Abstract
Background
Approximately 1/3 of newborns exposed antenatally to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) exhibit poor neonatal adaptation. Although several potential mechanisms have been proposed, the actual mechanism has not been elucidated.
Methods
We investigated outcomes in neonatal lambs exposed prenatally or postnatally to fluoxetine (FX). Daily FX injections (50 mg) were given intravenously (i.v.) to five pregnant ewes via implanted catheters beginning at 131–132 days gestation (term = 147 days) for 2 weeks. In another group, lambs with implanted vascular catheters had sterile water (n = 9) or FX (1 mg/kg, n = 12) injected i.v. on ~postnatal day (PND) 4.
Results
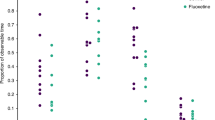
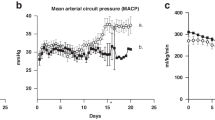
Prenatal FX-exposed lambs (n = 7) were hyperactive during PND 4 to 14 and their heart rate variability (HRV) was significantly lower than in control lambs (n = 7) on PND 2. In contrast, arterial pressure, heart rate, electrocardiogram, arterial blood gases, pH, glucose, lactate, cortisol, and sleep–activity cycles were not altered following postnatal FX injection.
Conclusion
This abnormal postnatal hyperactivity with antenatal FX exposure may reflect increased maturity in terms of locomotory activity. The results suggest that altered brain development may be involved in the poor neonatal adaptation in human infants exposed to FX in utero.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Andrade, S. E. et al. Use of antidepressant medications during pregnancy: a multisite study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 198, 194.e1–194.e5 (2008).
Oberlander, T. F., Warburton, W., Misri, S., Aghajanian, J. & Hertzman, C. Neonatal outcomes after prenatal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and maternal depression using population-based linked health data. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 63, 898–906 (2006).
Moses-Kolko, E. L. et al. Neonatal signs after late in utero exposure to serotonin reuptake inhibitors: literature review and implications for clinical applications. JAMA 293, 2372–2383 (2005).
Kieviet, N. et al. Serotonin and poor neonatal adaptation after antidepressant exposure in utero. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 29, 43–53 (2017).
Levinson-Castiel, R., Merlob, P., Linder, N., Sirota, L. & Klinger, G. Neonatal abstinence syndrome after in utero exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in term infants. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 160, 173–176 (2006).
Kieviet, N. et al. Risk factors for poor neonatal adaptation after exposure to antidepressants in utero. Acta Paediatr. 104, 384–391 (2015).
Morrison, J. L., Riggs, K. W. & Rurak, D. W. Fluoxetine during pregnancy: impact on fetal development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 17, 641–650 (2005).
Moss, T. J., Jakubowska, A. E., McCrabb, G. J., Billings, K. & Harding, R. Ventilatory responses to progressive hypoxia and hypercapnia in developing sheep. Respir. Physiol. 100, 33–44 (1995).
Rurak, D. W., Fay, S. & Gruber, N. C. Measurement of rest and activity in newborn lambs using actigraphy: studies in term and preterm lambs. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 20, 418–430 (2008).
Chow, T. W., Szeitz, A., Rurak, D. W. & Riggs, K. W. A validated enantioselective assay for the simultaneous quantitation of (R)-, (S)-fluoxetine and (R)-, (S)-norfluoxetine in ovine plasma using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. B 879, 349–358 (2011).
Altman, D. Some common problems in medical research. In: Practical Statistics for Medical Research. London: Chapman & Hall. (pp. 426–439). (1991).
Kim, J. et al. Stereoselective disposition of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 61, 155–163 (2006).
Kim, J., Riggs, K. W. & Rurak, D. W. Stereoselective pharmacokinetics of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in pregnant sheep. Drug Metab. Dispos. 32, 212–221 (2004).
Ring, B. J. et al. Identification of the human cytochromes p450 responsible for in vitro formation of R- and S-norfluoxetine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297, 1044–1050 (2001).
Alfaro, C. L., Lam, Y. W., Simpson, J. & Ereshefsky, L. CYP2D6 inhibition by fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine in a crossover study: intraindividual variability and plasma concentration correlations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 40, 58–66 (2000).
Rampono, J., Proud, S., Hackett, L. P., Kristensen, J. H. & Ilett, K. F. A pilot study of newer antidepressant concentrations in cord and maternal serum and possible effects in the neonate. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 7, 329–334 (2004).
Spencer, M. J. Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac) toxicity in a neonate. Pediatrics 92, 721–722 (1993).
