Abstract
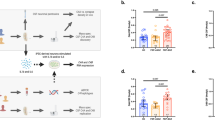
Abnormalities in the complement system have been described in patients with schizophrenia, with those individuals having greater frequency of complement component 4A (C4A) alleles and higher C4A transcript levels in postmortem brain tissue. Importantly, abnormalities in C4A and other complement molecules have been associated with synaptic pruning abnormalities that occur during neurodevelopment. A few studies have investigated C4 levels in living patients with schizophrenia, but all of them did so using peripheral blood samples. No studies have examined C4 levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), presumably a better biofluid choice given its intimate contact with the brain. Therefore, we report for the first time on C4 levels in CSF and plasma of patients with schizophrenia. In this study, we obtained CSF in 32 patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and 32 healthy volunteers and peripheral blood samples in 33 SSD and 31 healthy volunteers. C4 levels were measured using Abcam ELISA assays. Univariate analysis did not show a statistically significant difference in CSF C4 values between groups. However, a multivariable analysis showed a statistically significant increase in CSF C4 levels between groups after adjusting for sex and age. We also observed a high correlation between CSF C4 levels and age. By contrast, plasma C4 levels were not significantly different between groups. CSF and plasma C4 levels were not significantly correlated. Therefore, the use of CSF samples is critical and should be complementary to the use of peripheral blood samples to allow for a comprehensive understanding of complement C4 abnormalities in schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Woo JJ, Pouget JG, Zai CC, Kennedy JL. The complement system in schizophrenia: where are we now and what’s next?. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25:114–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0479-0.
Sekar A, Bialas AR, de Rivera H, Davis A, Hammond TR, Kamitaki N, et al. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature. 2016;530:177–83.
Gorelik A, Sapir T, Haffner-Krausz R, Olender T, Woodruff TM, Reiner O. Developmental activities of the complement pathway in migrating neurons. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15096. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15096.
Muraki K, Tanigaki K. Neuronal migration abnormalities and its possible implications for schizophrenia. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:74. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00074.
Sellgren CM, Gracias J, Watmuff B, Biag JD, Thanos JM, Whittredge PB, et al. Increased synapse elimination by microglia in schizophrenia patient-derived models of synaptic pruning. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:374–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0334-7.
Kamitaki N, Sekar A, Handsaker RE, de Rivera H, Tooley K, Morris DL, et al. Complement genes contribute sex-biased vulnerability in diverse disorders. Nature. 2020;582:577–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2277-x.
Gaya da Costa M, Poppelaars F, van Kooten C, Mollnes TE, Tedesco F, Würzner R, et al. Age and sex-associated changes of complement activity and complement levels in a healthy caucasian population. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2664. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02664.
Nilsson B, Hamad OA, Ahlström H, Kullberg J, Johansson L, Lindhagen L, et al. C3 and C4 are strongly related to adipose tissue variables and cardiovascular risk factors. Eur J Clin Investig. 2014;44:587–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.12275.
Laskaris L, Zalesky A, Weickert CS, Di Biase MA, Chana G, Baune BT, et al. Investigation of peripheral complement factors across stages of psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2019;204:30–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.11.035.
Zhou FC, Lee JWY, Zhang QH, Sun ZL, Bo Q, He XX, et al. Higher serum C-reactive protein levels in catatonic patients: a comparison to non-catatonic patients and healthy controls. Schizophr Bull. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbaa041. pii: sbaa041.
Melbourne JK, Rosen C, Feiner B, Sharma RP. C4A mRNA expression in PBMCs predicts the presence and severity of delusions in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder with psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2018;197:321–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.01.018.
Kopczynska M, Zelek W, Touchard S, Gaughran F, Di Forti M, Mondelli V, et al. Complement system biomarkers in first episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2019;204:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2017.12.012.
Donohoe G, Holland J, Mothersill D, McCarthy-Jones S, Cosgrove D, Harold D, et al. Genetically predicted complement component 4A expression: effects on memory function and middle temporal lobe activation. Psychol Med. 2018;48:1608–15. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291717002987.
Mondelli V, Di Forti M, Morgan BP, Murray RM, Pariante CM, Dazzan P. Baseline high levels of complement component 4 predict worse clinical outcome at 1-year follow-up in first-episode psychosis. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;S0889-1591:31082–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.01.014.
Brown E, Shah P, Kim J. Using chlorpromazineR to calculate chlorpromazine-equivalent doses. 2019. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/chlorpromazineR/vignettes/walkthrough.html. Accesed 8 July 2020.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2020. https://www.R-project.org/.
Leucht S, Samara M, Heres S, Davis JM. Dose equivalents for antipsychotic drugs: the DDD method. Schizophr Bull. 2016;42:S90–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv167.
Idonije OB, Akinlade KS, Ihenyen O, Arinola OG. Complement factors in newly diagnosed Nigerian schizoprenic patients and those on antipsychotic therapy. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2012;27:19–21.
Maes M, Delange J, Ranjan R, Meltzer HY, Desnyder R, Cooremans W, et al. Acute phase proteins in schizophrenia, mania and major depression: modulation by psychotropic drugs. Psychiatry Res. 1997;66:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-1781(96)02915-0.
Hansson O, Seibyl J, Stomrud E, Zetterberg H, Trojanowski JQ, Bittner T, et al. Swedish BioFINDER study group; Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease concord with amyloid-β PET and predict clinical progression: a study of fully automated immunoassays in BioFINDER and ADNI cohorts. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:1470–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.01.010.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Juan Cordero and Yuan-Shan Zhu at the CTSC Weill Cornell Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JAG collected all data, performed statistical analyses, and wrote the paper. EAB and CM assisted with data collection, data cleaning, and reviewed critically the paper. TL and AKM assisted with study design, data interpretation, and revised the paper critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallego, J.A., Blanco, E.A., Morell, C. et al. Complement component C4 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. 46, 1140–1144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00867-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00867-6
This article is cited by
-
Effect of olanzapine on changes in serum complement factors levels in patients with first-episode schizophrenia
BMC Psychiatry (2025)
-
Complement C4 exacerbates astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation and promotes α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease
npj Parkinson's Disease (2025)
-
Soluble terminal complement complex blood levels are elevated in schizophrenia
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2024)
-
Biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with psychotic disorders compared to healthy controls: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Association of elevated levels of peripheral complement components with cortical thinning and impaired logical memory in drug-naïve patients with first-episode schizophrenia
Schizophrenia (2023)