Abstract
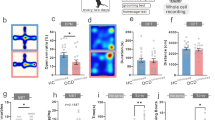
Adequate evidence has shown that gut microbial dysbiosis is an emerging disease phenotype of bipolar disorder (BD), and is closely related to clinical symptoms of this intractable disease. However, how gut microbiota affects the nervous system in BD remains largely unclear. In this study, we constructed a BD depression-like mouse model via fecal microbiota transplantation, and explored the changes of synaptic plasticity and connectivity in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of BD mice. We found that bipolar depression-like mice presented with a decrease in the density of dendritic spines in medial prefrontal neurons, and “Translation at postsynapse” as a key contributor to the changes in synaptic plasticity. In addition, analysis of synaptic connectivity in the mPFC revealed that compared to control mice, less connections were observed between ventral tegmental area and mPFC glutamate neurons and dopamine response was decreased in BD mice. These findings suggest that gut microbiota from BD depression patients induces the development of bipolar depression possibly by modulating aberrant synaptic connectivity and dopamine transmission in the VTA-mPFC pathway, which sheds light on the microbiota-gut-brain mechanisms underlying BD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data supporting the key findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary files.
References
Anderson IM, Haddad PM, Scott J. Bipolar disorder. BMJ. 2012;345:e8508.
Merikangas KR, Jin R, He JP, Kessler RC, Lee S, Sampson NA, et al. Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:241–51.
Nierenberg AA, Agustini B, Kohler-Forsberg O, Cusin C, Katz D, Sylvia LG, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder: a review. JAMA. 2023;330:1370–80.
Harrison PJ, Geddes JR, Tunbridge EM. The emerging neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Trends in Neurosciences. 2018;41:18–30.
Domenech P, Rheims S, Koechlin E. Neural mechanisms resolving exploitation-exploration dilemmas in the medial prefrontal cortex. Science. 2020;369:eabb0184.
Etkin A, Egner T, Kalisch R. Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:85–93.
Savitz JB, Price JL, Drevets WC. Neuropathological and neuromorphometric abnormalities in bipolar disorder: view from the medial prefrontal cortical network. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;42:132–47.
Nikolova VL, Hall MRB, Hall LJ, Cleare AJ, Stone JM, Young AH. Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: a review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:1343–54.
Rieder R, Wisniewski PJ, Alderman BL, Campbell SC. Microbes and mental health: A review. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;66:9–17.
Zmora N, Suez J, Elinav E. You are what you eat: diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:35–56.
Vinberg M, Ottesen NM, Meluken I, Sorensen N, Pedersen O, Kessing LV, et al. Remitted affective disorders and high familial risk of affective disorders associate with aberrant intestinal microbiota. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;139:174–84.
Zhao M, Ren Z, Zhao A, Tang Y, Kuang J, Li M, et al. Gut bacteria-driven homovanillic acid alleviates depression by modulating synaptic integrity. Cell Metab. 2024;36:1000–12 e6.
Shi H, Ge X, Ma X, Zheng M, Cui X, Pan W, et al. A fiber-deprived diet causes cognitive impairment and hippocampal microglia-mediated synaptic loss through the gut microbiota and metabolites. Microbiome. 2021;9:223.
Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Björkholm B, Samuelsson A, et al. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:3047–52.
Lai J, Zhang P, Jiang J, Mou T, Li Y, Xi C, et al. New evidence of gut microbiota involvement in the neuropathogenesis of bipolar depression by TRANK1 modulation: joint clinical and animal data. Front Immunol. 2021;12:789647.
Li Z, Lai J, Zhang P, Ding J, Jiang J, Liu C, et al. Multi-omics analyses of serum metabolome, gut microbiome and brain function reveal dysregulated microbiota-gut-brain axis in bipolar depression. Mol Psychiatry, 2022;27:4123–35.
Malhi GS, Bell E, Bassett D, Boyce P, Bryant R, Hazell P, et al. The 2020 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guidelines for mood disorders. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2021;55:7–117.
