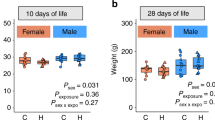
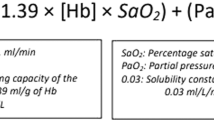
Abstract
Background
Anemia is a nearly universal diagnosis in preterm infants, caused by phlebotomy, and exacerbated by the underlying erythropoietic immaturity. Newborn infants are exposed to the unique stressor of fetal-to-neonatal transition, which requires significant adaptation ex utero. Accordingly, the preterm infant’s response to anemia may alter the ability to confront underlying illness. This study utilized our preclinical mouse model of phlebotomy-induced anemia (PIA) to comprehensively investigate associated hematological changes.
Methods
C57BL/6 mice were subjected to timed phlebotomy between postnatal days 2–-10 to induce severe anemia. Complete blood counts were determined by the Sysmex XT-2000iV analyzer.
Results
Anemic pups showed a gradual reduction of RBC and hemoglobin (Hb) and increased reticulocyte (RET) counts and red cell distribution width (RDW), however, with reduced RET-Hb from postnatal day (P) of 4 onwards. Elevated levels of high fluorescent RET and immature reticulocyte fraction (IRF) were noted in anemic mouse pups, but low and medium fluorescent RET were reduced. Also, the reduction of mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) were noted in anemic pups. No changes were seen in lymphocytes, but monocytes and neutrophils were significantly elevated from P4-P6.
Conclusions
PIA in mouse pups is associated with hematological changes that may be exacerbating factors in neonatal diseases.
Impact
-
Anemia is common and often severe in premature infants.
-
Investigation of hematological parameters in settings of preclinical anemia may be an index of therapeutic strategies.
-
Preclinical model evaluating the effects of neonatal anemia on the remainder of complete blood count.
-
Detailed time kinetic phlebotomy-induced anemic mice enable us to study the impact on developmental delays in erythropoiesis and possible strategic intervention.
-
Hematological effects of severe anemia in mice might provide insight on how best to investigate anemia in preterm infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cibulskis, C. C., Maheshwari, A., Rao, R. & Mathur, A. M. Anemia of prematurity: how low is too low? J. Perinatol. 41, 1244–1257 (2021).
Maheshwari, A., Patel, R. M. & Christensen, R. D. Anemia, red blood cell transfusions, and necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 27, 47–51 (2018).
MohanKumar, K. et al. Severe neonatal anemia increases intestinal permeability by disrupting epithelial adherens junctions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 318, G705–G716 (2020).
Stockman, J. A. 3rd The anemia of prematurity and the decision when to transfuse. Adv. Pediatr. 30, 191–219 (1983).
Stockman, J. A. 3rd Anemia of prematurity. Current concepts in the issue of when to transfuse. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 33, 111–128 (1986).
Whitehead, H. V., Vesoulis, Z. A., Maheshwari, A., Rambhia, A. & Mathur, A. M. Progressive anemia of prematurity is associated with a critical increase in cerebral oxygen extraction. Early Hum. Dev. 140, 104891 (2019).
Whitehead, H. V., Vesoulis, Z. A., Maheshwari, A., Rao, R. & Mathur, A. M. Anemia of prematurity and cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy: should transfusion thresholds in preterm infants be revised? J. Perinatol. 38, 1022–1029 (2018).
Widness, J. A. Pathophysiology of anemia during the neonatal period, including anemia of prematurity. Neoreviews 9, e520 (2008).
Kling, P. J. Iron nutrition, erythrocytes, and erythropoietin in the NICU: erythropoietic and neuroprotective effects. Neoreviews 21, e80–e88 (2020).
Ohlsson, A. & Aher, S. M. Early erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 11, CD004863 (2017).
Ohlsson, A. & Aher, S. M. Early erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2, CD004863 (2020).
Moreno-Fernandez, J., Ochoa, J. J., Latunde-Dada, G. O. & Diaz-Castro, J. Iron deficiency and iron homeostasis in low birth weight preterm infants: a systematic review. Nutrients 11, 1090 (2019).
