Abstract
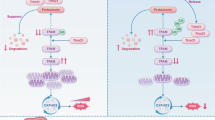
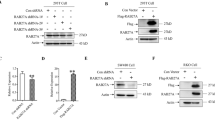
Chemoresistance is not only related to tumor cells themselves, but also regulated by the interaction between cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. RAB22A, a member of the RAB family of small GTPases that was identified by our group previously as an oncogene in colorectal cancer (CRC). In this study, we demonstrated that elevated expression of RAB22A in CRC cells, particularly in chemoresistant CRC cells, is associated with increased exosome secretion and enhanced chemoresistance. Mechanistically, RAB22A augments exosome secretion by inhibiting the ubiquitination and degradation of pyruvate kinase type M2 (PKM2), then promoting the phosphorylation of synaptosome-associated protein 23 (SNAP-23). Furthermore, RAB22A not only directly promotes chemoresistance in CRC cells but also indirectly induces acquired drug resistance of other CRC cells in the TME by promoting the secretion of RAB22A-PKM2-rich exosomes, thereby triggering intercellular chemoresistance transmission. Together, we reveal an essential role of RAB22A-PKM2-SNAP-23 signaling cascade in exosome induction in chemoresistant CRC cells and intercellular chemoresistance transmission, highlighting that targeting the RAB22A/PKM2/pSNAP axis is a potential novel strategy to reverse chemoresistance, and suggest circulating exosomal RAB22A and PKM2 as markers to predict the efficacy of chemotherapy in CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ma SC, Zhang JQ, Yan TH, Miao MX, Cao YM, Cao YB, et al. Novel strategies to reverse chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2023;12:11073–96.
Cui K, Wang K, Huang Z. Ferroptosis and the tumor microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43:315.
Pan W, Miao Q, Yin W, Li X, Ye W, Zhang D, et al. The role and clinical applications of exosomes in cancer drug resistance. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024;7:43.
Wilczynski B, Dabrowska A, Kulbacka J, Baczynska D. Chemoresistance and the tumor microenvironment: the critical role of cell-cell communication. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22:486.
Yin Y, Yao S, Hu Y, Feng Y, Li M, Bian Z, et al. The Immune-microenvironment confers chemoresistance of colorectal cancer through macrophage-derived IL6. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:7375–87.
Shin AE, Giancotti FG, Rustgi AK. Metastatic colorectal cancer: mechanisms and emerging therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023;44:222–36.
Thomas LL, Fromme JC. GTPase cross-talk regulates TRAPPII activation of Rab11 homologues during vesicle biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2016;215:499–513.
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:19–30.
Cebrian I, Croce C, Guerrero NA, Blanchard N, Mayorga LS. Rab22a controls MHC-I intracellular trafficking and antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:1753–65.
Wen F, Meng F, Li X, Li Q, Liu J, Zhang R, et al. Characterization of prognostic value and immunological roles of RAB22A in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1086342.
Fan B, Wang L, Wang J. RAB22A as a predictor of exosome secretion in the progression and relapse of multiple myeloma. Aging. 2024;16:4169–90.
He M, Shen L, Jiang C, Gao G, Wang K, Jiao Y, et al. Rab22a is a novel prognostic marker for cell progression in breast cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45:1037–46.
Zeng C, Zhong L, Liu W, Zhang Y, Yu X, Wang X, et al. Targeting the lysosomal degradation of Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein for osteosarcoma lung metastasis. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2205483.
Liao D, Zhong L, Yin J, Zeng C, Wang X, Huang X, et al. Chromosomal translocation-derived aberrant Rab22a drives metastasis of osteosarcoma. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:868–81.
Yin Y, Zhang B, Wang W, Fei B, Quan C, Zhang J, et al. miR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:6187–99.
Bian Z, Jin L, Zhang J, Yin Y, Quan C, Hu Y, et al. LncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-204-5p. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23892.
Fusco C, De Rosa G, Spatocco I, Vitiello E, Procaccini C, Frige C, et al. Extracellular vesicles as human therapeutics: a scoping review of the literature. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024;13:e12433.
Yin Y, Liu B, Cao Y, Yao S, Liu Y, Jin G, et al. Colorectal cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles promote tumor immune evasion by upregulating PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2102620.
Hsu C, Morohashi Y, Yoshimura S, Manrique-Hoyos N, Jung S, Lauterbach MA, et al. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J Cell Biol. 2010;189:223–32.
Wang T, Gilkes DM, Takano N, Xiang L, Luo W, Bishop CJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:E3234–42.
Teng P, Cui K, Yao S, Fei B, Ling F, Li C, et al. SIRT5-mediated ME2 desuccinylation promotes cancer growth by enhancing mitochondrial respiration. Cell Death Differ. 2024;31:65–77.
