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3494.
Patel RM, Knezevic A, Shenvi N, Hinkes M, Keene S, Roback JD, et al. Association of red blood cell transfusion, anemia, and necrotizing enterocolitis in very low-birth-weight infants. JAMA. 2016;315:889–97.
Garg P, Pinotti R, Lal CV, Salas AA. Transfusion-associated necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants: an updated meta-analysis of observational data. J Perinat Med. 2018;46:677–85.
Garg PM, Ravisankar S, Bian H, Macgilvray S, Shekhawat PS. Relationship between packed red blood cell transfusion and severe form of necrotizing enterocolitis: a case control study. Indian Pediatr. 2015;52:1041–5.
Cremer M, Sola-Visner M, Roll S, Josephson CD, Yilmaz Z, Bührer C, et al. Platelet transfusions in neonates: practices in the United States vary significantly from those in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. Transfusion. 2011;51:2634–41.
Patel RM, Josephson CD, Shenvi N, Maheshwari A, Easley KA, Stowell S, et al. Platelet transfusions and mortality in necrotizing enterocolitis. Transfusion. 2019;59:981–8.
Kenton AB, Hegemier S, Smith EO, O’Donovan DJ, Brandt ML, Cass DL, et al. Platelet transfusions in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis do not lower mortality but may increase morbidity. J Perinatol. 2005;25:173–7.
Curley A, Stanworth SJ, Willoughby K, Fustolo-Gunnink SF, Venkatesh V, Hudson C, et al. Randomized trial of platelet-transfusion thresholds in neonates. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:242–51.
Lin L, Xia X, Liu W, Wang Y, Hua Z. Clinical characteristics of neonatal fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis in a tertiary Children’s hospital in the last 10 years. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0224880.
Hyman PE, Abrams CE, Zipser RD. Enhanced urinary immunoreactive thromboxane in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. A diagnostic indicator of thrombotic activity. Am J Dis Child. 1987;141:686–9.
Hsueh W, Caplan MS, Qu XW, Tan XD, De Plaen IG, Gonzalez-Crussi F. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: clinical considerations and pathogenetic concepts. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2003;6:6–23.
Namachivayam K, MohanKumar K, Shores DR, Jain SK, Fundora J, Everett AD, et al. Targeted inhibition of thrombin attenuates murine neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:10958–69.
Namachivayam K, MohanKumar K, Garg L, Torres BA, Maheshwari A. Neonatal mice with necrotizing enterocolitis-like injury develop thrombocytopenia despite increased megakaryopoiesis. Pediatr Res. 2017;81:817–24.
Cremer M, Weimann A, Szekessy D, Hammer H, Bührer C, Dame C. Low immature platelet fraction suggests decreased megakaryopoiesis in neonates with sepsis or necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol. 2013;33:622–6.
Cekmez F, Tanju IA, Canpolat FE, Aydinoz S, Aydemir G, Karademir F, et al. Mean platelet volume in very preterm infants: a predictor of morbidities? Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2013;17:134–7.
Desiraju S, Bensadoun J, Bateman D, Kashyap S. The role of absolute monocyte counts in predicting severity of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol. 2020;40:922–7.
MohanKumar K, Kaza N, Jagadeeswaran R, Garzon SA, Bansal A, Kurundkar AR, et al. Gut mucosal injury in neonates is marked by macrophage infiltration in contrast to pleomorphic infiltrates in adult: evidence from an animal model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G93–102.
Remon J, Kampanatkosol R, Kaul RR, Muraskas JK, Christensen RD, Maheshwari A. Acute drop in blood monocyte count differentiates NEC from other causes of feeding intolerance. J Perinatol. 2014;34:549–54.
Wang YC, Chan OW, Chiang MC, Yang PH, Chu SM, Hsu JF, et al. Red blood cell transfusion and clinical outcomes in extremely low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017;58:216–22.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Robert Christensen (Professor and Division Chief of Neonatology at Intermountain Medical Center, Utah), Dr Akhil Maheshwari (Professor, Department of Pediatrics/Neonatology at John Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore), and Dr Martha C. Sola-Visner (Department of Neonatology, Boston Children Hospital, and Boston, Massachusetts) for critically reviewing the manuscript and providing for all the feedback and guidance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PMG designed the study. PMG, VO, AC, BV, HH, HM, JLP, MAYA, CDJ collected and analyzed the data. PMG, MAYA wrote the manuscript. All the authors contributed to and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, P.M., O’Connor, A., Ansari, M.A.Y. et al. Hematological predictors of mortality in neonates with fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol 41, 1110–1121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01044-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01044-3
This article is cited by
-
Fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis: clinical features and a predictive model
BMC Pediatrics (2025)
-
Survival status and predictors of mortality among thrombocytopenic neonates admitted at comprehensive specialized hospital neonatal intensive care units in East Amhara, Ethiopia, 2023 a multi-center prospective follow-up study
BMC Pediatrics (2025)
-
Predicting surgical NEC in neonates: risk factors and model development
BMC Gastroenterology (2025)
-
Rapidly progressive necrotizing enterocolitis: Risk factors and a predictive model
Pediatric Research (2025)
-
Gestational age-specific hematological features in preterm infants with necrotizing enterocolitis
Pediatric Research (2024)