Abstract
Background
The use of probiotics/synbiotic to assist in the treatment of overweight/obese children is currently a hot topic. However, the therapeutic effect is controversial. This meta-analysis assesses their effects and safety in overweight/obese children.
Methods
PubMed, Cochrane, Web of Science, and Embase were searched (2000- April 2024) for RCTs on probiotics/synbiotics in overweight/obese children. Primary outcomes included anthropometric measures, lipid profiles, insulin sensitivity, inflammatory markers, and liver enzymes. Result stability and heterogeneity sources were assessed by sensitivity and subgroup analyses. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on age, intervention time, complications and treatment methods. Review Manager 5.4.1 and STATA 15.0 were used to conduct the statistical analysis.
Results
A total of 16 studies were included (n = 763). L. acidophilus is the most commonly used. We found significant reductions in BMI-z, CRP and TNF-α. Synbiotics/probiotics are more effective when the treatment lasted for more than 3 months or when the patients was under 12 years old. All indicators lost significance in patients with NAFLD.
Conclusions
Probiotics/synbiotics significantly improved BMI-z, CRP, and TNF-α in overweight/obese children. Patients without complications under the age of 12 or those whose treatment lasts for more than 3 months will gain more benefits.
Impact
-
This study found that probiotics/synbiotics could significantly improve BMI-Zscore, CRP, and TNF-α in overweight/obese children.
-
This meta-analysis, incorporating the latest randomized controlled trials (RCTs), identified factors influencing probiotic/synbiotic efficacy through subgroup analysis: probiotic/synbiotic type, treatment duration, patient age, and the presence of complications.
-
This study provides further evidence supporting the effectiveness of probiotics/synbiotics in treating overweight/obese children.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight [Internet]. Geneva: WHO; 2025 [cited 2025 Oct 13]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Hampl, S. E., et al. Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and treatment of children and adolescents with obesity. Pediatrics 151, e2022060640 (2023).
Roy, S. M., et al. Infant BMI or weight-for-length and obesity risk in early childhood. Pediatrics 137, e20153492 (2016).
Skinner, A. C., et al. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children, 1999-2016. Pediatrics 141, e20173459 (2018).
Montero, D., Walther, G., Perez-Martin, A., Roche, E. & Vinet, A. Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress in obese children and adolescents: markers and effect of lifestyle intervention. Obes. Rev. 13, 441–455 (2012).
Aggarwal, B. & Jain, V. Obesity in children: definition, etiology and approach. Indian J. Pediatr. 85, 463–471, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-017-2531-x (2018).
anchez, M., Panahi, S. & Tremblay, A. Childhood obesity: a role for gut microbiota?. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 12, 162–175 (2015).
Backhed, F. et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15718–15723 (2004).
etraroli, M., Castellone, E., Patianna, V. & Esposito, S. Gut microbiota and obesity in adults and children: the state of the art. Front. Pediatr. 9, 657020 (2021).
Subspecialty Group of Endocrinologic, Hereditary and Metabolic Diseases, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association; Subspecialty Group of Child Health Care, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association; Subspecialty Group of Clinical Nutrition, the Society of Pediarics, Chinese Medical Association; Editorial Board. Chin. J. Pediatr. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 60, 507–515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20220112-00043
Mead, E., et al. Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children from the age of 6 to 11 years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 6, CD012651 (2017).
Abenavoli, L., et al. Gut microbiota and obesity: a role for probiotics. Nutrients 11, 2690 (2019).
Steer, T. et al. “Perspectives on the role of the human gut microbiota and its modulation by pro- and prebiotics”. Nutr. Res. Rev. 13, 229–254 (2000).
Gibson, G. R., et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 491–502 (2017).
Zhang, Q., Wu, Y. & Fei, X. Effect of probiotics on body weight and body-mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 67, 571–580 (2015).
Derrien, M., Alvarez, A. S. & de Vos, W. M. The gut microbiota in the first decade of life. Trends Microbiol. 27, 997–1010 (2019).
Li, H. Y. et al. Effects and mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics on metabolic diseases targeting gut microbiota: a narrative review. Nutrients 13, 3211 (2021).
Krumbeck, J. A., et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium strains and galactooligosaccharides improve intestinal barrier function in obese adults but show no synergism when used together as synbiotics. Microbiome 6, 121 (2018).
Vallianou, N., Stratigou, T., Christodoulatos, G. S., Tsigalou, C. & Dalamaga, M. Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, postbiotics, and obesity: current evidence, controversies, and perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 9, 179–192 (2020).
Li, Y., Liu, T., Qin, L. & Wu, L. Effects of probiotic administration on overweight or obese children: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 21, 525 (2023).
Loy, M. H., Usseglio, J., Lasalandra, D. & Gold, M. A. Probiotic use in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity: a scoping review. Child Obes. 19, 145–159 (2023).
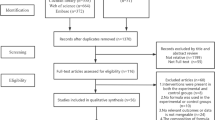
Page, M. J. et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71 (2021).
Wan, X., Wang, W., Liu, J. & Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Method 14, 135 (2014).
Luo, D., Wan, X., Liu, J. & Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 27, 1785–1805 (2018).
Follmann, D., Elliott, P., Suh, I. & Cutler, J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 45, 769–773 (1992).
Landis, J. R. & Koch, G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33, 159–174 (1977).
Higgins, J. P. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002).
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315, 629–634 (1997).
