Abstract
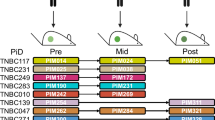
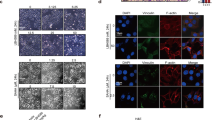
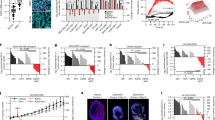
The gradual emergence of a novel therapeutic approach lies in the restoration of tumor suppressive machinery. PTEN is a crucial negative regulator of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Protein neddylation modification contributes to PTEN inactivation and fuels breast cancer progression. Here, we highlight that an elevated level of PTEN neddylation is markedly associated with resistance to palbociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor used in luminal subtype breast cancer patients. Mechanistically, PTEN neddylation activates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and more notably, upregulates the activity of the AP-1 transcription factor. Our data showed that PTEN neddylation stabilizes JUND, a transcription factor involved in the AP-1 complex, by disrupting its interaction with the E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH. Consequently, activated JUND leads to the release of cytokines and chemokines, which in turn may drive an inflammatory tumor microenvironment, potentially contributing to drug resistance. Then, we identified Echinacoside as a potent inhibitor of PTEN neddylation both in vivo and in vitro by disrupting its interaction with XIAP, the E3 ligase responsible for PTEN neddylation. Combination of Echinacoside effectively overcome resistance to palbociclib in breast cancer treatment. These findings highlight targeting PTEN neddylation as a promising strategy for restoring tumor suppressor activity and overcoming resistance.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
RNA-seq data have been deposited at SRA (PRJNA1143082 and PRJNA1144658) and are publicly available as of the date of publication. All data are available in the main text or the supplementary materials.
References
Nolan E, Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE. Deciphering breast cancer: from biology to the clinic. Cell. 2023;186:1708–28.
Harbeck N, Gnant M. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389:1134–50.
Giuliano M, Schettini F, Rognoni C, Milani M, Jerusalem G, Bachelot T, et al. Endocrine treatment versus chemotherapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1360–9.
Goel S, Bergholz JS, Zhao JJ. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6 in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:356–72.
Morrison L, Loibl S, Turner NC. The CDK4/6 inhibitor revolution - a game-changing era for breast cancer treatment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2024;21:89–105.
O’Sullivan CC, Clarke R, Goetz MP, Robertson J. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors for treatment of hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2023;9:1273–82.
Portman N, Alexandrou S, Carson E, Wang S, Lim E, Caldon CE. Overcoming CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in ER-positive breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019;26:R15–R30.
Lloyd MR, Spring LM, Bardia A, Wander SA. Mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 blockade in advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:821–30.
Cai Z, Wang J, Li Y, Shi Q, Jin L, Li S, et al. Overexpressed cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci China Life Sci. 2023;66:94–109.
Palafox M, Monserrat L, Bellet M, Villacampa G, Gonzalez-Perez A, Oliveira M, et al. High p16 expression and heterozygous RB1 loss are biomarkers for CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in ER(+) breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2022;13:5258.
Kudo R, Safonov A, Jones C, Moiso E, Dry JR, Shao H, et al. Long-term breast cancer response to CDK4/6 inhibition defined by TP53-mediated geroconversion. Cancer Cell. 2024;42:1919–35.
Zhou Y, Jin X, Ma J, Ding D, Huang Z, Sheng H, et al. HDAC5 loss impairs RB repression of pro-oncogenic genes and confers CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in cancer. Cancer Res. 2021;81:1486–99.
Herrera-Abreu MT, Palafox M, Asghar U, Rivas MA, Cutts RJ, Garcia-Murillas I, et al. Early adaptation and acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2301–13.
Wander SA, Cohen O, Gong X, Johnson GN, Buendia-Buendia JE, Lloyd MR, et al. The genomic landscape of intrinsic and acquired resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:1174–93.
Clark AS, Makhlin I, DeMichele A. Setting the pick: can PI3K inhibitors circumvent CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance?. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:371–3.
Di Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP. The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell. 2000;100:387–90.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:283–96.
Lee YR, Chen M, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: new modes and prospects. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:547–62.
Papa A, Pandolfi PP. The PTEN-PI3K axis in cancer. Biomolecules. 2019;9:153.
Costa C, Wang Y, Ly A, Hosono Y, Murchie E, Walmsley CS, et al. PTEN loss mediates clinical cross-resistance to CDK4/6 and PI3Kα inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:72–85.
Dosil MA, Mirantes C, Eritja N, Felip I, Navaridas R, Gatius S, et al. Palbociclib has antitumour effects on Pten-deficient endometrial neoplasias. J Pathol. 2017;242:152–64.
