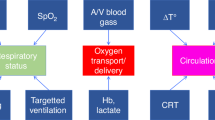
Abstract
Background
The aim of this systematic qualitative review was to give an overview of reference ranges defined as normal values or centile charts of regional tissue oxygen saturation measured by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in term and preterm neonates.
Methods
A systematic search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials was performed. Additional articles were identified by manual search of cited references. Only human studies in neonates were included.
Results
Nineteen studies were identified. Eight described regional tissue oxygen saturation during fetal-to-neonatal transition, six during the first 3 days after birth, four during the first 7 days after birth, and one during the first 8 weeks after birth. Nine described regional tissue oxygen saturation in term, nine in preterm neonates, and one in both. Eight studies published centile charts for cerebral regional tissue oxygen saturation, and only five included large cohorts of infants. Eleven studies described normal values for cerebral, muscle, renal, and abdominal regional tissue oxygen saturation, the majority with small sample sizes. Four studies of good methodological quality were identified describing centile charts of cerebral regional tissue oxygen saturation.
Conclusions
In clinical settings, quality centile charts are available and should be the preferred method when using NIRS monitoring.
Impact
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) enables a bed-side non-invasive continuous monitoring of tissue oxygenation.
-
When using NIRS monitoring in a clinical setting, centile charts with good quality are available and should be preferred to normal values.
-
High-quality reference ranges of regional tissue oxygenation in term and preterm born neonates are an important step toward routine clinical application of NIRS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Harrison, W. N., Wasserman, J. R. & Goodman, D. C. Regional variation in neonatal intensive care admissions and the relationship to bed supply. J. Pediatr. 192, 73.e4–79.e4 (2018).
Jamieson, K., Davey, M. J. & Nixon, G. M. Oximetry knowledge in neonatal units in Victoria, Australia: can we do better? Acta Paediatr. 108, 468–472 (2019).
Van Bel, F., Lemmers, P. & Naulaers, G. Monitoring neonatal regional cerebral oxygen saturation in clinical practice: value and pitfalls. Neonatology 94, 237–244 (2008).
Pichler, G. et al. Cerebral oxygen saturation to guide oxygen delivery in preterm neonates for the immediate transition after birth: a 2-center randomized controlled pilot feasibility trial. J. Pediatr. 170, 73.e4–78.e4 (2016).
Hyttel-Sorensen, S. et al. Cerebral near infrared spectroscopy oximetry in extremely preterm infants: phase II randomised clinical trial. BMJ 350, g7635 (2015).
Pichler, G. et al. Reference ranges for regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation and fractional oxygen extraction in neonates during immediate transition after birth. J. Pediatr. 163, 1558–1563 (2013).
Baik, N. et al. Reference ranges for cerebral tissue oxygen saturation index in term neonates during immediate neonatal transition after birth. Neonatology 108, 283–286 (2015).
Naulaers, G. Cerebral tissue oxygenation index in very premature infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 87, 189F–192F (2002).
van der Heide, M. et al. Regional splanchnic oxygen saturation for preterm infants in the first week after birth: reference values. Pediatr. Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-01323-3 (2021).
Patel, A. K. et al. Abdominal near-infrared spectroscopy measurements are lower in preterm infants at risk for necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 15, 735–741 (2014).
Wolfsberger, C. et al. Changes in peripheral muscle oxygenation measured with near-infrared spectroscopy in preterm neonates within the first 24 h after birth. Physiol. Meas. 41, 075003 (2020).
Hoeller, N. et al. Cerebral and peripheral muscle oxygenation and perfusion: course in moderate and late preterm neonates during the first day after birth. Physiol. Int. 107, 267–279 (2020).
Howarth, C. et al. Gut and cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants over the first 8 weeks of life: what is normal? Arch. Dis. Child. 104, A80 (2019).
Xue, H. et al. Cerebral oxygen changes in neonates during immediate transition after birth and early life: an observational study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 14, 4703–4715 (2020).
Montaldo, P. et al. Cerebral, renal and mesenteric regional oxygen saturation of term infants during transition. J. Pediatr. Surg. 50, 1273–1277 (2015).
Harer, M. W., Adegboro, C. O., Richard, L. J. & McAdams, R. M. Non-invasive continuous renal tissue oxygenation monitoring to identify preterm neonates at risk for acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. 36, 1617–1625 (2021).
Fauchère, J. C. et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy measurements of cerebral oxygenation in newborns during immediate postnatal adaptation. J. Pediatr. 156, 372–376 (2010).
Fuchs, H. et al. Brain oxygenation monitoring during neonatal resuscitation of very low birth weight infants. J. Perinatol. 32, 356–362 (2012).
Alderliesten, T. et al. Reference values of regional cerebral oxygen saturation during the first 3 days of life in preterm neonates. Pediatr. Res. 79, 55–64 (2016).
