Abstract
Objective
To analyze the association between gestational age (GA) and postmenstrual age (PMA) at successful noninvasive respiratory support (NRS) —which includes noninvasive ventilation with neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NIV-NAVA), nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP), and high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC)— weaning and to identify the risk factors affecting PMA at successful NRS weaning.
Study design
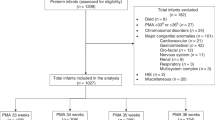
This retrospective cohort study included 449 preterm infants born before 32 weeks’ GA who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit between 2015 and 2023.
Results
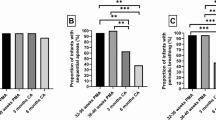
The median PMA at successful weaning was 36.0 weeks. PMA at successful weaning was negatively correlated with GA. Only a small number of infants with earlier GA achieved successful weaning before 36 weeks of PMA. Earlier GA, small for GA, bubbly/cystic appearance on X-rays, and bowel perforation with ileostomy were identified as risk factors for delayed weaning.
Conclusion
Clinical interventions should consider these risks to optimize weaning outcomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Crowley PA. Antenatal corticosteroid therapy: a meta-analysis of the randomized trials, 1972 to 1994. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;173:322–35.
Speer CP, Sweet DG, Halliday HL. Surfactant therapy: past, present and future. Early Hum Dev. 2013;89:S22–4.
Marter LJV, Allred EN, Pagano M, Sanocka U, Parad R, Moore M, et al. Do clinical markers of barotrauma and oxygen toxicity explain interhospital variation in rates of chronic lung disease? The Neonatology Committee for the Developmental Network. Pediatrics. 2000;105:1194–201.
Rojas MA, Gonzalez A, Bancalari E, Claure N, Poole C, Silva-Neto G. Changing trends in the epidemiology and pathogenesis of neonatal chronic lung disease. J Pediatr. 1995;126:605–10.
Howlett A, Ohlsson A, Plakkal N. Inositol for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;3:CD000366.
Kinsella JP, Greenough A, Abman SH. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lancet. 2006;367:1421–31.
Walsh MC, Yao Q, Gettner P, Hale E, Collins M, Hensman A, et al. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics. 2004;114:1305–11.
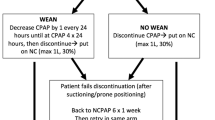
Rastogi S, Rajasekhar H, Gupta A, Bhutada A, Rastogi D, Wung JT. Factors affecting the weaning from nasal CPAP in preterm neonates. Int J Pediatr. 2012;2012:416073.
Chen IL, Chen HL. Impact of Illness Severity and interventions on successful weaning from nasal CPAP in very preterm neonates: an observational study. Children. 2022;9:673.
Arai H, Ito M, Ito T, Ota S, Takahashi T. Bubbly and cystic appearance on chest radiograph of extremely preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia is associated with wheezing disorder. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109:711–9.
Ito M, Kato S, Saito M, Miyahashi N, Arai H, Namba F, et al. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants: a scoping review for identifying risk factors. Biomedicines. 2023;11:553.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:452–8.
Delft B, Ginderdeuren FV, Lefevere J, Delft C, Cools F. Weaning strategies for the withdrawal of non-invasive respiratory support applying continuous positive airway pressure in preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2020;4:e000858.
Talbot LJ, Sinyard RD, Rialon KL, Englum BR, Tracy ET, Rice HE. Influence of weight at enterostomy reversal on surgical outcomes in infants after emergent neonatal stoma creation. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52:35–9.
Biniwale MA, Ehrenkranz RA. The role of nutrition in the prevention and management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2006;30:200–8.
Garcia-Anton A, Dreyfus L, Portefaix A, Baudin F, Plaisant F, Loppinet T, et al. Factors of late respiratory support or oxygen weaning in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2025;60:e27367.
Wai KC, Keller RL, Lusk LA, Ballard RA, Chan DK. Characteristics of extremely low gestational age newborns undergoing tracheotomy: a secondary analysis of The Trial of Late Surfactant Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;143:13–9.
Ikeda K, Hasegawa H, Yamada Y, Mizogami M, Wasa M. Airway diseases in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol. 2025;45:50–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SE and AN conceived and designed the study. SE performed material preparation, data collection, and the literature review. SE also analyzed and interpreted the results and drafted the manuscript. TT and AN supported the statistical analyses. AN supervised the study, including data analysis and interpretation. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Japanese Red Cross Medical Center (approval code: 1675) and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Because this was a retrospective observational study, the requirement for written informed consent was waived, and the study proceeded using an opt-out approach.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eguchi, S., Takeda, T. & Nakao, A. Duration of noninvasive respiratory support in preterm infants: Association with gestational age and risk factors for delayed weaning. J Perinatol 46, 50–54 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02492-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02492-x