Jha MK, Mathew SJ. Pharmacotherapies for treatment-resistant depression: how antipsychotics fit in the rapidly evolving therapeutic landscape. Am J Psychiatry. 2023;180:190–9.
Chen Y, Li Y, Fan Y, Chen S, Chen L, Chen Y, et al. Gut microbiota-driven metabolic alterations reveal gut–brain communication in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2302310.
McIntyre RS, Subramaniapillai M, Shekotikhina M, Carmona NE, Lee Y, Mansur RB, et al. Characterizing the gut microbiota in adults with bipolar disorder: a pilot study. Nutr Neurosci. 2021;24:173–80.
Li D, Sun T, Tong Y, Le J, Yao Q, Tao J, et al. Gut-microbiome-expressed 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase degrades estradiol and is linked to depression in premenopausal females. Cell Metabolism. 2023;35:685–.e5.
Marizzoni M, Mirabelli P, Mombelli E, Coppola L, Festari C, Lopizzo N, et al. A peripheral signature of Alzheimer’s disease featuring microbiota-gut-brain axis markers. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy. 2023;15:101.
Liśkiewicz P, Kaczmarczyk M, Misiak B, Wroński M, Bąba-Kubiś A, Skonieczna-Żydecka K, et al. Analysis of gut microbiota and intestinal integrity markers of inpatients with major depressive disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2021;106:110076.
Radjabzadeh D, Bosch JA, Uitterlinden AG, Zwinderman AH, Ikram MA, van Meurs JBJ, et al. Gut microbiome-wide association study of depressive symptoms. Nature Communications. 2022;13:7128.
Hepple RT, Rice CL. Innervation and neuromuscular control in ageing skeletal muscle. Journal of Physiology-London. 2016;594:1965–78.
Nakamura Y, Okada N, Koshiyama D, Kamiya K, Abe O, Kunimatsu A, et al. Differences in functional connectivity networks related to the midbrain dopaminergic system-related area in various psychiatric disorders. Schizophr Bull. 2020;46:1239–48.
Nakahata Y, Yasuda R. Plasticity of spine structure: local signaling, translation and cytoskeletal reorganization. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience. 2018;10:29.
Ortega MA, Alvarez-Mon MA, García-Montero C, Fraile-Martínez O, Monserrat J, Martinez-Rozas L, et al. Microbiota-gut-brain axis mechanisms in the complex network of bipolar disorders: potential clinical implications and translational opportunities. Molecular Psychiatry. 2023;28:2645–73.
Gielow MR, Zaborszky L. The input-output relationship of the cholinergic basal forebrain. Cell Reports. 2017;18:1817–30.
Beier KT, Steinberg EE, DeLoach KE, Xie S, Miyamichi K, Schwarz L, et al. Circuit architecture of VTA dopamine neurons revealed by systematic input-output mapping. Cell. 2015;162:622–34.
Ogawa SK, Cohen JY, Hwang D, Uchida N, Watabe-Uchida M. Organization of monosynaptic inputs to the serotonin and dopamine neuromodulatory systems. Cell Reports. 2014;8:1105–18.
Schwarz LA, Luo LQ. Organization of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system. Current Biology. 2015;25:R1051–R1056.
Redlich R, Dohm K, Grotegerd D, Opel N, Zwitserlood P, Heindel W, et al. Reward processing in unipolar and bipolar depression: a functional MRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:2623–31.
Sidor MM, Spencer SM, Dzirasa K, Parekh PK, Tye KM, Warden MR, et al. Daytime spikes in dopaminergic activity drive rapid mood-cycling in mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20:1406–19.
Zhang Y, Fan Q, Hou Y, Zhang X, Yin Z, Cai X, et al. Bacteroides species differentially modulate depression-like behavior via gut-brain metabolic signaling. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;102:11–22.
Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:786–96.
Liu Y, Wang H, Gui S, Zeng B, Pu J, Zheng P, et al. Proteomics analysis of the gut-brain axis in a gut microbiota-dysbiosis model of depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:568.
