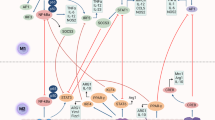
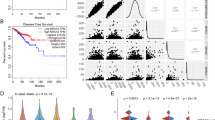
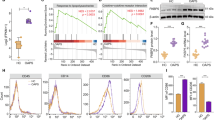
Abstract
Identifying novel factors driving M2-macrophage polarization may help understand immune modulation in cancers. We identified DARPP-32, a protein phosphatase inhibitor, to be significantly upregulated in FBXW7 knock out THP-1 spontaneously polarized to M2 macrophages. DARPP-32 levels remarkably increased in macrophages treated with different M2-inducers while it copiously decreased upon treatment with M1 inducer Lipopolysaccharide/IFN-γ. Intriguingly, mere DARPP-32 over-expression robustly promoted M2-macrophage polarization in different macrophage cell lines and murine primary bone marrow derived macrophages, even without any external stimulation. Conversely, DARPP-32 depletion hampered the IL-4 induced M2-polarization. Strikingly, DARPP-32 overexpression also dampened the classical M1 activation profile of macrophages in response to LPS, skewing their function towards more anti-inflammatory M2-like phenotype. Mechanistically, Thr34-phosphorylated DARPP-32 positively regulates JAK1-STAT6 signalling by directly binding and inhibiting protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1, a key regulator of immune cell signalling and macrophage activation. In line with increased DARPP-32 levels in M2-polarized macrophages, which are often tumor-associated macrophages, we also observed markedly increased DARPP-32 levels in tumor-infiltrating macrophages within primary TNBC tumors. We also observed an increase in DARPP-32 levels in macrophages co-cultured with tumor cells. This is first comprehensive study that demonstrate a novel function of DARPP-32 as a driver/regulator of macrophage polarization towards anti-inflammatory M2-phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials used in this study are available on request to corresponding author.
References
Biswas SK, Gangi L, Paul S, Schioppa T, Saccani A, Sironi M, et al. A distinct and unique transcriptional program expressed by tumor-associated macrophages (defective NF-kappaB and enhanced IRF-3/STAT1 activation). Blood. 2006;107:2112–22.
Petty AJ, Owen DH, Yang Y, Huang X. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers. 2021;13:5318.
He L, Jhong JH, Chen Q, Huang KY, Strittmatter K, Kreuzer J, et al. Global characterization of macrophage polarization mechanisms and identification of M2-type polarization inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2021;37:109955.
Chowdhury S, Trivedi AK. Origin, production and molecular determinants of macrophages for their therapeutic targeting. Cell Biol Int. 2023;47:15–29.
Anderson NR, Minutolo NG, Gill S, Klichinsky M. Macrophage-Based Approaches for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2021;81:1201–8.
Giatromanolaki A, Mitrakas A, Anestopoulos I, Kontosis A, Koukourakis IM, Pappa A, et al. Expression of CD47 and SIRPalpha Macrophage Immune-Checkpoint Pathway in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2022;14:1801.
Yumimoto K, Akiyoshi S, Ueo H, Sagara Y, Onoyama I, Ueo H, et al. F-box protein FBXW7 inhibits cancer metastasis in a non-cell-autonomous manner. J Clin Investig. 2015;125:621–35.
Mishra M, Thacker G, Sharma A, Singh AK, Upadhyay V, Sanyal S, et al. FBW7 Inhibits Myeloid Differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia via GSK3-Dependent Ubiquitination of PU.1. Mol Cancer Res: MCR. 2021;19:261–73.
McWhorter FY, Wang T, Nguyen P, Chung T, Liu WF. Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:17253–8.
Zhong L, Zhang Y, Li M, Song Y, Liu D, Yang X, et al. E3 ligase FBXW7 restricts M2-like tumor-associated macrophage polarization by targeting c-Myc. Aging. 2020;12:24394–423.
Svenningsson P, Nishi A, Fisone G, Girault JA, Nairn AC, Greengard P. DARPP-32: an integrator of neurotransmission. Annu Rev Pharm Toxicol. 2004;44:269–96.
