Abstract
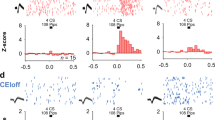
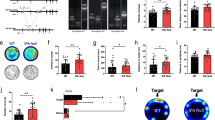
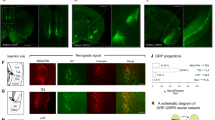
Fear is an adaptive state that drives defensive behavioral responses to specific and imminent threats. The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) is a critical site of adaptations that are required for the acquisition and expression of fear, in part due to alterations in the activity of inputs to the CeA. Here, we characterize a novel GABAergic input to the CeA from the ventral periaqueductal gray (vPAG) using fiber photometry and ex vivo whole-cell slice electrophysiology combined with optogenetics and pharmacology. GABA transmission from this ascending vPAG-CeA input was enhanced by serotonin via activation of serotonin type 2 C (5HT2C) receptors. Results suggest that these receptors are presynaptic. Interestingly, we found that GABA release from the vPAG-CeA input is enhanced following fear learning via activation of 5HT2C receptors and that this pathway is dynamically engaged in response to aversive stimuli. Additionally, we characterized serotonin release in the CeA during fear learning and recall for the first time using fiber photometry coupled to a serotonin biosensor. Together, these findings describe a mechanism by which serotonin modulates GABA release from ascending vPAG GABA inputs to the CeA and characterize a role for this pathway in fear.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Herry C, Johansen JP. Encoding of fear learning and memory in distributed neuronal circuits. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:1644–54.
Martinez RC, de Oliveira AR, Brandao ML. Conditioned and unconditioned fear organized in the periaqueductal gray are differentially sensitive to injections of muscimol into amygdaloid nuclei. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006;85:58–65.
Dejean C, Courtin J, Rozeske RR, Bonnet MC, Dousset V, Michelet T, et al. Neuronal Circuits for Fear Expression and Recovery: Recent Advances and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;78:298–306.
Tovote P, Fadok JP, Luthi A. Neuronal circuits for fear and anxiety. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015;16:317–31.
George DT, Ameli R, Koob GF. Periaqueductal Gray Sheds Light on Dark Areas of Psychopathology. Trends Neurosci. 2019;42:349–60.
LeDoux JE, Iwata J, Cicchetti P, Reis DJ. Different projections of the central amygdaloid nucleus mediate autonomic and behavioral correlates of conditioned fear. J Neurosci. 1988;8:2517–29.
Vianna DM, Graeff FG, Landeira-Fernandez J, Brandao ML. Lesion of the ventral periaqueductal gray reduces conditioned fear but does not change freezing induced by stimulation of the dorsal periaqueductal gray. Learn Mem. 2001;8:164–9.
Zanoveli JM, Carvalho MC, Cunha JM, Brandao ML. Extracellular serotonin level in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala and dorsal periaqueductal gray under unconditioned and conditioned fear states: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res. 2009;1294:106–15.
Ciocchi S, Herry C, Grenier F, Wolff SB, Letzkus JJ, Vlachos I, et al. Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits. Nature. 2010;468:277–82.
Kim EJ, Horovitz O, Pellman BA, Tan LM, Li Q, Richter-Levin G, et al. Dorsal periaqueductal gray-amygdala pathway conveys both innate and learned fear responses in rats. Proc Natl Acad. 2013;110:14795–14800.
Haubensak W, Kunwar PS, Cai H, Ciocchi S, Wall NR, Ponnusamy R, et al. Genetic dissection of an amygdala microcircuit that gates conditioned fear. Nature. 2010;468:270–6.
Li H, Penzo MA, Taniguchi H, Kopec CD, Huang ZJ, Li B. Experience-dependent modification of a central amygdala fear circuit. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16:332–9.
Penzo MA, Robert V, Li B. Fear conditioning potentiates synaptic transmission onto long-range projection neurons in the lateral subdivision of central amygdala. J Neurosci. 2014;34:2432–7.
Penzo MA, Robert V, Tucciarone J, De Bundel D, Wang M, Van Aelst L, et al. The paraventricular thalamus controls a central amygdala fear circuit. Nature. 2015;519:455–9.
Johansen JP, Tarpley JW, LeDoux JE, Blair HT. Neural substrates for expectation-modulated fear learning in the amygdala and periaqueductal gray. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:979–86.
