Abstract
Objective
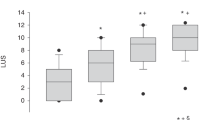
To investigate the association between lung ultrasound score (LUS) and left ventricular eccentricity index at end-systole (LVEI-s) and end-diastole (LVEI-d) in preterm infants with respiratory failure.
Study Design
This prospective pilot study included 38 ultrasounds on 20 premature infants with Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN) and Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) requiring non-invasive ventilation at birth. LUS, LVEI-s, and LVEI-d were obtained daily for 72 h. Linear regression analysis was performed to determine correlation.
Results
LUS positively correlated with LVEI-s (r = 0.47, p = <0.01) and LVEI-d (r = 0.63, p = <0.01) during the 72-hour study period in the RDS group, but not the TTN group. Correlation increased over the first 24 h (LVEI-s: r = 0.69, p = <0.01; LVEI-d: r = 0.68, p = <0.01) in the RDS group.
Conclusion
As LUS increases, both LVEI-s and LVEI-d demonstrate measurable changes in infants with RDS. This association may enhance precision in diagnostic stratification and optimizing fluid management in neonatal lung disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting these findings is not openly available but can be made available by the corresponding author upon request.
References
Selewski DT, Akcan-Arikan A, Bonachea EM, Gist KM, Goldstein SL, Hanna M, et al. The impact of fluid balance on outcomes in critically ill near-term/term neonates: a report from the AWAKEN study group. Pediatr Res. 2019;85:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-018-0183-9.
Selewski DT, Gist KM, Nathan AT, Goldstein SL, Boohaker LJ, Akcan-Arikan A, et al. The impact of fluid balance on outcomes in premature neonates: a report from the AWAKEN study group. Pediatr Res. 2020;87:550–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0579-1.
Engle WD, Arant BS Jr, Wiriyathian S, Rosenfeld CR. Diuresis and respiratory distress syndrome: physiologic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Pediatr. 1983;102:912–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80024-9.
Valentine GC, Perez KM, Wood TR, Mayock DE, Comstock BA, Puia-Dumitrescu M, et al. Postnatal maximal weight loss, fluid administration, and outcomes in extremely preterm newborns. J Perinatol. 2022;42:1008–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-022-01369-7.
Mäkelä PM, Immeli L, Leskinen M, Rinta-Koski OP, Sund R, Andersson S, et al. Actual electrolyte intake during the first week of life and morbidity in very-low-birthweight infants. Acta Paediatr. 2024;113:1833–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.17298.
Hallman M, Glumoff V, Rämet M. Surfactant in respiratory distress syndrome and lung injury. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001;129:287–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1095-6433(01)00324-5.
Oh W, Poindexter BB, Perritt R, Lemons JA, Bauer CR, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Association between fluid intake and weight loss during the first ten days of life and risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 2005;147:786–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.06.039.
Soullane S, Patel S, Claveau M, Wazneh L, Sant’Anna G, Beltempo M. Fluid status in the first 10 days of life and death/bronchopulmonary dysplasia among preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 2021;90:353–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01485-8.
Rahde Bischoff A, Bhombal S, Altman CA, Fraga MV, Punn R, Rohatgi RK, et al. Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Patients With Hemodynamic Instability. Pediatrics. 2022;150 https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2022-056415I.
Singh Y, Tissot C, Fraga M, Conlon T. Point-of-Care Ultrasound for the Neonatal and Pediatric Intensivist: A Practical Guide on the Use of POCUS. Springer International Publishing; 2023.
McCrary AW, Malowitz JR, Hornick CP, Hill KD, Cotten CM, Tatum GH, et al. Differences in Eccentricity Index and Systolic-Diastolic Ratio in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia at Risk of Pulmonary Hypertension. Am J Perinatol. 2016;33:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1556757.
Soliman RM, Elsayed Y, Said RN, Abdulbaqi AM, Hashem RH, Aly H. Prediction of extubation readiness using lung ultrasound in preterm infants. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021;56:2073–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.25383.
