Abstract
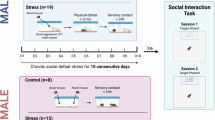
Social avoidance is highly detrimental for natural behavior. Despite much research on this topic, the mechanisms underlying the development of social avoidance as a consequence of social-related traumatic experiences remain highly elusive. To investigate this issue, we adapted a mouse model of social threat conditioning in which mice received shock punishment during exploration of an unfamiliar conspecific. This resulted in prominent and lasting reductions in social behavior, effects that were not observed in mice that received shock punishment in the absence of a social stimulus. Furthermore, the effects of social threat conditioning were independent of contextual settings, sex variables, and particular identity of the unfamiliar conspecifics that predicted shock punishment. Shedding new light into the neurobiological bases for this phenomenon, we found that optogenetic silencing of the prelimbic (PL), but not infralimbic (IL), prefrontal cortex during social threat conditioning produced profound forgetting and restoration of social behavior during subsequent sociability tests. Significant forgetting and recovery of social behavior was also observed with prelimbic inhibition of NMDARs. Collectively, these findings are consistent with the notion that social-related trauma is a prominent risk factor for social avoidance, and that traumatic experiences that involve social elements engage learning-related mechanisms in corticolimbic networks to promote long-term representations of social threat.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 13 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $19.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be shared for appropriate scientific use upon request. Viral vector sequences and other relevant information could be obtained from commercial suppliers (Addgene and UNC Vector Core).
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed. Arlington, VA, USA: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2013.
Rose GM, Tadi P. Social anxiety disorder. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Den Boer JA. Social anxiety disorder/social phobia: epidemiology, diagnosis, neurobiology, and treatment. Compr Psychiatry. 2000;41:405–15.
Spence SH, Rapee RM. The etiology of social anxiety disorder: an evidence-based model. Behav Res Ther. 2016;86:50–67.
Mizzi S, Pedersen M, Lorenzetti V, Heinrichs M, Labuschagne I. Resting-state neuroimaging in social anxiety disorder: a systematic review. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:164–79.
Bas-Hoogendam JM, Blackford JU, Brühl AB, Blair KS, van der Wee NJA, Westenberg PM. Neurobiological candidate endophenotypes of social anxiety disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;71:362–78.
Toth I, Neumann ID. Animal models of social avoidance and social fear. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;354:107–18.
Haller J, Bakos N. Stress-induced social avoidance: a new model of stress-induced anxiety? Physiol Behav. 2002;77:327–32.
Toth I, Neumann ID, Slattery DA. Social fear conditioning: a novel and specific animal model to study social anxiety disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:1433–43.
McTaggart EM, Miller NW, Ortiz-Juza MM, Pégard NC, Rodriguez-Romaguera J. A fully automated social interaction chamber for studying social threat learning in mice. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024;18:1481935.
Toth I, Neumann ID, Slattery DA. Social fear conditioning as an animal model of social anxiety disorder. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2013;63:9.42.1-9.42.13.
Brühl AB, Delsignore A, Komossa K, Weidt S. Neuroimaging in social anxiety disorder—a meta-analytic review resulting in a new neurofunctional model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;47:260–80.
Brühl AB, Hänggi J, Baur V, Rufer M, Delsignore A, Weidt S, et al. Increased cortical thickness in a frontoparietal network in social anxiety disorder. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35:2966–77.
Buff C, Brinkmann L, Neumeister P, Feldker K, Heitmann C, Gathmann B, et al. Specifically altered brain responses to threat in generalized anxiety disorder relative to social anxiety disorder and panic disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2016;12:698–706.
Qi C-C, Wang Q-J, Ma X-Z, Chen H-C, Gao L-P, Yin J, et al. Interaction of basolateral amygdala, ventral hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex regulates the consolidation and extinction of social fear. Behav Brain Funct. 2018;14:7.
Xu H, Liu L, Tian Y, Wang J, Li J, Zheng J, et al. A disinhibitory microcircuit mediates conditioned social fear in the prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2019;102:668–.e5.
Calhoon GG, Tye KM. Resolving the neural circuits of anxiety. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:1394–404.