Hemmings HC Jr, Greengard P, Tung HY, Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984;310:503–5.
Walaas SI, Aswad DW, Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983;301:69–71.
Greengard P, Allen PB, Nairn AC. Beyond the dopamine receptor: the DARPP-32/protein phosphatase-1 cascade. Neuron. 1999;23:435–47.
Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Nishi A, Yan Z, Meijer L, Fienberg AA, et al. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons. Nature. 1999;402:669–71.
Girault JA, Nairn AC. DARPP-32 40 years later. Adv Pharm. 2021;90:67–87.
Bhattacharjee A, Shukla M, Yakubenko VP, Mulya A, Kundu S, Cathcart MK. IL-4 and IL-13 employ discrete signaling pathways for target gene expression in alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;54:1–16.
Sethi A, Mishra S, Upadhyay V, Dubey P, Siddiqui S, Singh AK, et al. USP10 deubiquitinates and stabilizes CD44 leading to enhanced breast cancer cell proliferation, stemness and metastasis. Biochemical J. 2024;481:1877–1900.
Luo YP, Zhou H, Krueger J, Kaplan C, Liao D, Markowitz D, et al. The role of proto-oncogene Fra-1 in remodeling the tumor microenvironment in support of breast tumor cell invasion and progression. Oncogene. 2010;29:662–73.
Hamada M, Tsunakawa Y, Jeon H, Yadav MK, Takahashi S. Role of MafB in macrophages. Exp Anim. 2020;69:1–10.
Yadav MK, Inoue Y, Nakane-Otani A, Tsunakawa Y, Jeon H, Samir O, et al. Transcription factor MafB is a marker of tumor-associated macrophages in both mouse and humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521:590–5.
Antwi EB, Olins A, Teif VB, Bieg M, Bauer T, Gu Z, et al. Whole-genome fingerprint of the DNA methylome during chemically induced differentiation of the human AML cell line HL-60/S4. Biol Open. 2020;9:bio044222.
Doyle SL, O’Neill LA. Toll-like receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharm. 2006;72:1102–13.
Wang G, Jin S, Huang W, Li Y, Wang J, Ling X, et al. LPS-induced macrophage HMGB1-loaded extracellular vesicles trigger hepatocyte pyroptosis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:337.
Rahal OM, Wolfe AR, Mandal PK, Larson R, Tin S, Jimenez C, et al. Blocking Interleukin (IL)4- and IL13-Mediated Phosphorylation of STAT6 (Tyr641) Decreases M2 Polarization of Macrophages and Protects Against Macrophage-Mediated Radioresistance of Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;100:1034–43.
Lu X, Malumbres R, Shields B, Jiang X, Sarosiek KA, Natkunam Y, et al. PTP1B is a negative regulator of interleukin 4-induced STAT6 signaling. Blood. 2008;112:4098–108.
Su TH, Shiau CW, Jao P, Yang NJ, Tai WT, Liu CJ, et al. Src-homology protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 agonist, SC-43, reduces liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1728.
Zhu S, Soutto M, Chen Z, Blanca Piazuelo M, Kay Washington M, Belkhiri A, et al. Activation of IGF1R by DARPP-32 promotes STAT3 signaling in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2019;38:5805–16.
Chen Z, Zhu S, Hong J, Soutto M, Peng D, Belkhiri A, et al. Gastric tumour-derived ANGPT2 regulation by DARPP-32 promotes angiogenesis. Gut. 2016;65:925–34.
Pu Y, Ji Q. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Regulate PD-1/PD-L1 Immunosuppression. Front Immunol. 2022;13:874589.
Stockmann C, Doedens A, Weidemann A, Zhang N, Takeda N, Greenberg JI, et al. Deletion of vascular endothelial growth factor in myeloid cells accelerates tumorigenesis. Nature. 2008;456:814–8.
Yang Q, Guo N, Zhou Y, Chen J, Wei Q, Han M. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor progression and relevant advance in targeted therapy. Acta Pharmaceut Sin B. 2020;10:2156–70.