Kelner J, Moote D, Shah R, Anuar A, Golioto A. Lung Ultrasound Score for Prediction of Surfactant Administration in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Failure. J Perinatol. 2024;44:1258–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-024-02090-3.
Corsini I, Ficial B, Ciarcià M, Capasso L, Migliaro F, Rodriguez-Fanjul J, et al. Lung ultrasound scores in neonatal clinical practice: A narrative review of the literature. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2022;57:1157–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.25875.
Thandaveshwara D, Chandrashekar Reddy AH, Gopalakrishna MV, Doreswamy SM. Saturation oxygenation pressure index: a non-invasive bedside measure for severity of respiratory disease in neonates on CPAP. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:1287–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-020-03877-0.
Brat R, Yousef N, Klifa R, Reynaud S, Shankar Aguilera S, De Luca D. Lung Ultrasonography Score to Evaluate Oxygenation and Surfactant Need in Neonates Treated With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169:e151797 https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.1797.
Pezza L, Sartorius V, Loi B, Regiroli G, Centorrino R, Lanciotti L, et al. Evolution of Ultrasound-Assessed Lung Aeration and Gas Exchange in Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Transient Tachypnea of the Neonate. J Pediatr. 2023;256:44–52.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.11.037.
Burkett DA, Patel SS, Mertens L, Friedberg MK, Ivy DD. Relationship Between Left Ventricular Geometry and Invasive Hemodynamics in Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;13:e009825. https://doi.org/10.1161/circimaging.119.009825.
Schweintzger S, Kurath-Koller S, Burmas A, Grangl G, Fandl A, Noessler N, et al. Normal Echocardiographic Reference Values of the Right Ventricular to Left Ventricular Endsystolic Diameter Ratio and the Left Ventricular Endsystolic Eccentricity Index in Healthy Children and in Children With Pulmonary Hypertension. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:950765. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.950765.
Hamrick SEG, Sallmon H, Rose AT, Porras D, Shelton EL, Reese J, et al. Patent Ductus Arteriosus of the Preterm Infant. Pediatrics. 2020;146. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-1209.
Yin TJ, Hu YS, Cheng S, Yong QJ. Dynamic changes of pulmonary arterial pressure in perinatal neonates with pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute lung injury/respiratory distress syndrome. Medicine (Baltim). 2019;98:e14830 https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000014830.
Possmayer F, Zuo YY, Veldhuizen RAW, Petersen NO. Pulmonary Surfactant: A Mighty Thin Film. Chem Rev. 2023;123:13209–90. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00146.
Kang C, Zhao E, Zhou Y, Zhao H, Liu Y, Gao N, et al. Dynamic Changes of Pulmonary Arterial Pressure and Ductus Arteriosus in Human Newborns From Birth to 72 h of Age. Medicine (Baltim). 2016;95:e2599. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000002599.
Stewart DL, Elsayed Y, Fraga MV, Coley BD, Annam A, Milla SS, et al. Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in the NICU for Diagnostic and Procedural Purposes. Pediatrics. 2022;150. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2022-060053.
Cativo Calderon EH, Mene-Afejuku TO, Valvani R, Cativo DP, Tripathi D, Reyes HA, et al. D-Shaped Left Ventricle, Anatomic, and Physiologic Implications. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2017;2017:4309165. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4309165.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the University of Connecticut/Connecticut Children’s for supporting this research, the families agreeing to participate in the study, and the bedside nursing staff caring for the enrolled infants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JK helped design the study, performed the ultrasounds, acquired the data for analysis, interpreted the data, and helped to write the manuscript. NH and HC helped design the study, interpret the results, and write the manuscript. SP helped design the study, interpret the results, ensure the quality of the ultrasound images, and write the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kelner, J., Hussain, N., Chicaiza, H. et al. Lung ultrasound score and left ventricular eccentricity index in preterm infants with respiratory failure – a pilot study. J Perinatol 46, 26–30 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02429-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02429-4