Campos AC, Fogaça MV, Aguiar DC, Guimarães FS. Animal models of anxiety disorders and stress. Braz J Psychiatry. 2013;35:S101–111.
Kraeuter A-K, Guest PC, Sarnyai Z. The open field test for measuring locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavior. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1916:99–103.
Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J Vis Exp. 2015;6:e52434.
Felix-Ortiz AC, Terrell JM, Gonzalez C, Msengi HD, Boggan MB, Ramos AR, et al. Prefrontal regulation of safety learning during ethologically relevant thermal threat. eNeuro. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0140-23.2024.
Villalon SA, Felix-Ortiz AC, Lozano-Ortiz K, McCarrey JR, Burgos-Robles A. Impacts of social isolation stress in safety learning and the structure of defensive behavior during a spatial-based learning task involving thermal threat. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024;18:1503097.
Xu C, Peng B, Liu S. Using intra-brain drug infusion to investigate neural mechanisms underlying reward-seeking behavior in mice. STAR Protoc. 2022;3:101221.
Gruene TM, Flick K, Stefano A, Shea SD, Shansky RM. Sexually divergent expression of active and passive conditioned fear responses in rats. Elife. 2015;4:e11352.
Mitchell JR, Trettel SG, Li AJ, Wasielewski S, Huckleberry KA, Fanikos M, et al. Darting across space and time: parametric modulators of sex-biased conditioned fear responses. Learn Mem. 2022;29:171–80.
Bolles RC. Avoidance and escape learning: simultaneous acquisition of different responses. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969;68:355–8.
Furuyama T, Yamamoto R, Kato N, Ono M. Modified fear conditioning for inducing flight behaviors in mice. J Vis Exp. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3791/66266.
Molewijk HE, van der Poel AM, Olivier B. The ambivalent behaviour ‘stretched approach posture’ in the rat as a paradigm to characterize anxiolytic drugs. Psychopharmacology. 1995;121:81–90.
Yang M, Augustsson H, Markham CM, Hubbard DT, Webster D, Wall PM, et al. The rat exposure test: a model of mouse defensive behaviors. Physiol Behav. 2004;81:465–73.
Holly KS, Orndorff CO, Murray TA. MATSAP: an automated analysis of stretch-attend posture in rodent behavioral experiments. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31286.
Burgos-Robles A, Vidal-Gonzalez I, Santini E, Quirk GJ. Consolidation of fear extinction requires NMDA receptor-dependent bursting in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2007;53:871–80.
Hansen KB, Yi F, Perszyk RE, Furukawa H, Wollmuth LP, Gibb AJ, et al. Structure, function, and allosteric modulation of NMDA receptors. J General Physiol. 2018;150:1081–105.
Sotres-Bayon F, Quirk GJ. Prefrontal control of fear: more than just extinction. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20:231–5.
Bayer H, Bertoglio LJ. Infralimbic cortex controls fear memory generalization and susceptibility to extinction during consolidation. Sci Rep. 2020;10:15827.
Santini E, Quirk GJ, Porter JT. Fear conditioning and extinction differentially modify the intrinsic excitability of infralimbic neurons. J Neurosci. 2008;28:4028–36.
Vidal-Gonzalez I, Vidal-Gonzalez B, Rauch SL, Quirk GJ. Microstimulation reveals opposing influences of prelimbic and infralimbic cortex on the expression of conditioned fear. Learn Mem. 2006;13:728–33.
Boudjafad Z, Lguensat A, Elmardadi K, Dahi A, Bennis M, Ba-M’hamed S, et al. The socially enriched environment test: a new approach to evaluate social behavior in a mouse model of social anxiety disorder. Learn Mem. 2022;29:390–400.
Liebowitz MR, Gorman JM, Fyer AJ, Klein DF. Social phobia. Review of a neglected anxiety disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985;42:729–36.
Tei S, Kauppi J-P, Jankowski KF, Fujino J, Monti RP, Tohka J, et al. Brain and behavioral alterations in subjects with social anxiety dominated by empathic embarrassment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:4385–91.
Li D, Chokka P, Tibbo P. Toward an integrative understanding of social phobia. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2001;26:190–202.
