Abstract
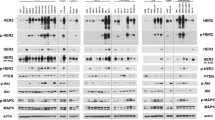
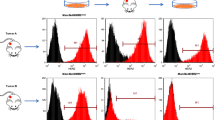
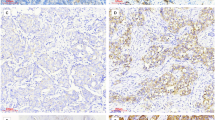
While mechanisms for metastasis were extensively studied in cancer cells from patients with detectable tumors, pathways underlying metastatic dissemination from early lesions before primary tumors appear are poorly understood. Her2 promotes breast cancer early dissemination by suppressing p38, but how Her2 downregulates p38 is unclear. Here, we demonstrate that in early lesion breast cancer models, Her2 inhibits p38 by inducing Skp2 through Akt-mediated phosphorylation, which promotes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Tpl2, a p38 MAP3K. The early disseminating cells are Her2+Skp2highTpl2lowp-p38lowE-cadherinlow in the MMTV-Her2 breast cancer model. In human breast carcinoma, high Skp2 and low Tpl2 expression are associated with the Her2+ status; Tpl2 expression positively correlates with that of activated p38; Skp2 expression negatively correlates with that of Tpl2 and activated p38. Moreover, the Her2-Akt-Skp2-Tpl2-p38 axis plays a key role in the disseminating phenotypes in early lesion breast cancer cells; inhibition of Tpl2 enhances early dissemination in vivo. These findings identify the Her2-Akt-Skp2-Tpl2-p38 cascade as a novel mechanism mediating breast cancer early dissemination and a potential target for novel therapies targeting early metastatic dissemination.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01652-5
References
Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:453–8.
Narod SA, Iqbal J, Giannakeas V, Sopik V, Sun P. Breast cancer mortality after a diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1:888–96.
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH. Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:448–56.
Abbruzzese JL, Abbruzzese MC, Hess KR, Raber MN, Lenzi R, Frost P. Unknown primary carcinoma: natural history and prognostic factors in 657 consecutive patients. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:1272–80.
Riethmuller G, Klein CA. Early cancer cell dissemination and late metastatic relapse: clinical reflections and biological approaches to the dormancy problem in patients. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001;11:307–11.
Lopez-Lazaro M. The migration ability of stem cells can explain the existence of cancer of unknown primary site. Rethinking metastasis. Oncoscience. 2015;2:467–75.
Eyles J, Puaux AL, Wang X, Toh B, Prakash C, Hong M, et al. Tumor cells disseminate early, but immunosurveillance limits metastatic outgrowth, in a mouse model of melanoma. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:2030–9.
Kang Y, Pantel K. Tumor cell dissemination: emerging biological insights from animal models and cancer patients. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:573–81.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–90.
Vleminckx K, Vakaet L Jr, Mareel M, Fiers W, van Roy F. Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell. 1991;66:107–19.
Aberle H, Schwartz H, Kemler R. Cadherin-catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function. J Cell Biochem. 1996;61:514–23.
Behrens J, Vakaet L, Friis R, Winterhager E, Van Roy F, Mareel MM, et al. Loss of epithelial differentiation and gain of invasiveness correlates with tyrosine phosphorylation of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex in cells transformed with a temperature-sensitive v-SRC gene. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:757–66.
Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004;303:1483–7.
Enslen H, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ. Selective activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase isoforms by the MAP kinase kinases MKK3 and MKK6. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1741–8.
Cuadrado A, Nebreda AR. Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 2010;429:403–17.
Shi Y, Gaestel M. In the cellular garden of forking paths: how p38 MAPKs signal for downstream assistance. Biol Chem. 2002;383:1519–36.
Gantke T, Sriskantharajah S, Sadowski M, Ley SC. IkappaB kinase regulation of the TPL-2/ERK MAPK pathway. Immunol Rev. 2012;246:168–82.
Salmeron A, Ahmad TB, Carlile GW, Pappin D, Narsimhan RP, Ley SC. Activation of MEK-1 and SEK-1 by Tpl-2 proto-oncoprotein, a novel MAP kinase kinase kinase. EMBO J. 1996;15:817–26.
Dumitru CD, Ceci JD, Tsatsanis C, Kontoyiannis D, Stamatakis K, Lin JH, et al. TNF-alpha induction by LPS is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent pathway. Cell. 2000;103:1071–83.
Pattison MJ, Mitchell O, Flynn HR, Chen CS, Yang HT, Ben-Addi H, et al. TLR and TNF-R1 activation of the MKK3/MKK6-p38alpha axis in macrophages is mediated by TPL-2 kinase. Biochem J. 2016;473:2845–61.