Berglund, S., Westrup, B. & Domellof, M. Iron supplements reduce the risk of iron deficiency anemia in marginally low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 126, e874–e883 (2010).
Stockman, J. A. 3rd et al. Anemia of prematurity: determinants of the erythropoietin response. J. Pediatr. 105, 786–792 (1984).
Finne, P. H. & Halvorsen, S. Regulation of erythropoiesis in the fetus and newborn. Arch. Dis. Child. 47, 683–687 (1972).
Counsilman, C. E. et al. Iatrogenic blood loss in extreme preterm infants due to frequent laboratory tests and procedures. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 34, 2660–2665 (2021).
Jakacka, N., Snarski, E. & Mekuria, S. Prevention of iatrogenic anemia in critical and neonatal care. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 25, 191–197 (2016).
Rosebraugh, M. R., Widness, J. A., Nalbant, D. & Veng-Pedersen, P. A mathematical modeling approach to quantify the role of phlebotomy losses and need for transfusions in neonatal anemia. Transfusion 53, 1353–1360 (2013).
Christensen, R. D., Henry, E., Jopling, J. & Wiedmeier, S. E. The CBC: reference ranges for neonates. Semin. Perinatol. 33, 3–11 (2009).
Jopling, J., Henry, E., Wiedmeier, S. E. & Christensen, R. D. Reference ranges for hematocrit and blood hemoglobin concentration during the neonatal period: data from a multihospital health care system. Pediatrics 123, E333–E337 (2009).
Kates, E. H. & Kates, J. S. Anemia and polycythemia in the newborn. Pediatr. Rev. 28, 33–34 (2007).
Farhi, L. E., Plewes, J. L. & Olszowka, A. J. Lung carbonate dehydratase (carbonic anhydrase), CO2 stores and CO2 transport. Ciba Found. Symp. 235–249 (1976).
Raymond, S. L. et al. Immunological defects in neonatal sepsis and potential therapeutic approaches. Front. Pediatr. 5, 14 (2017).
Arthur, C. M. et al. Anemia induces gut inflammation and injury in an animal model of preterm infants. Transfusion 59, 1233–1245 (2019).
MohanKumar, K. et al. A murine neonatal model of necrotizing enterocolitis caused by anemia and red blood cell transfusions. Nat. Commun. 10, 3494 (2019).
White, J. R. et al. Evaluation of hematologic variables in newborn C57/Bl6 mice up to day 35. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 45, 87–95 (2016).
Parodi, E., Romano, F. & Ramenghi, U. How we use reticulocyte parameters in workup and management of pediatric hematologic diseases. Front. Pediatr. 8, 588617 (2020).
Juul, S. Erythropoiesis and the approach to anemia in premature infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 25, 97–99 (2012).
Juul, S. Erythropoietin in anemia of prematurity. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 25, 80–84 (2012).
Al-Ghananim, R. T. et al. Reticulocyte hemoglobin content during the first month of life in critically ill very low birth weight neonates differs from term infants, children, and adults. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 30, 326–334 (2016).
Wollmann, M., Gerzson, B. M., Schwert, V., Figuera, R. W. & Ritzel Gde, O. Reticulocyte maturity indices in iron deficiency anemia. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 36, 25–28 (2014).
Ford, J. Red blood cell morphology. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 35, 351–357 (2013).
Kline, N. E. A practical approach to the child with anemia. J. Pediatr. Health Care 10, 99–105 (1996).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Sysmex America, Scientific Marketing Department for the instrument loan (Sysmex XT-2000iV) and technical support.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health awards HL124078, HL133022, and HD105880 (to K.M.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.M. designed the study and wrote the manuscript; Y.C., S.D., K.N., P.G., L.H., and K.M. performed key experiments and data analysis. All the authors contributed to and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, Y., Desiraju, S., Namachivayam, K. et al. Hematological changes in neonatal mice with phlebotomy-induced anemia. Pediatr Res 92, 1575–1579 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02023-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02023-w
This article is cited by
-
Immune landscape in liver of neonatal mice with phlebotomy-induced anemia
Pediatric Research (2025)
-
Stored RBC transfusions leads to the systemic inflammatory response syndrome in anemic murine neonates
Inflammation Research (2024)