Bian Z, Yang F, Xu P, Gao G, Yang C, Cao Y, et al. LINC01852 inhibits the tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by suppressing SRSF5-mediated alternative splicing of PKM. Mol Cancer. 2024;23:23.
Lin RC, Scheller RH. Mechanisms of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:19–49.
Wei Y, Wang D, Jin F, Bian Z, Li L, Liang H, et al. Pyruvate kinase type M2 promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating synaptosome-associated protein 23. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14041.
Xavier CPR, Belisario DC, Rebelo R, Assaraf YG, Giovannetti E, Kopecka J, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in the transfer of drug resistance competences to cancer cells. Drug Resist Updat. 2022;62:100833.
Almanza G, Searles S, Zanetti M. Delivery of miR-214 via extracellular vesicles downregulates Xbp1 expression and pro-inflammatory cytokine genes in macrophages. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024;5:249–58.
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B. Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8:237–55.
Zhong L, Liao D, Li J, Liu W, Wang J, Zeng C, et al. Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis through its secretion into exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:59.
Lin Y, Wei D, He X, Huo L, Wang J, Zhang X, et al. RAB22A sorts epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) from early endosomes to recycling endosomes for microvesicles release. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024;13:e12494.
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE, Wei R, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452:230–3.
Wang D, Zhao C, Xu F, Zhang A, Jin M, Zhang K, et al. Cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells induced by hypoxia transmit resistance to sensitive cells through exosomal PKM2. Theranostics. 2021;11:2860–75.
Li G, Wang D, Zhai Y, Pan C, Zhang J, Wang C, et al. Glycometabolic reprogramming-induced XRCC1 lactylation confers therapeutic resistance in ALDH1A3-overexpressing glioblastoma. Cell Metab. 2024;36:1696–710.e1610.
Bian Z, Zhang J, Li M, Feng Y, Wang X, Zhang J, et al. LncRNA-FEZF1-AS1 promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating PKM2 signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4808–19.
Paumet F, Le Mao J, Martin S, Galli T, David B, Blank U, et al. Soluble NSF attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) in RBL-2H3 mast cells: functional role of syntaxin 4 in exocytosis and identification of a vesicle-associated membrane protein 8-containing secretory compartment. J Immunol. 2000;164:5850–7.
Guo Z, Turner C, Castle D. Relocation of the t-SNARE SNAP-23 from lamellipodia-like cell surface projections regulates compound exocytosis in mast cells. Cell. 1998;94:537–48.
Cosen-Binker LI, Binker MG, Wang CC, Hong W, Gaisano HY. VAMP8 is the v-SNARE that mediates basolateral exocytosis in a mouse model of alcoholic pancreatitis. J Clin Investig. 2008;118:2535–51.
Madera-Salcedo IK, Cruz SL, Gonzalez-Espinosa C. Morphine prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF secretion in mast cells blocking IkappaB kinase activation and SNAP-23 phosphorylation: correlation with the formation of a beta-arrestin/TRAF6 complex. J Immunol. 2013;191:3400–9.
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:213–28.
Jin G, Liu Y, Zhang J, Bian Z, Yao S, Fei B, et al. A panel of serum exosomal microRNAs as predictive markers for chemoresistance in advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmcol. 2019;84:315–25.
Lin Z, Ji Y, Zhou J, Li G, Wu Y, Liu W, et al. Exosomal circRNAs in cancer: Implications for therapy resistance and biomarkers. Cancer Lett. 2023;566:216245.
Marima R, Basera A, Miya T, Damane BP, Kandhavelu J, Mirza S, et al. Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer: interplay, modulation, and therapeutic avenues. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024;9:887–900.
Funding
This study was partially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82472939, 82173193, 82473060, and 82173063), Basic Research Program of Jiangsu Province (BK20241762), Middle-aged People of Wuxi Health Committee (BJ2023060), and Wuxi Medical Key Discipline (ZDXK2021002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaohui Huang and Yuan Yin conceived and designed the project. Liang Ming, Yan Qin, Junhui Tang, Bingxin Liu, Yuhang Liu, Guoying Jin, and Lingzhen Jiang performed all the experiments, Junhui Tang. Bingxin Liu and Surui Yao performed the statistical analyses. Yan Qin and Xiaowe Qi were responsible for clinical sample collection and pathological analysis. Zhaohui Huang and Yuan Yin wrote the paper. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Ming, L., Qin, Y. et al. RAB22A triggers intercellular chemoresistance transmission in colorectal cancer by promoting exosome release via the PKM2-pSNAP23 axis. Oncogene 44, 4205–4217 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03566-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03566-y