Fang Y, Chen B, Liu Z, Gong AY, Gunning WT, Ge Y, et al. Age-related GSK3β overexpression drives podocyte senescence and glomerular aging. J Clin Invest. 2022;132:e141848.
Washizuka S, Ikeda A, Kato N, Kato T. Possible relationship between mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms and lithium response in bipolar disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003;6:421–4.
Mohamadian M, Fallah H, Ghofrani-Jahromi Z, Rahimi-Danesh M, Shokouhi Qare Saadlou MS, Vaseghi S. Mood and behavior regulation: interaction of lithium and dopaminergic system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023;396:1339–59.
Arey RN, Enwright JF III, Spencer SM, Falcon E, Ozburn AR, et al. An important role for cholecystokinin, a CLOCK target gene, in the development and treatment of manic-like behaviors. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:342–50.
Coque L, Mukherjee S, Cao JL, Spencer S, Marvin M, Falcon E, et al. Specific role of VTA dopamine neuronal firing rates and morphology in the reversal of anxiety-related, but not depression-related behavior in the ClockΔ19 mouse model of mania. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:1478–88.
Lam RW, Kennedy SH, Adams C, Bahji A, Beaulieu S, Bhat V, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) 2023 Update on Clinical Guidelines for Management of Major Depressive Disorder in Adults: Réseau canadien pour les traitements de l’humeur et de l’anxiété (CANMAT) 2023 : Mise à jour des lignes directrices cliniques pour la prise en charge du trouble dépressif majeur chez les adultes. Can J Psychiatry. 2024;69:641–87.
Parker BJ, Wearsch PA, Veloo ACM, Rodriguez-Palacios A. The genus alistipes: gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front Immunol. 2020;11:906.
Edwinson AL, Yang L, Peters S, Hanning N, Jeraldo P, Jagtap P, et al. Gut microbial beta-glucuronidases regulate host luminal proteases and are depleted in irritable bowel syndrome. Nat Microbiol. 2022;7:680–94.
Lu Y, Cui A, Zhang X. Commensal microbiota-derived metabolite agmatine triggers inflammation to promote colorectal tumorigenesis. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2348441.
Bangsgaard Bendtsen KM, Krych L, Sorensen DB, Pang W, Nielsen DS, Josefsen K, et al. Gut microbiota composition is correlated to grid floor induced stress and behavior in the BALB/c mouse. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46231.
Jiang H, Ling Z, Zhang Y, Mao H, Ma Z, Yin Y, et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun. 2015;48:186–94.
Zhuge A, Li S, Lou P, Wu W, Wang K, Yuan Y, et al. Longitudinal 16S rRNA sequencing reveals relationships among alterations of gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in mice. Microbiol Spectr. 2022;10:e0004722.
Ren F, Jin Q, Jin Q, Qian Y, Ren X, Liu T, et al. Genetic evidence supporting the causal role of gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease and chronic systemic inflammation in CKD: a bilateral two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1287698.
Misiak B, Pawlak E, Rembacz K, Kotas M, Zebrowska-Rozanska P, Kujawa D, et al. Associations of gut microbiota alterations with clinical, metabolic, and immune-inflammatory characteristics of chronic schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;171:152–60.
Jang KK, Heaney T, London M, Ding Y, Putzel G, Yeung F, et al. Antimicrobial overproduction sustains intestinal inflammation by inhibiting Enterococcus colonization. Cell Host Microbe. 2023;31:1450–.e8.
Guo Y, Kitamoto S, Caballero-Flores G, Kim Y, Watanabe D, Sugihara K, et al. Oral pathobiont Klebsiella chaperon usher pili provide site-specific adaptation for the inflamed gut mucosa. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2333463.
Pujo J, Petitfils C, Le Faouder P, Eeckhaut V, Payros G, Maurel S, et al. Bacteria-derived long chain fatty acid exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in colitis. Gut. 2021;70:1088–97.
Morais LH, Schreiber HLT, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:241–55.
Li D, Liu R, Wang M, Peng R, Fu S, Fu A, et al. 3beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expressed by gut microbes degrades testosterone and is linked to depression in males. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30:329–39 e5.
