Abstract
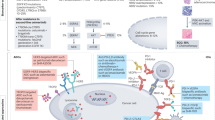
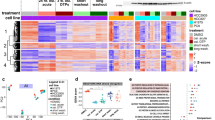
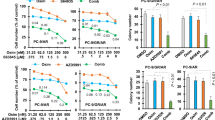
While third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs), such as osimertinib, have significantly improved patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), acquired resistance remains a major clinical challenge, and its underlying mechanisms are incompletely understood. In this study, we demonstrate that YTHDC2 expression is significantly downregulated in osimertinib-resistant patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tissues and lung cancer cell lines compared to their osimertinib-sensitive counterparts. Further investigation revealed that YTHDC2 overcomes osimertinib resistance in lung cancer cells by promoting cuproptosis. Mechanistically, YTHDC2 binds to m6A-modified sites (specifically at nucleotides A1223 and A2824) within the mRNA of the copper transporter SLC31A1 in an m6A-dependent manner. This interaction enhances SLC31A1 mRNA stability and protein expression, thereby increasing intracellular copper transport and inducing cuproptosis in tumor cells. Additionally, we found that the copper ionophore disulfiram (DSF) overcame osimertinib resistance by augmenting YTHDC2 expression. Collectively, our findings elucidate a novel YTHDC2-SLC31A1-cuproptosis axis as a key mechanism underlying EGFR-TKI resistance and propose new therapeutic strategies for its reversal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are included in the manuscript or available from corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J. 2022;135:584–90.
Abu Rous F, Singhi EK, Sridhar A, Faisal MS, Desai A. Lung cancer treatment advances in 2022. Cancer Investig. 2022;41:12–24.
Melosky B, Kambartel K, Häntschel M, Bennetts M, Nickens DJ, Brinkmann J, et al. Worldwide prevalence of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Mol Diagnosis Ther. 2021;26:7–18.
Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Ahn M-J, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum–pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:629–40.
Tsuboi M, Herbst RS, John T, Kato T, Majem M, Grohé C, et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:137–47.
Lu S, Kato T, Dong X, Ahn MJ, Quang LV, Soparattanapaisarn N, et al. Osimertinib after chemoradiotherapy in stage III EGFR-mutated NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2024;391:585–97.
Zhang H, Wang SQ, Wang L, Lin H, Zhu JB, Chen R, et al. m6A methyltransferase METTL3-induced lncRNA SNHG17 promotes lung adenocarcinoma gefitinib resistance by epigenetically repressing LATS2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:657.
Lin Z, Li J, Zhang J, Feng W, Lu J, Ma X, et al. Metabolic reprogramming driven by IGF2BP3 promotes acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitorsin non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:2187–207.
Fan W, Xing Y, Yan S, Liu W, Ning J, Tian F, et al. DUSP5 regulated by YTHDF1-mediated m6A modification promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and EGFR-TKI resistance via the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2024;24:208.
Meng Q, Wang S, Zhou S, Liu H, Ma X, Zhou X, et al. Dissecting the m6A methylation affection on afatinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics J. 2019;20:227–34.
Ji Y, Zhao Q, Feng W, Peng Y, Hu B, Chen Q. N6-methyladenosine modification of CIRCKRT17 initiated by METTL3 promotes osimertinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma by EIF4A3 to enhance YAP1 stability. Cancers. 2022;14:5582.
Fan S, Lv X, Zhang C, Zeng B, Liang Y, Chen D, et al. METTL14-Mediated Bim mRNA m6A Modification Augments Osimertinib Sensitivity in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2024: OF1-OF13.
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375:1254–61.
Xu X, Qiu S, Zeng B, Huang Y, Wang X, Li F, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethyltransferase FTO mediated m6A modification of estrogen receptor alpha in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2024;43:1288–302.
Ma L, Chen T, Zhang X, Miao Y, Tian X, Yu K, et al. The m6A reader YTHDC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by suppressing SLC7A11-dependent antioxidant function. Redox Biol. 2021;38:101801.
Chen X, Cheng G, Zhu L, Liu T, Yang X, Liu R, et al. Alarmin S100A8 imparts chemoresistance of esophageal cancer by reprogramming cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5:101576.
Qu Y, Gao N, Zhang S, Gao L, He B, Wang C, et al. Role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in cancer. MedComm. 2024;5:e715.
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y, et al. Ythdc2 is an N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 2017;27:1115–27.