Ozawa, J. et al. Defining the reference range of regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation using a new portable near-infrared spectroscopy device for term infants. Early Hum. Dev. 141, 104941 (2020).
Kato, R., Hosono, S. & Takahashi, S. Reference value of brain tissue oxygen saturation in newborns immediately after birth. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1232, 19–24 (2020).
Roerdink, S. J. et al. Reference values of near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS): diversity between different devices. In 3rd Congress of Joint European Neonatal Societies (JENS, 2019).
Bailey, S., Hendricks-Munoz, K. & Mally, P. Cerebral, renal, and splanchnic tissue oxygen saturation values in healthy term newborns. Am. J. Perinatol. 31, 339–344 (2013).
Bernal, N. P., Hoffman, G. M., Ghanayem, N. S. & Arca, M. J. Cerebral and somatic near-infrared spectroscopy in normal newborns. J. Pediatr. Surg. 45, 1306–1310 (2010).
Hessel, T. W., Hyttel-Sorensen, S. & Greisen, G. Cerebral oxygenation after birth - a comparison of INVOS ® and FORE-SIGHTTM near-infrared spectroscopy oximeters. Acta Paediatr. 103, 488–493 (2014).
Schneider, A. et al. Comparison of four near-infrared spectroscopy devices shows that they are only suitable for monitoring cerebral oxygenation trends in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 103, 934–938 (2014).
Pocivalnik, M. et al. Regional tissue oxygen saturation: comparability and reproducibility of different devices. J. Biomed. Opt. 16, 057004 (2011).
Liberati, A. et al. The PRISMA Statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 6, e1000100 (2009).
Uchida, T. et al. Examiner’s finger-mounted fetal tissue oximetry: a preliminary report on 30 cases. J. Perinat. Med. 44, 745–749 (2016).
Pichler, G. et al. Is renal tissue oxygen desaturation during severe hypoxia underestimated? An observational study in term newborn piglets. Nephrology 20, 107–109 (2015).
Guo, Y. et al. Statistical methods for characterizing transfusion-related changes in regional oxygenation using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in preterm infants. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 28, 2710–2723 (2019).
Baik, N. et al. Cerebral haemorrhage in preterm neonates: does cerebral regional oxygen saturation during the immediate transition matter? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 100, F422–F427 (2015).
Binder-Heschl, C. et al. Oxygen saturation targeting during delivery room stabilization: what does this mean for regional cerebral oxygenation? Front. Pediatr. 7, 1–8 (2019).
Pichler, G. et al. Cerebral regional tissue oxygen saturation to guide oxygen delivery in preterm neonates during immediate transition after birth (COSGOD III): an investigator-initiated, randomized, multi-center, multi-national, clinical trial on additional cerebral tissue. Trials 20, 1–10 (2019).
Hansen, M. L. et al. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring versus treatment as usual for extremely preterm infants: a protocol for the SafeBoosC randomised clinical phase III trial. Trials 20, 811 (2019).
Kleiser, S. et al. Comparison of tissue oximeters on a liquid phantom with adjustable optical properties: an extension. Biomed. Opt. Express 9, 86 (2018).
Dix, L. M. L., van Bel, F., Baerts, W. & Lemmers, P. M. A. Comparing near-infrared spectroscopy devices and their sensors for monitoring regional cerebral oxygen saturation in the neonate. Pediatr. Res. 74, 557–563 (2013).
Alderliesten, T. et al. Low cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants is associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Pediatr. 207, 109.e2–116.e2 (2018).
Hyttel-Sorensen, S., Kleiser, S., Wolf, M. & Greisen, G. Calibration of a prototype NIRS oximeter against two commercial devices on a blood-lipid phantom. Biomed. Opt. Express 4, 1662 (2013).
Funding
Financial support of publication costs by the European Society for Paediatric Research (ESPR) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
All members of the European Special Interest Group “Near InfraRed Spectroscopy” are listed in the Appendix. All these members have substantially contributed to the conception and revision of the manuscript and approved the final version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Patient consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruckner, M., Wolfsberger, C.H., Dempsey, E.M. et al. Normal regional tissue oxygen saturation in neonates: a systematic qualitative review. Pediatr Res 96, 844–855 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01786-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01786-y
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of kidney oxygenation monitoring with near infrared spectroscopy in preterm neonates: kidney location, depth, and laterality differences
Journal of Perinatology (2025)
-
Brain oxygenation monitoring during neonatal stabilization and resuscitation and its potential for improving preterm infant outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis with Bayesian analysis
European Journal of Pediatrics (2025)
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy for kidney oxygen monitoring in a porcine model of hemorrhagic shock, hemodilution, and REBOA
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Biomarker und Neuromonitoring zur Entwicklungsprognose nach perinataler Hirnschädigung
Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde (2022)
-
Early brain and abdominal oxygenation in extremely low birth weight infants
Pediatric Research (2022)