Abstract
Background
Sepsis is associated with increased neonatal morbidity and mortality. The Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (nSOFA) score was developed as a tool to assess neonates with late-onset sepsis (LOS). Absolute values and changes in nSOFA scores are associated with mortality in LOS. Few studies have investigated the nSOFA score in neonatal early-onset sepsis (EOS).
This study assesses the relationship of the nSOFA score with morbidity in preterm neonates with EOS.
Methods
Retrospective, single-center, cohort study. nSOFA scores were determined for very preterm neonates at seven time points within the first 36 hours of life. Peak and median nSOFA scores were compared between (i) survivors with versus without major morbidity (ii) survivors without major morbidity versus the combined outcome of mortality or major morbidity and (iii) survivors versus non-survivors.
Results
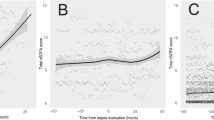
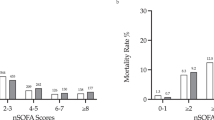
Peak and median nSOFA scores were significantly higher in survivors with versus without major morbidity. That was also true for the combined outcome of mortality or major morbidity. Peak and median nSOFA scores trended higher in non-survivors versus survivors.
Conclusions
The nSOFA score discriminates between very preterm neonates likely (versus unlikely) to develop major morbidity. The nSOFA score may have applicability as an assessment tool in neonatal EOS.
Impact
-
The neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (nSOFA) score provides an operationalized assessment of organ dysfunction in late-onset neonatal sepsis. This study demonstrates the nSOFA score’s utility in early-onset sepsis (EOS).
-
This study provides data to support the nSOFA score’s utility in discriminating major morbidity and mortality in neonates < 32 weeks gestational age with EOS. A higher nSOFA score was associated with increased morbidity in neonates < 32 weeks gestational age with EOS.
-
A validated nSOFA score for EOS has the potential to improve prognostication and provide a basis for risk-stratifying neonates with EOS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Heron, M. Deaths: Leading Causes for 2017. Natl Vital-. Stat. Rep. Cent. Dis. Control Prev. Natl Cent. Health Stat. Natl Vital-. Stat. Syst. 68, 1–77 (2019).
Stoll, B. J. et al. Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis: The Burden of Group B Streptococcal and E. coli Disease Continues. Pediatrics 127, 817–826 (2011).
Schrag, S. J. et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis, 2005 to 2014. Pediatrics 138, e20162013 (2016).
Klinger, G. et al. Outcome of early-onset sepsis in a national cohort of very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 125, e736–e740 (2010).
Lehner, R., Leitich, H., Jirecek, S., Földy, M. & Kaider, A. Retrospective Analysis Of Severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage And Early-onset Neonatal Sepsis In Very Low Birth-weight Infants. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol Infect. Dis. 20, 833–834 (2001).
Stoll, B. J. et al. Early-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: A report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J. Pediatr. 129, 72–80 (1996).
Al-Essa, M., Azad, R. V. & Rashwan, N. Threshold stage of retinopathy of prematurity: maternal and neonatal risk factors. Ann. Saudi Med. 20, 129–131 (2000).
Graham, E. M., Holcroft, C. J., Rai, K. K., Donohue, P. K. & Allen, M. C. Neonatal cerebral white matter injury in preterm infants is associated with culture positive infections and only rarely with metabolic acidosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 191, 1305–1310 (2004).
Stafford, I. A. et al. The strong correlation between neonatal early-onset Group B Streptococcal disease and necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 223, 93–97 (2018).
Lamireau, N., Greiner, E. & Hascoët, J. M. Risk factors associated with necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants: A case–control study. Arch. Pédiatr. 30, 477–482 (2023).
de Grooth, H. J. et al. SOFA and mortality endpoints in randomized controlled trials: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Crit. Care. 21, 38 (2017).
Matics, T. J. & Sanchez-Pinto, L. N. Adaptation and validation of a pediatric sequential organ failure assessment score and evaluation of the Sepsis-3 definitions in critically ill children. JAMA Pediatr. 171, e172352 (2017).
Wynn, J. L. & Polin, R. A. A neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score predicts mortality to late-onset sepsis in preterm very low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 88, 85–90 (2020).
Fleiss, N. et al. Evaluation of the neonatal sequential organ failure assessment and mortality risk in preterm infants with late-onset infection. JAMA Netw. Open. 4, e2036518 (2021).
Wynn, J. L. et al. Multicenter validation of the neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score for prognosis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Pediatr. 236, 297–300.e1 (2021).
Yeo, K. T., Goh, G. L., Park, W. Y., Wynn, J. L. & Aziz, K. B. Evaluation of the Neonatal sequential organ failure assessment and mortality risk in neonates with early-onset infection. Neonatology 120, 796–800 (2023).
Puopolo, K. M. et al. Management of neonates born at ≤34 6/7 weeks’ gestation with suspected or proven early-onset bacterial sepsis. Pediatrics 142, e20182896 (2018).
Kim, F. et al. Revisiting the definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants at a single center quaternary neonatal intensive care unit. J. Perinatol. 41, 756–763 (2021).
Papile, L. A., Burstein, J., Burstein, R. & Koffler, H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: A study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J. Pediatr. 92, 529–534 (1978).
Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity*. The International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity Revisited. Arch. Ophthalmol. 123, 991–999 (2005).
Walsh, M. C. & Kliegman, R. M. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Treatment based on staging criteria. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 33, 179–201 (1986).
Lewis, A. N. et al. Evaluation of the neonatal sequential organ failure assessment and mortality risk in preterm infants with necrotizing Enterocolitis. Neonatology 119, 334–344 (2022).
Salimi, U., Dummula, K., Tucker, M. H., Dela Cruz, C. S. & Sampath, V. Postnatal sepsis and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants: mechanistic insights into “New BPD. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 66, 137–145 (2022).
Dammann, O. & Stansfield, B. K. Neonatal sepsis as a cause of retinopathy of prematurity: An etiological explanation. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 98, 101230 (2024).
Strunk, T. et al. Infection-induced inflammation and cerebral injury in preterm infants. Lancet Infect. Dis. 14, 751–762 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate David Bateman for his guidance regarding statistical analysis as well as the NYP Pediatrics Department and the Division of Neonatology for institutional support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; - Drs. Tagerman, Sahni, Polin. Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and - Drs. Tagerman, Sahni, Polin. Final approval of the version to be published. - Drs. Tagerman, Sahni, Polin.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tagerman, M., Sahni, R. & Polin, R. The neonatal SOFA score in very preterm neonates with early-onset sepsis. Pediatr Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04068-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04068-z