Wang J, Tan L, Jia B, Yu X, Yao R, Ouyang N, et al. Downregulation of m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes the proliferation and migration of malignant lung cells via CYLD/NF-κB Pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:2633–51.
Leonetti A, Sharma S, Minari R, Perego P, Giovannetti E, Tiseo M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:725–37.
Schoenfeld AJ, Chan JM, Kubota D, Sato H, Rizvi H, Daneshbod Y, et al. Tumor analyses reveal squamous transformation and off-target alterations as early resistance mechanisms to first-line osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:2654–63.
Sun Y, Liu Y, Wang P, Chang L, Huang J. The m6A reader YTHDC2 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by destabilizing MRPL12. Mol Biotechnol. 2023;66:1051–61.
Zhang H, Zhou J, Li J, Wang Z, Chen Z, Lv Z, et al. N6-methyladenosine promotes translation of VEGFA to accelerate angiogenesis in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:2208–25.
Ma L, Zhang X, Yu K, Xu X, Chen T, Shi Y, et al. Targeting SLC3A2 subunit of system XC- is essential for m6A reader YTHDC2 to be an endogenous ferroptosis inducer in lung adenocarcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:25–43.
Li Y. Copper homeostasis: emerging target for cancer treatment. IUBMB Life. 2020;72:1900–8.
Qiu Z, Liu Q, Wang L, Xiong Y, Wu J, Wang M, et al. The copper transporter, SLC31A1, transcriptionally activated by ELF3, imbalances copper homeostasis to exacerbate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through mitochondrial dysfunction. Chem-Biol Interact. 2024;393:110943.
Kong F-S, Ren C-Y, Jia R, Zhou Y, Chen J-H, Ma Y. Systematic pan-cancer analysis identifies SLC31A1 as a biomarker in multiple tumor types. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16:61.
Yu Z, Zhou R, Zhao Y, Pan Y, Liang H, Zhang JS, et al. Blockage of SLC31A1-dependent copper absorption increases pancreatic cancer cell autophagy to resist cell death. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12568.
Wu G, Peng H, Tang M, Yang M, Wang J, Hu Y, et al. ZNF711 down-regulation promotes CISPLATIN resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer via interacting with JHDM2A and suppressing SLC31A1 expression. eBioMedicine. 2021;71:103558.
Lu Y, Pan Q, Gao W, Pu Y, Luo K, He B, et al. Leveraging disulfiram to treat cancer: Mechanisms of action, delivery strategies, and treatment regimens. Biomaterials. 2022;281:121335.
Hu Y, Qian Y, Wei J, Jin T, Kong X, Cao H, et al. The disulfiram/copper complex induces autophagic cell death in colorectal cancer by targeting ULK1. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:752825.
Li Y, Fu S-Y, Wang L-H, Wang F-Y, Wang N-N, Cao Q, et al. Copper improves the anti-angiogenic activity of disulfiram through the EGFR/Src/VEGF pathway in gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2015;369:86–96.
Ni X, Ye C, Yu X, Zhang Y, Hou Y, Zheng Q, et al. Overcoming the compensatory increase in NRF2 induced by NPL4 inhibition enhances disulfiram/copper-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;960:176110.
Kita Y, Hamada A, Saito R, Teramoto Y, Tanaka R, Takano K, et al. Systematic chemical screening identifies disulfiram as a repurposed drug that enhances sensitivity to cisplatin in bladder cancer: a summary of preclinical studies. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:1027–38.
Hendrych M, Říhová K, Adamová B, Hradil V, Stiborek M, Vlček P, et al. Disulfiram increases the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in organotypic cultures of colorectal carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113465.
Li P, Sun Q, Bai S, Wang H, Zhao L. Combination of the cuproptosis inducer disulfiram and anti‑PD‑L1 abolishes NSCLC resistance by ATP7B to regulate the HIF‑1 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2023;53:19.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82472771, 82273139, 82272679, 82303043, 32470821); Shanghai Eastern Talent Plan - Youth Project (QNWS2024061); Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, Clinical Research Special Project for Young Scholars (20234Y0019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jizhuang Luo: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition. Xin Xu: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Funding acquisition. Yaohui Chen: Formal analysis, Data curation. Yiwen Huang: Formal analysis, Data curation. Yiman Huang: Formal analysis. Yajuan Zhang: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition. Lifang Ma: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition. Tianxiang Chen: Supervision, Conceptualization, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors approved the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., Xu, X., Chen, Y. et al. YTHDC2 inhibits the resistance of lung cancer to EGFR-TKI through cuproptosis. Oncogene 45, 431–445 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03660-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03660-1