Van Ameringen M, Mancini C, Farvolden P, Oakman J. The neurobiology of social phobia: from pharmacotherapy to brain imaging. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2000;2:358–66.
Bartlett AA, Singh R, Hunter RG. Anxiety and epigenetics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;978:145–66.
Lin E, Tsai S-J. Gene-environment interactions and role of epigenetics in anxiety disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:93–102.
Bebchuk JM, Tancer ME. Neurobiology of social phobia. CNS Spectr. 1999;4:42–48.
Wang J, Tian Y, Zeng L-H, Xu H. Prefrontal disinhibition in social fear: a vital action of somatostatin interneurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:611732.
Lucas EK, Clem RL. GABAergic interneurons: The orchestra or the conductor in fear learning and memory? Brain Res Bull. 2018;141:13–19.
Courtin J, Chaudun F, Rozeske RR, Karalis N, Gonzalez-Campo C, Wurtz H, et al. Prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons shape neuronal activity to drive fear expression. Nature. 2014;505:92–96.
Etkin A, Egner T, Kalisch R. Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:85–93.
Burgos-Robles A, Vidal-Gonzalez I, Quirk GJ. Sustained conditioned responses in prelimbic prefrontal neurons are correlated with fear expression and extinction failure. J Neurosci. 2009;29:8474–82.
Allsop SA, Wichmann R, Mills F, Burgos-Robles A, Chang C-J, Felix-Ortiz AC, et al. Corticoamygdala transfer of socially derived information gates observational learning. Cell. 2018;173:1329–42.
Fernandez-Leon JA, Engelke DS, Aquino-Miranda G, Goodson A, Rasheed MN, Do-Monte FH. Neural correlates and determinants of approach-avoidance conflict in the prelimbic prefrontal cortex. eLife. 2021;10:e74950.
Bravo-Rivera C, Sotres-Bayon F. From isolated emotional memories to their competition during conflict. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020;14:36.
Burgos-Robles A, Kimchi EY, Izadmehr EM, Porzenheim MJ, Ramos-Guasp WA, Nieh EH, et al. Amygdala inputs to prefrontal cortex guide behavior amid conflicting cues of reward and punishment. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20:824–35.
Anastasiades PG, Carter AG. Circuit organization of the rodent medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Neurosci. 2021;44:550–63.
Yang S-S, Mack NR, Shu Y, Gao W-J. Prefrontal GABAergic interneurons gate long-range afferents to regulate prefrontal cortex-associated complex behaviors. Front Neural Circuits. 2021;15:716408.
Jodo E, Katayama T, Okamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hoshino K, Kayama Y. Differences in responsiveness of mediodorsal thalamic and medial prefrontal cortical neurons to social interaction and systemically administered phencyclidine in rats. Neuroscience. 2010;170:1153–64.
Hoover WB, Vertes RP. Anatomical analysis of afferent projections to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Struct Funct. 2007;212:149–79.
Zhou T, Zhu H, Fan Z, Wang F, Chen Y, Liang H, et al. History of winning remodels thalamo-PFC circuit to reinforce social dominance. Science. 2017;357:162–8.
Zhou T, Sandi C, Hu H. Advances in understanding neural mechanisms of social dominance. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018;49:99–107.
Vander Weele CM, Siciliano CA, Matthews GA, Namburi P, Izadmehr EM, Espinel IC, et al. Dopamine enhances signal-to-noise ratio in cortical-brainstem encoding of aversive stimuli. Nature. 2018;563:397–401.
Jercog D, Winke N, Sung K, Fernandez MM, Francioni C, Rajot D, et al. Dynamical prefrontal population coding during defensive behaviours. Nature. 2021;595:690–4.
Janak PH, Tye KM. From circuits to behaviour in the amygdala. Nature. 2015;517:284–92.
Johansen JP, Tarpley JW, LeDoux JE, Blair HT. Neural substrates for expectation-modulated fear learning in the amygdala and periaqueductal gray. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:979–86.
Gore F, Schwartz EC, Brangers BC, Aladi S, Stujenske JM, Likhtik E, et al. Neural representations of unconditioned stimuli in basolateral amygdala mediate innate and learned responses. Cell. 2015;162:134–45.
