Abstract
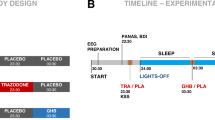
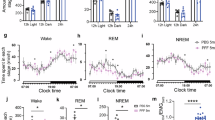
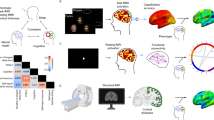
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) is an endogenous GHB/GABAB receptor agonist, which has demonstrated potency in consolidating sleep and reducing excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy. Little is known whether GHB’s efficacy reflects the promotion of physiological sleep mechanisms and no study has investigated its sleep consolidating effects under low sleep pressure. GHB (50 mg/kg p.o.) and placebo were administered in 20 young male volunteers at 2:30 a.m., the time when GHB is typically given in narcolepsy, in a randomized, double-blinded, crossover manner. Drug effects on sleep architecture and electroencephalographic (EEG) sleep spectra were analyzed. In addition, current source density (CSD) analysis was employed to identify the effects of GHB on the brain electrical sources of neuronal oscillations. Moreover, lagged-phase synchronization (LPS) analysis was applied to quantify the functional connectivity among sleep-relevant brain regions. GHB prolonged slow-wave sleep (stage N3) at the cost of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Furthermore, it enhanced delta–theta (0.5–8 Hz) activity in NREM and REM sleep, while reducing activity in the spindle frequency range (13–15 Hz) in sleep stage N2. The increase in delta power predominated in medial prefrontal cortex, parahippocampal and fusiform gyri, and posterior cingulate cortex. Theta power was particularly increased in the prefrontal cortex and both temporal poles. Moreover, the brain areas that showed increased theta power after GHB also exhibited increased lagged-phase synchronization among each other. Our study in healthy men revealed distinct similarities between GHB-augmented sleep and physiologically augmented sleep as seen in recovery sleep after prolonged wakefulness. The promotion of the sleep neurophysiological mechanisms by GHB may thus provide a rationale for GHB-induced sleep and waking quality in neuropsychiatric disorders beyond narcolepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Fernandez-Mendoza J, Vgontzas AN. Insomnia and its impact on physical and mental health. Curr Psychiatr Rep. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-013-0418-8
Ohayon MM, Caulet M, Lemoine P. Comorbidity of mental and insomnia disorders in the general population. Compr Psychiatry. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-440X(98)90059-1
Weissman MM, Greenwald S, Niño-Murcia G, Dement WC. The morbidity of insomnia uncomplicated by psychiatric disorders. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-8343(97)00056-X
Wafford KA, Ebert B. Emerging anti-insomnia drugs: tackling sleeplessness and the quality of wake time. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2464
Winsky-Sommerer R. Role of GABAA receptors in the physiology and pharmacology of sleep. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06716.x
Akeju O, Brown EN. Neural oscillations demonstrate that general anesthesia and sedative states are neurophysiologically distinct from sleep. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2017.04.011
Landolt HP, Gillin JC. GABA(A1a) receptors: Involvement in sleep regulation and potential of selective agonists in the treatment of insomnia. CNS Drugs. 2000. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200013030-00005
Feinberg I, Maloney T, Campbell IG. Effects of hypnotics on the sleep EEG of healthy young adults: new data and psychopharmacologic implications. J Psychiatr Res. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3956(00)00038-8
Mamelak M. Narcolepsy and depression and the neurobiology of gammahydroxybutyrate. Prog Neurobiol. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.07.004
Büchele F, Hackius M, Schreglmann SR, Omlor W, Werth E, Maric A, et al. Sodium oxybate for excessive daytime sleepiness and sleep disturbance in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3171
Huang Y-S, Guilleminault C. Narcolepsy: action of two gamma-aminobutyric acid type B agonists, baclofen and sodium oxybate. Pediatr Neurol. 2009;41:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2009.02.008
Ondo WG, Perkins T, Swick T, Hull KL, Jimenez JE, Garris TS, et al. Sodium oxybate for excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2008;65:1337–1340. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.65.10.1337