Bessette, N. W. & Rurak, D. W. Chronic fetal and maternal instrumentation in pregnant sheep: effect on gestation length and birthweight. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 22, 459–467 (2010).
Rurak, D. et al. Third trimester fetal heart rate and Doppler middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity characteristics during prenatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure. Pediatr. Res. 70, 96–101 (2011).
Dwyer, C. M., Calvert, S. K., Farish, M., Donbavand, J. & Pickup, H. E. Breed, litter and parity effects on placental weight and placentome number, and consequences for the neonatal behaviour of the lamb. Theriogenology 63, 1092–1110 (2005).
Pedersen, L. H., Henriksen, T. B. & Olsen, J. Fetal exposure to antidepressants and normal milestone development at 6 and 19 months of age. Pediatrics 125, e600–e608 (2010).
Nguyen, T. T. Cardiovascular, metabolic, endocrine and behavioral aspects of development in postnatal lambs in relation to acute fluoxetine administration. PhD Thesis, University of British Columbia (https://open.library.ubc.ca/cIRcle/collections/ubctheses/24/items/1.0073940) (2013).
Zeskind, P. S. & Stephens, L. E. Maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use during pregnancy and newborn neurobehavior. Pediatrics 113, 368–375 (2004).
Chambers, C. D. et al. Weight gain in infants breastfed by mothers who take fluoxetine. Pediatrics 104, e61 (1999).
Morrison, J. L., Chien, C., Riggs, K. W., Gruber, N. & Rurak, D. Effect of maternal fluoxetine administration on uterine blood flow, fetal blood gas status and growth. Pedia. Res 51, 433–442 (2002).
Davidson, S. et al. Effect of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in utero on fetal growth: potential role for the IGF-I and HPA axes. Pediatr. Res. 65, 236–241 (2009).
Ortiz, J. & Artigas, F. Effects of monoamine uptake inhibitors on extracellular and platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat blood: different effects of clomipramine and fluoxetine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 105, 941–946 (1992).
Maurer-Spurej, E., Pittendreigh, C. & Solomons, K. The influence of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on human platelet serotonin. Thromb. Haemost. 91, 119–128 (2004).
Alvarez, J. C. et al. Decreased platelet serotonin transporter sites and increased platelet inositol triphosphate levels in patients with unipolar depression: effects of clomipramine and fluoxetine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 66, 617–624 (1999).
Nelson, M. et al. Ritanserin and serotonergic mechanisms in blood pressure and fluid regulation in sheep. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 14, 555–563 (1987).
Watts, S. W. & Davis, R. P. 5-Hydroxtryptamine receptors in systemic hypertension: an arterial focus. Cardiovasc. Ther. 29, 54–67 (2011).
Lange, S., Van Leeuwen, P., Geue, D., Hatzmann, W. & Gronemeyer, D. Influence of gestational age, heart rate, gender and time of day on fetal heart rate variability. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 481–486 (2005).
Massin, M. & von Bernuth, G. Normal ranges of heart rate variability during infancy and childhood. Pediatr. Cardiol. 18, 297–302 (1997).
Oberlander, T. F. et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function in 3-month old infants with prenatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant exposure. Early Hum. Dev. 84, 689–697 (2008).
Raap, D. K., Van & de Kar, L. D. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and neuroendocrine function. Life. Sci. 65, 1217–1235 (1999).
Jongsma, M. E., Bosker, F. J., Cremers, T. I., Westerink, B. H. & den Boer, J. A. The effect of chronic selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment on serotonin 1B receptor sensitivity and HPA axis activity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 29, 738–744 (2005).
Mulder, E. J., Ververs, F. F., de Heus, R. & Visser, G. H. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors affect neurobehavioral development in the human fetus. Neuropsychopharmacology 36, 1961–1971 (2011).
Kivisto, J., Lehto, S. M., Halonen, K., Georgiadis, L. & Heinonen, S. Maternal use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lengthening of the umbilical cord: indirect evidence of increased foetal activity—a retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 11, e0154628 (2016).
Pawluski, J. L., Galea, L. A., Brain, U., Papsdorf, M. & Oberlander, T. F. Neonatal S100B protein levels after prenatal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pediatrics 124, e662–e670 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-84477). TAN was a recipient of IWRH and CFRI studentship award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.A., Chow, T., Riggs, W. et al. Postnatal outcomes in lambs exposed antenatally and acutely postnatally to fluoxetine. Pediatr Res 85, 1032–1040 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0309-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0309-8
This article is cited by
-
The Serotonergic System and Bone Metabolism During Pregnancy and Lactation and the Implications of SSRI Use on the Maternal-Offspring Dyad
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2023)