Senger K, Pham VC, Varfolomeev E, Hackney JA, Corzo CA, Collier J, et al. The kinase TPL2 activates ERK and p38 signaling to promote neutrophilic inflammation. Sci Signal. 2017;10.
Gong J, Fang C, Zhang P, Wang PX, Qiu Y, Shen LJ, et al. Tumor progression locus 2 in hepatocytes potentiates both liver and systemic metabolic disorders in mice. Hepatology. 2019;69:524–44.
Beinke S, Robinson MJ, Hugunin M, Ley SC. Lipopolysaccharide activation of the TPL-2/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is regulated by IkappaB kinase-induced proteolysis of NF-kappaB1 p105. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:9658–67.
Dodhiawala PB, Khurana N, Zhang D, Cheng Y, Li L, Wei Q, et al. TPL2 enforces RAS-induced inflammatory signaling and is activated by point mutations. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:4771–90.
Cho J, Melnick M, Solidakis GP, Tsichlis PN. Tpl2 (tumor progression locus 2) phosphorylation at Thr290 is induced by lipopolysaccharide via an Ikappa-B Kinase-beta-dependent pathway and is required for Tpl2 activation by external signals. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20442–8.
Bulavin DV, Fornace AJ Jr. p38 MAP kinase’s emerging role as a tumor suppressor. Adv Cancer Res. 2004;92:95–118.
Zheng H, Seit-Nebi A, Han X, Aslanian A, Tat J, Liao R, et al. A posttranslational modification cascade involving p38, Tip60, and PRAK mediates oncogene-induced senescence. Mol Cell. 2013;50:699–710.
Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, Kelly K, Siebenlist U. Cell cycle arrest and reversion of Ras-induced transformation by a conditionally activated form of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:3857–68.
She QB, Bode AM, Ma WY, Chen NY, Dong Z. Resveratrol-induced activation of p53 and apoptosis is mediated by extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinases and p38 kinase. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1604–10.
Wen HC, Avivar-Valderas A, Sosa MS, Girnius N, Farias EF, Davis RJ, et al. p38alpha signaling induces anoikis and lumen formation during mammary morphogenesis. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra34.
Huang S, New L, Pan Z, Han J, Nemerow GR. Urokinase plasminogen activator/urokinase-specific surface receptor expression and matrix invasion by breast cancer cells requires constitutive p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12266–72.
Anwar T, Arellano-Garcia C, Ropa J, Chen YC, Kim HS, Yoon E, et al. p38-mediated phosphorylation at T367 induces EZH2 cytoplasmic localization to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2801.
Wu MZ, Chen SF, Nieh S, Benner C, Ger LP, Jan CI, et al. Hypoxia drives breast tumor malignancy through a TET-TNFalpha-p38-MAPK signaling axis. Cancer Res. 2015;75:3912–24.
Harper KL, Sosa MS, Entenberg D, Hosseini H, Cheung JF, Nobre R, et al. Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2(+) mammary cancer. Nature. 2016;540:588–92.
Kim G, Khanal P, Kim JY, Yun HJ, Lim SC, Shim JH, et al. COT phosphorylates prolyl-isomerase Pin1 to promote tumorigenesis in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2015;54:440–8.
Kim K, Kim G, Kim JY, Yun HJ, Lim SC, Choi HS. Interleukin-22 promotes epithelial cell transformation and breast tumorigenesis via MAP3K8 activation. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:1352–61.
Decicco-Skinner KL, Trovato EL, Simmons JK, Lepage PK, Wiest JS. Loss of tumor progression locus 2 (tpl2) enhances tumorigenesis and inflammation in two-stage skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2011;30:389–97.
Gkirtzimanaki K, Gkouskou KK, Oleksiewicz U, Nikolaidis G, Vyrla D, Liontos M, et al. TPL2 kinase is a suppressor of lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E1470–1479.
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ, Brugge JS. ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:785–92.
Husemann Y, Geigl JB, Schubert F, Musiani P, Meyer M, Burghart E, et al. Systemic spread is an early step in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:58–68.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:704–15.
Xu L, Chen S, Bergan RC. MAPKAPK2 and HSP27 are downstream effectors of p38 MAP kinase-mediated matrix metalloproteinase type 2 activation and cell invasion in human prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:2987–98.
Han Y, Zhang L, Wang W, Li J, Song M. Livin promotes the progression and metastasis of breast cancer through the regulation of epithelialmesenchymal transition via the p38/GSK3beta pathway. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:3574–82.
Yan MH, Hao JH, Zhang XG, Shen CC, Zhang DJ, Zhang KS, et al. Advancement in TPL2-regulated innate immune response. Immunobiology. 2019;224:383–7.