Pignatelli M, Bonci A. Spiraling connectivity of NAc-VTA circuitry. Neuron. 2018;97:261–2.
Mukherjee S, Coque L, Cao JL, Kumar J, Chakravarty S, Asaithamby A, et al. Knockdown of clock in the ventral tegmental area through RNA interference results in a mixed state of mania and depression-like behavior. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68:503–11.
Coque L, Mukherjee S, Cao JL, Spencer S, Marvin M, Falcon E, et al. Specific role of VTA dopamine neuronal firing rates and morphology in the reversal of anxiety-related, but not depression-related behavior in the ClockDelta19 mouse model of mania. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:1478–88.
Bloodgood DW, Sugam JA, Holmes A, Kash TL. Fear extinction requires infralimbic cortex projections to the basolateral amygdala. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8:60.
Liu WZ, Zhang WH, Zheng ZH, Zou JX, Liu XX, Huang SH, et al. Identification of a prefrontal cortex-to-amygdala pathway for chronic stress-induced anxiety. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2221.
Lieberman MD, Eisenberger NI, Crockett MJ, Tom SM, Pfeifer JH, Way BM. Putting feelings into words: affect labeling disrupts amygdala activity in response to affective stimuli. Psychol Sci. 2007;18:421–8.
Colich NL, Hanford LC, Weissman DG, Allen NB, Shirtcliff EA, Lengua LJ, et al. Childhood trauma, earlier pubertal timing, and psychopathology in adolescence: the role of corticolimbic development. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2023;59:101187.
Liu H, Tang Y, Womer F, Fan G, Lu T, Driesen N, et al. Differentiating patterns of amygdala-frontal functional connectivity in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40:469–77.
Perlman SB, Almeida JRC, Kronhaus DM, Versace A, LaBarbara EJ, Klein CR, et al. Amygdala activity and prefrontal cortex–amygdala effective connectivity to emerging emotional faces distinguish remitted and depressed mood states in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disorders. 2012;14:162–74.
Kataoka N, Shima Y, Nakajima K, Nakamura K. A central master driver of psychosocial stress responses in the rat. Science. 2020;367:1105–12.
Yu X, Ba W, Zhao G, Ma Y, Harding EC, Yin L, et al. Dysfunction of ventral tegmental area GABA neurons causes mania-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:5213–28.
Huang L, Chen Y, Jin S, Lin L, Duan S, Si K, et al. Organizational principles of amygdalar input-output neuronal circuits. Mol Psychiatry, 2021;26:7118–29.
Reardon TR, Murray AJ, Turi GF, Wirblich C, Croce KR, Schnell MJ, et al. Rabies Virus CVS-N2c(ΔG) Strain Enhances Retrograde Synaptic Transfer and Neuronal Viability. Neuron. 2016;89:711–24.
Wang T, Hao L, Yang K, Feng W, Guo Z, Liu M, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation derived from mild cognitive impairment individuals impairs cerebral glucose uptake and cognitive function in wild-type mice: Bacteroidetes and TXNIP-GLUT signaling pathway. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2395907.
Zhu F, Ju Y, Wang W, Wang Q, Guo R, Ma Q, et al. Metagenome-wide association of gut microbiome features for schizophrenia. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1612.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC2506200), STI 2030-Major Projects (2021ZD0200401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82571735,82471542,82201676), Key R&D Program of Zhejiang Province (2023C03077, 2024C03150, 2025C01119, 2024C03098, 2025C02109), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH Hu, W.Gong, JB Lai, K Si were responsible for the overall experimental design. YW Chen performed mice experiments, Stereotaxic injections, Tissue processing, Image acquisition and data analysis. AY Tang performed the mice experiments, fecal sample collect and mice behavior test data analysis. All the authors discussed the results and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, A., Chen, Y., Si, K. et al. Gut microbiota modulates synaptic plasticity, connectivity, and dopamine transmission in the VTA-mPFC pathway in bipolar depression. Mol Psychiatry (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03398-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03398-y