Wang S, Wang J, Chen Z, Luo J, Guo W, Sun L, et al. Targeting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages is a potential therapeutic approach to overcome antitumor drug resistance. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024;8:31.
Li M, He L, Zhu J, Zhang P, Liang S. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages for cancer treatment. Cell Biosci. 2022;12:85.
Xing L, Xu L, Zhang Y, Che Y, Wang M, Shao Y, et al. Recent Insight on Regulations of FBXW7 and Its Role in Immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2022;12:925041.
Trizzino M, Zucco A, Deliard S, Wang F, Barbieri E, Veglia F, et al. EGR1 is a gatekeeper of inflammatory enhancers in human macrophages. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eaaz8836.
Yin L, Zhang J, Sun Y. Early growth response-1 is a new substrate of the GSK3beta-FBXW7 axis. Neoplasia. 2022;34:100839.
Zhao D, Zheng HQ, Zhou Z, Chen C. The Fbw7 tumor suppressor targets KLF5 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation and suppresses breast cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2010;70:4728–38.
Huang SC, Everts B, Ivanova Y, O’Sullivan D, Nascimento M, Smith AM, et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:846–55.
Semrau MS, Giachin G, Covaceuszach S, Cassetta A, Demitri N, Storici P, et al. Molecular architecture of the glycogen- committed PP1/PTG holoenzyme. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6199.
Na YR, Jung D, Gu GJ, Jang AR, Suh YH, Seok SH. The early synthesis of p35 and activation of CDK5 in LPS-stimulated macrophages suppresses interleukin-10 production. Sci Signal. 2015;8:ra121.
Kaplan MH, Schindler U, Smiley ST, Grusby MJ. Stat6 is required for mediating responses to IL-4 and for development of Th2 cells. Immunity. 1996;4:313–9.
Haque SJ, Harbor P, Tabrizi M, Yi T, Williams BR. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp-1 is a negative regulator of IL-4- and IL-13-dependent signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33893–6.
Bayik D, Lathia JD. Cancer stem cell-immune cell crosstalk in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:526–36.
Li W, Wu F, Zhao S, Shi P, Wang S, Cui D. Correlation between PD-1/PD-L1 expression and polarization in tumor-associated macrophages: A key player in tumor immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022;67:49–57.
Horikawa N, Abiko K, Matsumura N, Hamanishi J, Baba T, Yamaguchi K, et al. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Ovarian Cancer Inhibits Tumor Immunity through the Accumulation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Clin Cancer Res J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2017;23:587–99.
Lin EY, Li JF, Bricard G, Wang W, Deng Y, Sellers R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor restores delayed tumor progression in tumors depleted of macrophages. Mol Oncol. 2007;1:288–302.
Acknowledgements
Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), India to Sangita & Shivkant is acknowledged. Funding from Department of Biotechnology (DBT)-BioCARe to Swati Srivastava is also acknowledged. Fellowship from University Grants Commission (UGC) to Agniv Shome is acknowledged. We also thank Mr. A. L. Vishwakarma and Ms. Rima Ray Sarkar from FACS facility (Sophisticated and Analytical Instrument Facility, SAIF) and confocal microscopy unit, CSIR-CDRI respectively. CSIR-CDRI Manuscript communication number for this article is 11050.
Funding
This study was supported by funds from the Lady Tata Memorial Trust (LTMT), Mumbai (GAP0239) to AKT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experimental design: SC and AKT; Data generation: SC, AS, SS, SKM, AShome, SSingh; Data Analysis: SC, SS, VU, AKS, and AKT; Clinical Sample and data analysis: MLB, AM and AKT; Manuscript preparation: SC, SS and AKT; Fund acquisition and Project monitoring: AKT.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, S., Sethi, A., Srivastava, S. et al. DARPP-32 is a novel regulator of M2-macrophage polarization: Sustains STAT6 phosphorylation by directly binding and inhibiting tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Oncogene 44, 4639–4656 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03610-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03610-x