Swick TJ. Sodium oxybate: a potential new pharmacological option for the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2011;3:167–178. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X11411599
Van Cauter E, Plat L, Scharf MB, Leproult R, Cespedes S, L’Hermite-Balériaux M, et al. Simultaneous stimulation of slow-wave sleep and growth hormone secretion by gamma-hydroxybutyrate in normal young men. J Clin Investig. 1997;100:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI119587
Vienne J, Lecciso G, Constantinescu I, Schwartz S, Franken P, Heinzer R, et al. Differential effects of sodium oxybate and baclofen on EEG, sleep, neurobehavioral performance, and memory. Sleep. 2012;35:1071–83. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1992
Tononi G, Cirelli C. Sleep and the price of plasticity: from synaptic and cellular homeostasis to memory consolidation and integration. Neuron. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.025
Walker MP. The role of sleep in cognition and emotion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04416.x
Morawska MM, Buchele F, Moreira CG, Imbach LL, Noain D, Baumann CR. Sleep modulation alleviates axonal damage and cognitive decline after rodent traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 2016;36:3422–3429. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3274-15.2016
Lapierre O, Montplaisir J, Lamarre M, Bedard MA. The effect of gamma-hydroxybutyrate on nocturnal and diurnal sleep of normal subjects: further considerations on REM sleep-triggering mechanisms. Sleep. 1990. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/13.1.24
Borbely AA. A two process model of sleep regulation. Hum Neurobiol. 1982. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12371
Borbely AA, Achermann P. Sleep homeostasis and models of sleep regulation [see comments]. J Biol Rhythms. 1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4160-6645-3.00037-2
Finelli LA, Borbély AA, Achermann P. Functional topography of the human nonREM sleep electroencephalogram. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0953-816X.2001.01597.x
Bersagliere A, Pascual-Marqui RD, Tarokh L, Achermann P. Mapping slow waves by EEG topography and source localization: effects of sleep deprivation. Brain Topogr. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0595-6
Holst SC, Bersagliere A, Bachmann V, Berger W, Achermann P, Landolt H-P. Dopaminergic role in regulating neurophysiological markers of sleep homeostasis in humans. J Neurosci. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4128-13.2014
Bachmann V, Klein C, Bodenmann S, Schäfer N, Berger W, Brugger P, et al. The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism modulates sleep intensity: EEG frequency- and state-specificity. Sleep. 2012. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1690
Jasper HH. The ten-tweny electrode system of the international federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(58)90053-1
Retey JV, Adam M, Gottselig JM, Khatami R, Durr R, Achermann P, et al. Adenosinergic mechanisms contribute to individual differences in sleep deprivation-induced changes in neurobehavioral function and brain rhythmic activity. J Neurosci. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1538-06.2006
Valomon A, Holst SC, Borrello A, Weigend S, Müller T, Berger W, et al. Effects of COMT genotype and tolcapone on lapses of sustained attention after sleep deprivation in healthy young men. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0018-8
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL Jr., Quan SF. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. In: AASM manual for scoring sleep. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201200111
Liechti ME, Quednow BB, Liakoni E, Dornbierer D, Von Rotz R, Gachet MS, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of γ-hydroxybutyrate in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81:980–988. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12863
Buzsáki G, Draguhn A. Neuronal olscillations in cortical networks. Science. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1099745
Uhlhaas PJ, Singer,W. Abnormal neural oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2774
Varela F, Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J. The brainweb: Phase synchronization and large-scale integration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1038/35067550