McNally GP, Johansen JP, Blair HT. Placing prediction into the fear circuit. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34:283–92.
Roy M, Shohamy D, Daw N, Jepma M, Wimmer GE, Wager TD. Representation of aversive prediction errors in the human periaqueductal gray. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:1607–12.
Rizvi TA, Ennis M, Behbehani MM, Shipley MT. Connections between the central nucleus of the amygdala and the midbrain periaqueductal gray: topography and reciprocity. J Comp Neurol. 1991;303:121–31.
Bienkowski MS, Rinaman L. Common and distinct neural inputs to the medial central nucleus of the amygdala and anterior ventrolateral bed nucleus of stria terminalis in rats. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218:187–208.
Fu W, Le Maitre E, Fabre V, Bernard JF, David Xu ZQ, Hokfelt T. Chemical neuroanatomy of the dorsal raphe nucleus and adjacent structures of the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518:3464–94.
Challis C, Boulden J, Veerakumar A, Espallergues J, Vassoler FM, Pierce RC, et al. Raphe GABAergic neurons mediate the acquisition of avoidance after social defeat. J Neurosci. 2013;33:13978–88, 13988a.
Lowery-Gionta EG, DiBerto J, Mazzone CM, Kash TL. GABA neurons of the ventral periaqueductal gray area modulate behaviors associated with anxiety and conditioned fear. Brain Struct Funct. 2018;223:3787–99.
Tovote P, Esposito MS, Botta P, Chaudun F, Fadok JP, Markovic M, et al. Midbrain circuits for defensive behaviour. Nature. 2016;534:206–12.
Burghardt NS, Bauer EP. Acute and chronic effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment on fear conditioning: implications for underlying fear circuits. Neuroscience. 2013;247:253–72.
Marcinkiewcz CA, Mazzone CM, D’Agostino G, Halladay LR, Hardaway JA, DiBerto JF, et al. Serotonin engages an anxiety and fear-promoting circuit in the extended amygdala. Nature. 2016;537:97–101.
Marcinkiewcz CA, Bierlein-De La Rosa G, Dorrier CE, McKnight M, DiBerto JF, Pati D, et al. Sex-Dependent Modulation of Anxiety and Fear by 5-HT1A Receptors in the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10:3154–66.
Unger EK, Keller JP, Altermatt M, Liang R, Matsui A, Dong C, et al. Directed Evolution of a Selective and Sensitive Serotonin Sensor via Machine Learning. Cell. 2020;183:1986–2002.e26.
Ren J, Friedmann D, Xiong J, Liu CD, Ferguson BR, Weerakkody T, et al. Anatomically Defined and Functionally Distinct Dorsal Raphe Serotonin Sub-systems. Cell. 2018;175:472–87 e20.
Rainnie DG. Serotonergic modulation of neurotransmission in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:69–85.
Spoida K, Masseck OA, Deneris ES, Herlitze S. Gq/5-HT2c receptor signals activate a local GABAergic inhibitory feedback circuit to modulate serotonergic firing and anxiety in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:6479–84.
Theile JW, Morikawa H, Gonzales RA, Morrisett RA. Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors in Ca2+-dependent ethanol potentiation of GABA release onto ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J Pharm Exp Ther. 2009;329:625–33.
Vong L, Ye C, Yang Z, Choi B, Chua S, Lowell BB. Leptin action on GABAergic neurons prevents obesity and reduces inhibitory tone to POMC neurons. Neuron. 2011;71:142–54.
Mathis A, Mamidanna P, Cury KM, Abe T, Murthy VN, Mathis MW, et al. DeepLabCut: markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1281–9.
Nilsson SR, Goodwin NL, Choong JJ, Hwang S, Wright HR, Norville ZC, et al. Simple Behavioral Analysis (SimBA) – an open source toolkit for computer classification of complex social behaviors in experimental animals. 2020. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.19.049452.
Martianova E, Aronson S, Proulx CD Multi-Fiber Photometry to Record Neural Activity in Freely-Moving Animals. J Vis Exp JoVE. 2019. 20 October 2019. https://doi.org/10.3791/60278.
Lowery-Gionta EG, Marcinkiewcz CA, Kash TL. Functional alterations in the dorsal raphe nucleus following acute and chronic ethanol exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:590–600.
Lowery-Gionta EG, Crowley NA, Bukalo O, Silverstein S, Holmes A, Kash TL. Chronic stress dysregulates amygdalar output to the prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology. 2018;139:68–75.