Lee JS, Yost SE, Li SM, Cui Y, Frankel PH, Yuan YC, et al. Genomic markers of CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancers. 2022;14:3159.
Lee YR, Chen M, Lee JD, Zhang J, Lin SY, Fu TM, et al. Reactivation of PTEN tumor suppressor for cancer treatment through inhibition of a MYC-WWP1 inhibitory pathway. Science. 2019;364:eaau0159.
Lin YX, Wang Y, Ding J, Jiang A, Wang J, Yu M, et al. Reactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by mRNA nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in preclinical models. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13:eaba9772.
Kamitani T, Kito K, Nguyen HP, Yeh ET. Characterization of NEDD8, a developmentally down-regulated ubiquitin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28557–62.
Enchev RI, Schulman BA, Peter M. Protein neddylation: beyond cullin-RING ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:30–44.
Zhang S, Yu Q, Li Z, Zhao Y, Sun Y. Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9:85.
Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Berger AJ, Gavin JM, Adhikari S, et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature. 2009;458:732–6.
Fu DJ, Wang T. Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme for cancer therapy: developments, clinical trials, challenges and future research directions. J Hematol Oncol. 2023;16:87.
Xie P, Peng ZQ, Chen YJ, Li HC, Du MG, Tan YW, et al. Neddylation of PTEN regulates its nuclear import and promotes tumor development. Cell Res. 2021;31:291–311.
Du MG, Peng ZQ, Gai WB, Liu F, Liu W, Chen YJ, et al. The absence of PTEN in breast cancer is a driver of MLN4924 resistance. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:667435.
Chakrabarti R, Wei Y, Hang J, Hang X, Andres Blanco M, Choudhury A, et al. ΔNp63 promotes stem cell activity in mammary gland development and basal-like breast cancer by enhancing Fzd7 expression and Wnt signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1–13.
Wan L, Lu X, Yuan S, Wei Y, Guo F, Shen M, et al. MTDH-SND1 interaction is crucial for expansion and activity of tumor-initiating cells in diverse oncogene- and carcinogen-induced mammary tumors. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:92–105.
Guerriero JL, Sotayo A, Ponichtera HE, Castrillon JA, Pourzia AL, Schad S, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition reduces breast tumours and metastases through anti-tumour macrophages. Nature. 2017;543:428–32.
Knudsen ES, Knudsen KE. Tailoring to RB: tumour suppressor status and therapeutic response. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:714–24.
Guiley KZ, Stevenson JW, Lou K, Barkovich KJ, Kumarasamy V, Wijeratne TU, et al. p27 allosterically activates cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and antagonizes palbociclib inhibition. Science. 2019;366:6471.
Dong F, Guo W, Zhang L, Wu S, Teraishi F, Davis JJ, et al. Downregulation of XIAP and induction of apoptosis by the synthetic cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor GW8510 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5:165–70.
Chen Q, Chen K, Guo G, Li F, Chen C, Wang S, et al. A critical role of CDKN3 in Bcr-Abl-mediated tumorigenesis. PloS One. 2014;9:e111611.
Eferl R, Wagner EF. AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:859–68.
Liu F, Wagner S, Campbell RB, Nickerson JA, Schiffer CA, Ross AH. PTEN enters the nucleus by diffusion. J Cell Biochem. 2005;96:221–34.
Planchon SM, Waite KA, Eng C. The nuclear affairs of PTEN. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:249–53.
Li Y, Xie P, Lu L, Wang J, Diao L, Liu Z, et al. An integrated bioinformatics platform for investigating the human E3 ubiquitin ligase-substrate interaction network. Nat Commun. 2017;8:347.
Wang X, Li Y, He M, Kong X, Jiang P, Liu X, et al. UbiBrowser 2.0: a comprehensive resource for proteome-wide known and predicted ubiquitin ligase/deubiquitinase-substrate interactions in eukaryotic species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D719–D728.
Paul J, Singh AK, Kathania M, Elviche TL, Zeng M, Basrur V, et al. IL-17-driven intestinal fibrosis is inhibited by Itch-mediated ubiquitination of HIC-5. Mucosal Immunol. 2018;11:427–36.
Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988;55:875–85.
Van Themsche C, Leblanc V, Parent S, Asselin E. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) regulates PTEN ubiquitination, content, and compartmentalization. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:20462–6.
Facino RM, Carini M, Aldini G, Saibene L, Pietta P, Mauri P. Echinacoside and caffeoyl conjugates protect collagen from free radical-induced degradation: a potential use of Echinacea extracts in the prevention of skin photodamage. Planta Med. 1995;61:510–4.
Wang W, Jiang S, Zhao Y, Zhu G. Echinacoside: a promising active natural products and pharmacological agents. Pharmacol Res. 2023;197:106951.