Wei J-A, Han Q, Luo Z, Liu L, Cui J, Tan J, et al. Amygdala neural ensemble mediates mouse social investigation behaviors. Natl Sci Rev. 2023;10:nwac179.
Gabriel M, Sparenborg S, Kubota Y. Anterior and medial thalamic lesions, discriminative avoidance learning, and cingulate cortical neuronal activity in rabbits. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76:441–57.
Glover EJ, Margaret Starr E, Gascon A, Clayton-Stiglbauer K, Amegashie CL, Selchick AH, et al. Involvement of cortical input to the rostromedial tegmental nucleus in aversion to foot shock. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023;48:1455–64.
Powell DA, Maxwell B, Penney J. Neuronal activity in the medial prefrontal cortex during Pavlovian eyeblink and nictitating membrane conditioning. J Neurosci. 1996;16:6296–306.
Gilmartin MR, McEchron MD. Single neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat exhibit tonic and phasic coding during trace fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci. 2005;119:1496–510.
Gilmartin MR, Balderston NL, Helmstetter FJ. Prefrontal cortical regulation of fear learning. Trends Neurosciences. 2014;37:455–64.
Gilmartin MR, Helmstetter FJ. Trace and contextual fear conditioning require neural activity and NMDA receptor-dependent transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem. 2010;17:289–96.
Arruda-Carvalho M, Clem RL. Pathway-selective adjustment of prefrontal-amygdala transmission during fear encoding. J Neurosci. 2014;34:15601–9.
Scharnowski F, Nicholson AA, Pichon S, Rosa MJ, Rey G, Eickhoff SB, et al. The role of the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in dorsomedial prefrontal-amygdala neural circuitry during positive-social emotion regulation. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020;41:3100–18.
Huang W-C, Zucca A, Levy J, Page DT. Social behavior is modulated by valence-encoding mPFC-amygdala sub-circuitry. Cell Rep. 2020;32:107899.
Diehl MM, Iravedra-Garcia JM, Morán-Sierra J, Rojas-Bowe G, Gonzalez-Diaz FN, Valentín-Valentín VP, et al. Divergent projections of the prelimbic cortex bidirectionally regulate active avoidance. Elife. 2020;9:e59281.
Murugan M, Jang HJ, Park M, Miller EM, Cox J, Taliaferro JP, et al. Combined social and spatial coding in a descending projection from the prefrontal cortex. Cell. 2017;171:1663–.e16.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Shatavia McBride and Hope Msengi for technical assistance. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Isabel Muzzio, Dr. Todd Troyer, and Dr. Edwin Barea-Rodriguez for sharing equipment, Dr. Alfonso Apicella for sharing supplies and for general feedback on the project, and Dr. Maria Diehl for comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Funding
KLO, ACFO, JMT, CG, KRW, AEK, ARR, SAV, ANM, and ABR were supported by the Baptist Health Foundation, UTSA NDRB Seed Grant Program, UTSA College of Sciences, UT-STAR Program, and NIH grants R25EB027605 and T34GM145507. JRR was supported by the North Carolina TraCS Institute, Foundation of Hope, Brain and Behavior Research Foundation, Kavli Foundation, Whitehall Foundation, and NIH grant R01MH132073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: ABR and JRR. Research design: ABR, KLO, and JRR. Validation of methods: ABR, KLO, and ACFO. Animal behavior: KLO, ACFO, JMT, CG, KRW, AEK, ARR, SAV, and ANM. Optogenetics: KLO, ACFO, AEK, and ARR. Drug experiment: ABR., KLO, and ARR. Data analysis: ABR, KLO, and ACFO. Histology: KLO, JMT, CG, KRW, ARR, and ANM. Article preparation: ABR, KLO, and JRR. Project supervision: ABR.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano-Ortiz, K., Felix-Ortiz, A.C., Terrell, J.M. et al. The prelimbic prefrontal cortex mediates the development of lasting social avoidance as a consequence of social threat conditioning. Neuropsychopharmacol. 50, 1875–1884 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-025-02073-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-025-02073-8