Abstract
Background
To explore changes in adipokines during different stages of lactation, particularly in the context of maternal obesity, and their effect on growth trajectories by age 6 months.
Methods
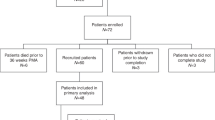
Mother-infant dyads (n = 303) were enrolled from a birth cohort study. Data concerning maternal pre-pregnancy weight, infants’ breastfeeding practices, and anthropometric data were obtained regularly. We determined and compared leptin and adiponectin in colostrum and 2-month postpartum milk, in obese/ overweight and normal-weight mothers. Linear regression analyses were used to analyze the relationship between adipokines during lactation and infant growth metrics, specifically weight-for-age z-scores (WAZ), up to 6 months of age.
Results
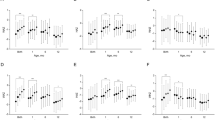
Obese and overweight mothers exhibited higher leptin in 2-month milk (P < 0.001). While univariate analysis suggested an inverse relationship between 2-month leptin and WAZ changes up to 6 months (Beta =−0.13, P = 0.042), adjustments for confounders rendered this association to nonsignificant (adjusted Beta = −0.12, P = 0.06). Multiple regression analysis identified WAZ at birth as an independent predictor of WAZ at six months (adjusted Beta = 0.36, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Insufficient evidence shows that leptin in the 2-month milk is independently associated with WAZ outcome at age 6 months, irrespective of maternal pre-pregnancy weight categories.
Impact
-
To date, large-scale study involving more than 300 mother-infant dyads, that explore the changes in adipokines during different stages of lactation in the context of maternal obesity, and their effect on infant growth is still lacking.
-
There is insufficient evidence showing that leptin in the colostrum or mature milk is independently associated with the weight outcome at 6 months of age, irrespective of maternal pre-pregnancy weight categories.
-
Birth weight z-scores is strongly associated with early postnatal growth. Longer follow-up studies are necessary to explore whether leptin in human milk could modulate later obesity risk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated for this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Young, B. E., Johnson, S. L. & Krebs, N. F. Biological determinants linking infant weight gain and child obesity: current knowledge and future directions. Adv. Nutr. 23, 675–86 (2012).
Ylöstalo, T. et al. Maternal weight, smoking, and diabetes provided early predictors of longitudinal body mass index growth patterns in childhood. Acta Paediatr. 113, 1076–1086 (2024).
Perrella, S. et al. Human milk composition promotes optimal infant growth, development and health. Semin. Perinatol. 45, 151380 (2021).
Mazzocchi, A. et al. Hormones in breast milk and effect on infants’ growth: a systematic review. Nutrients 11, 1845 (2019).
Horta, B. L., Rollins, N., Dias, M. S., Garcez, V. & Pérez-Escamilla, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization. Acta Paediatr. 112, 34–41 (2023).
Fields, D. A., Schneider, C. R. & Pavela, G. Narrative review of the associations between six bioactive components in breast milk and infant adiposity. Obesity 24, 1213–1221 (2016).
Miralles, O., Sánchez, J., Palou, A. & Picó, C. A physiological role of breast milk leptin in body weight control in developing infants. Obesity 14, 1371–1377 (2006).
Chan, D. et al. Adiponectin, leptin and insulin in breast milk: associations with maternal characteristics and infant body composition in the first year of life. Int J. Obes. 42, 36–43 (2018).
Weyermann, M., Brenner, H. & Rothenbacher, D. Adipokines in human milk and risk of overweight in early childhood: a prospective cohort study. Epidemiology 18, 722–9 (2007).
Woo, J. G. et al. Human milk adiponectin is associated with infant growth in two independent cohorts. Breastfeed. Med. 4, 101–9 (2009).
Fields, D. A. & Demerath, E. W. Relationship of insulin, glucose, leptin, IL-6 and TNF-alpha in human breast milk with infant growth and body composition. Pediatr. Obes. 7, 304–12 (2012).
Juan Castell, M. F., Peraita-Costa, I., Soriano, J. M., Llopis-Morales, A. & Morales-Suarez-Varela, M. A review of the relationship between the appetite-regulating hormone leptin present in human milk and infant growth. Breastfeed. Med. 17, 98–111 (2022).
Newburg, D. S., Woo, J. G. & Morrow, A. L. Characteristics and potential functions of human milk adiponectin. J. Pediatr. 156, S41–6 (2012).
Lis-Kuberka, J., Pupek, M. & Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. The mother-child dyad adipokine pattern: a review of current knowledge. Nutrients 15, 4059 (2023).