Khom S, Wolfe SA, Patel RR, Kirson D, Hedges DM, Varodayan FP, et al. Alcohol Dependence and Withdrawal Impair Serotonergic Regulation of GABA Transmission in the Rat Central Nucleus of the Amygdala. J Neurosci. 2020;40:6842–53.
Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1083–152.
Nicholson AA, Friston KJ, Zeidman P, Harricharan S, McKinnon MC, Densmore M, et al. Dynamic causal modeling in PTSD and its dissociative subtype: Bottom-up versus top-down processing within fear and emotion regulation circuitry. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017;38:5551–61.
Sengupta A, Holmes A. A Discrete Dorsal Raphe to Basal Amygdala 5-HT Circuit Calibrates Aversive Memory. Neuron. 2019;103:489–505.e7.
Amat J, Matus-Amat P, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Escapable and inescapable stress differentially alter extracellular levels of 5-HT in the basolateral amygdala of the rat. Brain Res. 1998;812:113–20.
Tokunaga R, Shimoju R, Takagi N, Shibata H, Kurosawa M. Serotonin release in the central nucleus of the amygdala in response to noxious and innocuous cutaneous stimulation in anesthetized rats. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66:307–14.
Ren J, Isakova A, Friedmann D, Zeng J, Grutzner SM, Pun A, et al. Single-cell transcriptomes and whole-brain projections of serotonin neurons in the mouse dorsal and median raphe nuclei. ELife. 2019;8:e49424.
Becamel C, Gavarini S, Chanrion B, Alonso G, Galeotti N, Dumuis A, et al. The serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors interact with specific sets of PDZ proteins. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:20257–66.
Namburi P, Beyeler A, Yorozu S, Calhoon GG, Halbert SA, Wichmann R, et al. A circuit mechanism for differentiating positive and negative associations. Nature. 2015;520:675–8.
Duvarci S, Popa D, Pare D. Central amygdala activity during fear conditioning. J Neurosci. 2011;31:289–94.
Wright KM, McDannald MA. Ventrolateral periaqueductal gray neurons prioritize threat probability over fear output. ELife. 2019;8:e45013.
Wright KM, Jhou TC, Pimpinelli D, McDannald MA. Cue-inhibited ventrolateral periaqueductal gray neurons signal fear output and threat probability in male rats. ELife. 2019;8:e50054.
Gruene TM, Flick K, Stefano A, Shea SD, Shansky RM. Sexually divergent expression of active and passive conditioned fear responses in rats. ELife. 2015;4:e11352.
Sramek JJ, Murphy MF, Cutler NR. Sex differences in the psychopharmacological treatment of depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2016;18:447–57.
Acknowledgements
Schematics for this manuscript were created using Biorender.com.
Funding
This work was supported by the Bowles Center for Alcohol Studies and NIAAA/ NIH: F32-AA022549 (EGLG); T32-AA007573 (EGLG); R01-AA019454 (TLK); U01-AA020911 (TLK); P60-AA011605 (TLK); T32-NS007431 (OJH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OJH, EGLG and TLK: designed the experiments. OJH, EGLG, JFD, JS, DWB, MH, AK, NMM and AJL: performed the experiments. OJH, EGLG, JFD, CMM and JAH: analyzed data. OJH, EGLG and TLK: interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hon, O.J., DiBerto, J.F., Mazzone, C.M. et al. Serotonin modulates an inhibitory input to the central amygdala from the ventral periaqueductal gray. Neuropsychopharmacol. 47, 2194–2204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-022-01392-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-022-01392-4
This article is cited by
-
Subcortical modulation of the salience network during negative emotional processing in mood and anxiety disorders
Molecular Psychiatry (2025)
-
Feed-forward inhibitory circuit from the anterior cingulate cortex regulates periaqueductal gray’s panic-like responses
Brain Structure and Function (2025)
-
The gut metabolite indole-3-propionic acid activates ERK1 to restore social function and hippocampal inhibitory synaptic transmission in a 16p11.2 microdeletion mouse model
Microbiome (2024)
-
Simple Behavioral Analysis (SimBA) as a platform for explainable machine learning in behavioral neuroscience
Nature Neuroscience (2024)
-
An innovative approach to examining the role of neurotransmitters in fear circuitry
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)