Babiloni C, Lizio R, Carducci F, Vecchio F, Redolfi A, Marino S, et al. Resting state cortical electroencephalographic rhythms and white matter vascular lesions in subjects with alzheimer’s disease: an italian multicenter study. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-101710
De Ridder D, Vanneste S, Kovacs S, Sunaert S, Dom G. Transient alcohol craving suppression by rTMS of dorsal anterior cingulate: an fMRI and LORETA EEG study. Neurosci Lett. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.03.074
Hochberg Y, Benjamini Y. More powerful procedures for multiple significance testing. Stat Med. 1990. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780090710
Pascual-Marqui RD, Lehmann D, Koukkou M, Kochi K, Anderer P, Saletu B, et al. Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Phil Transact R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0081
Mamelak M. Parkinson’s disease, the dopaminergic neuron and gammahydroxybutyrate. Neurol Ther. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-018-0091-2
Mamelak M. Alzheimer’ s disease, oxidative stress and gammahydroxybutyrate. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:1340–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.008
Walsh JK, Hall-Porter JM, Griffin KS, Dodson ER, Forst EH, Curry DT, et al. Enhancing slow wave sleep with sodium oxybate reduces the behavioral and physiological impact of sleep loss. Sleep. 2010;33:1217–25. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20857869
Ong JL, Lo JC, Gooley JJ, Chee MWL. EEG changes accompanying successive cycles of sleep restriction with and without naps in adolescents. Sleep. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx030
Maric A, Lustenberger C, Werth E, Baumann CR, Poryazova R, Huber R. Intraindividual increase of homeostatic sleep pressure across acute and chronic sleep loss: a high-density EEG study. Sleep. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx122
Marzano C, Ferrara M, Curcio G, De Gennaro L. The effects of sleep deprivation in humans: topographical electroencephalogram changes in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep versus REM sleep. J Sleep Res. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2009.00776.x
Borbély AA, Baumann F, Brandeis D, Strauch I, Lehmann D. Sleep deprivation: Effect on sleep stages and EEG power density in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1981. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(81)90225-X
Kaupmann K, Cryan JF, Wellendorph P, Mombereau C, Sansig G, Klebs K, et al. Specific gamma-hydroxybutyrate-binding sites but loss of pharmacological effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in GABA(B)(1)-deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. https://doi.org/3013 [pii]
Gauthier P, Arnaud C, Gandolfo G, Gottesmann C. Influence of a GABA(B) receptor antagonist on the sleep-waking cycle in the rat. Brain Res. 1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(97)00643-4
Juhász G, Emri Z, Kékesi KA, Salfay O, Crunelli V. Blockade of thalamic GABABreceptors decreases EEG synchronization. Neurosci Lett. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(94)90685-8
Vienne J, Bettler B, Franken P, Tafti M. Differential effects of GABAB receptor subtypes, {gamma}-hydroxybutyric acid, and Baclofen on EEG activity and sleep regulation. J Neurosci. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3145-10.2010
Bowery NGG, Hudson ALL, Price GWW. GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(87)90098-4
Szabo ST, Gold MS, Goldberger BA, Blier P. Effects of sustained gamma-hydroxybutyrate treatments on spontaneous and evoked firing activity of locus coeruleus norepinephrine neurons. Biol Psychiatr. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.12.013
Landolt HP, Meier V, Burgess HJ, Finelli LA, Cattelin F, Achermann P, et al. Serotonin-2 receptors and human sleep: effect of a selective antagonist on EEG power spectra. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. https://doi.org/S0893-133X(99)00052-4 [pii]/r10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00052-4
Von Rotz R, Kometer M, Dornbierer D, Gertsch J, Salomé Gachet M, Vollenweider FX, et al. Neuronal oscillations and synchronicity associated with gamma-hydroxybutyrate during resting-state in healthy male volunteers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4603-z
Crunelli V, Leresche N. A role for GABABreceptors in excitation and inhibition of thalamocortical cells. Trends Neurosci. 1991.