Alisi, A. et al. “Randomised clinical trial: the beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. ”. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 39.11, 1276–1285 (2014).
Kilic Yildirim, G., Dinleyici, M., Vandenplas, Y. & Dinleyici, E. C. Effects of multispecies synbiotic supplementation on anthropometric measurements, glucose and lipid parameters in children with exogenous obesity: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (probesity-2 trial). Front. Nutr. 9, 898037 (2022).
Atazadegan et al. “Effects of synbiotic supplementation on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight or obese children and adolescents: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial”. World J. Pediatr. 19, 356–365 (2023).
Ipar, N. et al. Effects of synbiotic on anthropometry, lipid profile and oxidative stress in obese children. Benef. Microbes 6, 775–782 (2015).
Kelishadi, R., Farajian, S., Safavi, M., Mirlohi, M. & Hashemipour, M. A randomized triple-masked controlled trial on the effects of synbiotics on inflammation markers in overweight children. J. Pediatr. 90, 161–168 (2014).
Kianifar et al. Effects of synbiotics on anthropometric indices of obesity in children: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Top. Clin. Nutr. 33, 118–126 (2018).
Famouri, F., Shariat, Z., Hashemipour, M., Keikha, M. & Kelishadi, R. Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 64, 413–417 (2017).
Goyal et al. “Probiotic and lifestyle modification in obese pediatrics with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease”. Indian J. Community Health 31, 427 (2019).
Jones, R. B. et al. Probiotic supplementation increases obesity with no detectable effects on liver fat or gut microbiota in obese Hispanic adolescents: a 16-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr. Obes. 13, 705–714 (2018).
Miccheli, A. et al. Urinary (1)H-NMR-based metabolic profiling of children with NAFLD undergoing VSL#3 treatment. Int. J. Obes. 39, 1118–1125 (2015).
Rodrigo, T. et al. Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 65, 304–311 (2022).
Vajro, P. et al. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG in pediatric obesity-related liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 52, 740–743 (2011).
Chen, A. C. et al. A multi-strain probiotic blend reshaped obesity-related gut dysbiosis and improved lipid metabolism in obese children. Front. Nutr. 9, 922993 (2022).
Gøbel, R. J., Larsen, N., Jakobsen, M., Mølgaard, C. & Michaelsen, K. F. Probiotics to adolescents with obesity: effects on inflammation and metabolic syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 55, 673–678 (2012).
Sanchis-Chordà, J. et al. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 supplementation improves inflammatory status in insulin-resistant obese children. Eur. J. Nutr. 58, 2789–2800 (2019).
Verma, A., Nelson, M. T., DePaolo, W. R., Hampe, C. & Roth, C. L. A randomized double-blind placebo controlled pilot study of probiotics in adolescents with severe obesity. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 20, 1289–1300 (2021).
Taylor, E. rinB. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 135, 731–752 (2021).
Canfora, E. E., Jocken, J. W. & Blaak, E. E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 577–591 (2015).
Ciccia, F. et al. Dysbiosis and zonulin upregulation alter gut epithelial and vascular barriers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 76, 1123–1132 (2017).
Kalliomäki, M., Collado, M. C., Salminen, S. & Isolauri, E. Early differences in fecal microbiota composition in children may predict overweight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87, 534–538 (2008).
Roswall, J. et al. Developmental trajectory of the healthy human gut microbiota during the first 5 years of life. Cell Host Microbe 29, 765–776.e3 (2021).
Zhang, P. et al. Oxidative stress and diabetes: antioxidative strategies. Front. Med. 14, 583–600 (2020).
Rani, V., Deep, G., Singh, R. K., Palle, K. & Yadav, U. C. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 148, 183–193 (2016).
Tilg, H., Adolph, T. E., Dudek, M. & Knolle, P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity. Nat. Metab. 3, 1596–1607 (2021).
Xiongzhong, R. & Yaxi, C. Metabolic inflammation and the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chin. J. Dig. 40, 581–584 (2020).
Zhang, M. M. et al. Use of pre-, pro-and synbiotics in patients with acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 3970 (2010).
Daniali, M., Nikfar, S. & Abdollahi, M. A brief overview on the use of probiotics to treat overweight and obese patients. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 15, 1–4 (2020).
Gao, H. et al. The functional roles of Lactobacillus acidophilus in different physiological and pathological processes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 1226–1233 (2022).
Cheng, F. S., Pan, D., Chang, B., Jiang, M. & Sang, L. X. Probiotic mixture VSL#3: an overview of basic and clinical studies in chronic diseases [published correction appears in World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jul 16;9(20): 5752-5753.doi: 10.12998/wjcc. v9.i20.5752]. World J. Clin. Cases 8, 1361–1384 (2020).
Sanders, M. E. et al. Safety assessment of probiotics for human use. Gut Microbes 1, 164–185 (2010).
Bernardeau, M., Guguen, M. & Vernoux, J. P. Beneficial lactobacilli in food and feed: long-term use, biodiversity and proposals for specific and realistic safety assessments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30, 487–513 (2006).
Funding
Research projects of the Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No.20231264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Meihao Ding: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing- Original draft, Data curation, Visualization were performed; Jiaxin Zhuang and Liyu Chen: Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Reviewing and Editing were performed; Jing Wang and Dandan Hu: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration were performed. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, M., Zhuang, J., Chen, L. et al. Efficacy and safety of probiotic/synbiotic supplementation for overweight or obese children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pediatr Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04412-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04412-3