Chen BD, Clark CR, Chou TH. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates monocyte and tissue macrophage proliferation and enhances their responsiveness to macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1988;71:997–1002.
Spiekermann K, Roesler J, Emmendoerffer A, Elsner J, Welte K. Functional features of neutrophils induced by G-CSF and GM-CSF treatment: differential effects and clinical implications. Leukemia. 1997;11:466–78.
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:159–75.
Burgoyne AM, Vann KR, Joshi S, Morales GA, Vega FM, Singh A, et al. A triple action CDK4/6-PI3K-BET inhibitor with augmented cancer cell cytotoxicity. Cell Discov. 2020;6:49.
Agostinetto E, Debien V, Marta GN, Lambertini M, Piccart-Gebhart M, de Azambuja E. CDK4/6 and PI3K inhibitors: a new promise for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51:e13535.
Lee CL, Cremona M, Farrelly A, Workman JA, Kennedy S, Aslam R, et al. Preclinical evaluation of the CDK4/6 inhibitor Palbociclib in combination with a PI3K or MEK inhibitor in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2023;24:2223388.
Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E131–E136.
Ruiz EJ, Lan L, Diefenbacher ME, Riising EM, Da Costa C, Chakraborty A, et al. JunD, not c-Jun, is the AP-1 transcription factor required for Ras-induced lung cancer. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e124985.
Watt AC, Cejas P, DeCristo MJ, Metzger-Filho O, Lam EYN, Qiu X, et al. CDK4/6 inhibition reprograms the breast cancer enhancer landscape by stimulating AP-1 transcriptional activity. Nat Cancer. 2021;2:34–48.
Yamamoto N, Shimizu T, Yonemori K, Kitano S, Kondo S, Iwasa S, et al. A first-in-human, phase 1 study of the NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor TAS4464 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest N Drugs. 2021;39:1036–46.
Zhou H, Lu J, Liu L, Bernard D, Yang CY, Fernandez-Salas E, et al. A potent small-molecule inhibitor of the DCN1-UBC12 interaction that selectively blocks cullin 3 neddylation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1150.
Zhou H, Zhou W, Zhou B, Liu L, Chern TR, Chinnaswamy K, et al. High-affinity peptidomimetic inhibitors of the DCN1-UBC12 protein-protein interaction. J Med Chem. 2018;61:1934–50.
Zheng YC, Guo YJ, Wang B, Wang C, Mamun MAA, Gao Y, et al. Targeting neddylation E2s: a novel therapeutic strategy in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:57.
Xu T, Ma Q, Li Y, Yu Q, Pan P, Zheng Y, et al. A small molecule inhibitor of the UBE2F-CRL5 axis induces apoptosis and radiosensitization in lung cancer. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7:354.
Liu J, Tang N, Liu N, Lei P, Wang F. Echinacoside inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Mol Histol. 2022;53:493–502.
Liang H, Yin G, Shi G, Liu Z, Liu X, Li J. Echinacoside regulates PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF cross signaling axis in proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer. Anal Biochem. 2024;684:115360.
Wei J, Zheng Z, Hou X, Jia F, Yuan Y, Yuan F, et al. Echinacoside inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis via modulating the gut microbiota and suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;318:116866.
Giese MA, Hind LE, Huttenlocher A. Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Blood. 2019;133:2159–67.
Teh JLF, Aplin AE. Arrested developments: CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance and alterations in the tumor immune microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:921–7.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Core Facility Center, Capital Medical University for providing platform support for this research.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82122052), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 32471305), Outstanding Young Talents Program in Chinese Institutes for Medical Research (No. CX23YQA03), Innovative Group Cultivation Project for Basic Medicine (No. CX25XT03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: PX; Methodology: FL, WXL, YXS, SHL, XKJ; Formal Analysis: FL; Investigation: PX, FL; Resources: SYS, YWT, ZZ; Writing-Original Draft: PX; Funding Acquisition: PX.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no competing financial, commercial, or professional interest that could influence the performance, interpretation, or reporting of the research presented in this manuscript. All authors have read and approved this declaration of interests, confirming that it accurately reflects their current situation.
Ethics approval
All animals were handled in strict accordance to the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” and the “Principles for the Utilization and Care of Vertebrate Animals”, and all animal work was approved by Capital Medical University Ethics Committee. The clinical samples were approved by the department of breast and thyroid surgery at the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen and Hunan Cancer Hospital. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their relatives. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Liu, W., Tan, Y. et al. PTEN neddylation aggravates CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 44, 2997–3013 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03468-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03468-z
This article is cited by
-
The role of neddylation in colorectal cancer and its therapeutic potential
Discover Oncology (2025)