Slack DN, Seternes OM, Gabrielsen M, Keyse SM. Distinct binding determinants for ERK2/p38alpha and JNK map kinases mediate catalytic activation and substrate selectivity of map kinase phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16491–500.
Candas D, Lu CL, Fan M, Chuang FY, Sweeney C, Borowsky AD, et al. Mitochondrial MKP1 is a target for therapy-resistant HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7498–509.
Mamillapalli R, Gavrilova N, Mihaylova VT, Tsvetkov LM, Wu H, Zhang H, et al. PTEN regulates the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27(KIP1) through the ubiquitin E3 ligase SCF(SKP2). Curr Biol. 2001;11:263–7.
Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker A, Wei W. Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:397–408.
Lin HK, Wang G, Chen Z, Teruya-Feldstein J, Liu Y, Chan CH, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cytosolic localization and oncogenic function of Skp2 by Akt/PKB. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:420–32.
Chan CH, Li CF, Yang WL, Gao Y, Lee SW, Feng Z, et al. The Skp2-SCF E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin sensitivity, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 2012;149:1098–111.
Ruiz-Saenz A, Dreyer C, Campbell MR, Steri V, Gulizia N, Moasser MM. HER2 amplification in tumors activates PI3K/Akt signaling independent of HER3. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3645–58.
Wisinski KB, Tevaarwerk AJ, Burkard ME, Rampurwala M, Eickhoff J, Bell MC, et al. Phase I study of an AKT Inhibitor (MK-2206) combined with lapatinib in adult solid tumors followed by dose expansion in advanced HER2+ breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:2659–67.
Krcova Z, Ehrmann J, Krejci V, Eliopoulos A, Kolar Z. Tpl-2/Cot and COX-2 in breast cancer. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2008;152:21–25.
del Barco Barrantes I, Nebreda AR. Roles of p38 MAPKs in invasion and metastasis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40:79–84.
Sosa MS, Avivar-Valderas A, Bragado P, Wen HC, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. ERK1/2 and p38alpha/beta signaling in tumor cell quiescence: opportunities to control dormant residual disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5850–7.
Chan CH, Lee SW, Wang J, Lin HK. Regulation of Skp2 expression and activity and its role in cancer progression. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010;10:1001–15.
Weidensdorfer D, Stohr N, Baude A, Lederer M, Kohn M, Schierhorn A, et al. Control of c-myc mRNA stability by IGF2BP1-associated cytoplasmic RNPs. RNA. 2009;15:104–15.
Kato H, Asamitsu K, Sun W, Kitajima S, Yoshizawa-Sugata N, Okamoto T, et al. Cancer-derived UTX TPR mutations G137V and D336G impair interaction with MLL3/4 complexes and affect UTX subcellular localization. Oncogene. 2020;39:3322–35.
Wei W, Shin YS, Xue M, Matsutani T, Masui K, Yang H, et al. Single-cell phosphoproteomics resolves adaptive signaling dynamics and informs targeted combination therapy in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:563–73.
Acknowledgements
We thank Cell Engineering and Tumor Tissue and Pathology Shared Resources of WFBCCC for support. This study was supported by NIH/NCI grants CA131231, CA172115, and P30CA012197 (PS) and Bilateral Inter-Governmental S&T Cooperation Project grants from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (81972882 and 2018YFE0114300) (RX). PS is an Anderson Oncology Research Professor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GW, JW, RX, and PS conceived and designed the study. GW, JW, MD, SH, AC, and DW executed the experiments; GW, JW, AC, KL, SS, HL, HL, and PS analyzed and interpreted the data. GW, JW, HL, HL, RX, and PS wrote and/or reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Wang, J., Chang, A. et al. Her2 promotes early dissemination of breast cancer by suppressing the p38 pathway through Skp2-mediated proteasomal degradation of Tpl2. Oncogene 39, 7034–7050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01481-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01481-y
This article is cited by
-
SKP2 protein as a prognostic biomarker for glioma and promotes tumor progression by regulating the cell cycle
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
A rapid imaging-based screen for induced-proximity degraders identifies a potent degrader of oncoprotein SKP2
Nature Biotechnology (2025)
-
Her2 promotes early dissemination of breast cancer by inhibiting the p38 pathway through the downregulation of MAP3K4
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Plasma THBS1 as a predictive biomarker for poor prognosis and brain metastasis in patients with HER2-enriched breast cancer
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Cluster analyses of the TCGA and a TMA dataset using the coexpression of HSP27 and CRYAB improves alignment with clinical-pathological parameters of breast cancer and suggests different epichaperome influences for each sHSP
Cell Stress and Chaperones (2022)