Sadr Dadres, G. et al. Relationship of maternal weight status before, during, and after pregnancy with breast milk hormone concentrations. Obesity 27, 621–628 (2019).
Fields, D. A. et al. Associations between human breast milk hormones and adipocytokines and infant growth and body composition in the first 6 months of life. Pediatr. Obes. 12, 78–85 (2017).
Ballard, O. & Morrow, A. L. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 60, 49–74 (2013).
Savino, F., Liguori, S. A. & Lupica, M. M. Adipokines in breast milk and preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 86, 77–80 (2010).
Martin, L. J. et al. Adiponectin is present in human milk and is associated with maternal factors. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 83, 1106–11 (2006).
Mente, A. et al. Ethnic variation in adiponectin and leptin levels and their association with adiposity and insulin resistance. Diab. Care 33, 1629–34 (2010).
Hua, M. C. et al. Introduction of various allergenic foods during infancy reduces risk of IgE sensitization at 12 months of age: a birth cohort study. Pediatr. Res 82, 733–740 (2017).
Hua, M. C. et al. Association of maternal allergy with human milk soluble CD14 and fatty acids, and early childhood atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 30, 204e13 (2019).
Chuang, F. C., Huang, H. Y., Chen, Y. H. & Huang, J. P. Optimal gestational weight gain in Taiwan: A retrospective cohort study. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 63, 220–224 (2024).
WHO. WHO child growth standards SAS igrowup package. In: WHO Anthro (version 322, January 2011) and macros. Geneva (Switzerland): WHO; (2011).
Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 854:1-452 (1995).
Heinze, G., Wallisch, C. & Dunkler, D. Variable selection - a review and recommendations for the practicing statistician. Biom. J. 60, 431–449 (2018).
Mączka, K., Stasiak, O., Przybysz, P., Grymowicz, M. & Smolarczyk, R. The Impact of the endocrine and immunological function of adipose tissue on reproduction in women with obesity. Int J. Mol. Sci. 25, 9391 (2024).
Unamuno, X. et al. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Invest 48, e12997 (2018).
Carlsen, E. M. et al. Newborn regional body composition is influenced by maternal obesity, gestational weight gain and the birthweight standard score. Acta Paediatr. 103, 939–45 (2014).
Szczyrska, J. Pediatric obesity- time to act as early as possible. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diab. Metab. 29, 267–273 (2023).
Shipp, G. M. et al. Maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, breastfeeding, and child BMI. Pediatrics 153, e2023061466 (2024).
Palou, M., Picó, C. & Palou, A. Leptin as a breast milk component for the prevention of obesity. Nutr. Rev. 76, 875–892 (2018).
Meyer, D. M. et al. The relationship between breast milk leptin and adiponectin with child body composition from 3 to 5 years: a follow-up study. Pediatr. Obes. 12, 125–129 (2017).
Kon, I. Y., Shilina, N. M., Gmoshinskaya, M. V. & Ivanushkina, T. A. The study of breast milk IGF-1, leptin, ghrelin and adiponectin levels as possible reasons of high weight gain in breast-fed infants. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 65, 317–23 (2014).
Quinn, E. A., Largado, F., Borja, J. B. & Kuzawa, C. W. Maternal characteristics associated with milk leptin content in a sample of Filipino women and associations with infant weight for age. J. Hum. Lact 31, 273–81 (2015).
Brunner, S. et al. Breast milk leptin and adiponectin in relation to infant body composition up to 2 years. Pediatr. Obes. 10, 67–73 (2015).
Weyermann, M., Beermann, C., Brenner, H. & Rothenbacher, D. Adiponectin and leptin in maternal serum, cord blood, and breast milk. Clin. Chem. 52, 2095–102 (2006).
Yang, C. et al. Association between maternal metabolic profiles in pregnancy, dietary patterns during lactation and breast milk leptin: a retrospective cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 130, 1537–47 (2023).
Acknowledgements
We thank the study participants and their parents for participating in the current study. Moreover, we are grateful to the research assistants of the PATCH study group for helping in data and sample collection and providing technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan (CMRPG2N0261-62, 2N0061, 2K0321-322, 2E0131-135, and 2B0041-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in the study design, participates recruitment, and written consent. MC Hua was involved in the laboratory work, statistical analysis and interpretation of its results. MC Hua wrote the first draft of manuscript, and JL Huang edited it. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Chang Gung Memory Hospital (202201630A3, 202102580B0A3, 201901820A3, 103-6519A3,100-0225B) and complied with the declaration of Helsinki. Written informed parental consent was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, MC., Yao, TC., Tsai, MH. et al. Associations of human milk leptin with maternal obesity and early infant weight trajectories. Pediatr Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-03984-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-03984-4