Williams SR, Turner JP, Crunelli V. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate promotes oscillatory activity of rat and cat thalamocortical neurons by a tonic GABAB receptor-mediated hyperpolarization. Neuroscience. 1995. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(94)00604-4
Xie X, Smart TG. γ-Hydroxybutyrate hyperpolarizes hippocampal neurones by activating GABAB receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(92)90347-7
Maddock RJ, Garrett AS, Buonocore, MH. Remembering familiar people: the posterior cingulate cortex and autobiographical memory retrieval. Neuroscience. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00108-7
Born J, Wagner U. Sleep, hormones, and memory. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogc.2009.10.001
Köhler S, Black SE, Sinden M, Szekely C, Kidron D, Parker JL, et al. Memory impairments associated with hippocampal versus parahippocampal-gyrus atrophy: an MR volumetry study in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(98)00017-7
Leech R, Sharp DJ. The role of the posterior cingulate cortex in cognition and disease. Brain . 2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt162
Mander BA, Rao V, Lu B, Saletin JM, Lindquist JR, Ancoli-Israel S, et al. Prefrontal atrophy, disrupted NREM slow waves and impaired hippocampal-dependent memory in aging. Nat Neurosci. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3324
Czeisler CA, Weitzman ED, Moore-Ede MC, Zimmerman JC, Knauer RS. Human sleep: Its duration and organization depend on its circadian phase. Science. 1980. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7434029
Dijk D, Czeisler C. Contribution of the circadian pacemaker and the sleep homeostat to sleep propensity, sleep structure, electroencephalographic slow waves, and sleep spindle activity in humans. J Neurosci. 1995. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03526.1995
Brunner DP, Dijk DJ, Tobler I, Borbély AA. Effect of partial sleep deprivation on sleep stages and EEG power spectra: evidence for non-REM and REM sleep homeostasis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(90)90136-8
Brancucci A, Berretta N, Mercuri NB, Francesconi W. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate and ethanol depress spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 2004;997:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.046
Cruz HG, Ivanova T, Lunn M-L, Stoffel M, Slesinger PA, Lüscher C. Bi-directional effects of GABAB receptor agonists on the mesolimbic dopamine system. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1181
Hechler V, Gobaille S, Bourguignon J‐J, Maitre, M. Extracellular events induced by γ‐hydroxybutyrate in striatum: a microdialysis study. J Neurochem. 1991. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02012.x
Kuschinsky W, Suda S, Sokoloff L. Influence of gamma-hydroxybutyrate on the relationship between local cerebral glucose utilization and local cerebral blood flow in the rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985;5:58–64.
Labouèbe G, Lomazzi M, Cruz HG, Creton C, Luján R, Li M, et al. RGS2 modulates coupling between GABAB receptors and GIRK channels in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1559–1568. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2006
Fritz BA, Kalarickal PL, Maybrier HR, Muench MR, Dearth D, Chen Y, et al. Intraoperative electroencephalogram suppression predicts postoperative delirium. Anesth Analg. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000000989
Gehring WJ, Coles MG, Meyer DE, Donchin E. A brain potential manifestation of error-related processing. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1995;44:261–72. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7649032 Retrieved from
Mamelak M. Alzheimer’ s disease, oxidative stress and gammahydroxybutyrate. Neurobiol Aging. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.008
Patat A, Trocherie S, Thebault JJ, Rosenzweig P, Dubruc C, Bianchetti G, et al. EEG profile of intravenous zolpidem in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245455
Soehle M, Dittmann A, Ellerkmann RK, Baumgarten G, Putensen C, Guenther U. Intraoperative burst suppression is associated with postoperative delirium following cardiac surgery: a prospective, observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-015-0051-7
Van Lier H, Drinkenburg WHIM, Van Eeten YJW, Coenen, AML. Effects of diazepam and zolpidem on EEG beta frequencies are behavior-specific in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.03.017
Acknowledgements
We thank Vinnie Kandra for her dedicated assistance in data collection and participant recruitment. Moreover, we thank Antonio Fernandez Guerrero for his valuable comments on the CSD and LPS analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dornbierer, D.A., Baur, D.M., Stucky, B. et al. Neurophysiological signature of gamma-hydroxybutyrate augmented sleep in male healthy volunteers may reflect biomimetic sleep enhancement: a randomized controlled trial. Neuropsychopharmacol. 44, 1985–1993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0382-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0382-z
This article is cited by
-
Prophylactic effect of intraoperative sodium oxybate on postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery: a randomized clinical trial
BMC Medicine (2025)
-
Brain state monitoring and neuromodulation in sleep disorders: current perspectives
The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery (2025)
-
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate to promote slow-wave sleep in major depressive disorder: a randomized crossover trial
Neuropsychopharmacology (2025)
-
Hallmarks of primary headache: part 3 – cluster headache
The Journal of Headache and Pain (2025)
-
Paradoxical pharmacological dissociations result from drugs that enhance delta oscillations but preserve consciousness
Communications Biology (2023)