Abstract
Introduction
Vertebral hemangioma (VH) is the most common angiomatous tumor usually asymptomatic and is incidentally noticed on MRI. The incidence of VH is rare in the pediatric population. The extraosseous extension is termed an Aggressive Vertebral Hemangioma (AVH) and these often need surgical management. Intraoperative stereotactic navigation for tumor excision helps in planning- localizing the tumor and delineating its margins.
Case presentation
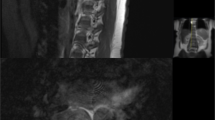
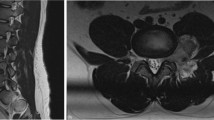
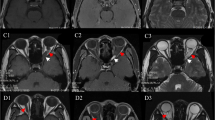
A 14-year-old boy presented with thoracic myelopathy signs. The MRI scan suggests T1 and T2 hyperintense signals within the T6 vertebral body with extramedullary extradural space occupying the lesion. The CT scan showed a “polka dot” appearance. Preoperative endovascular embolization followed by surgical decompression with posterior instrumented stabilization under O-arm navigation and tumor excision was planned. Cystic extradural lesion excised and vertebroplasty done at T6 level. Histopathology slides confirmed hemangioma.
Discussion
The most common age of involvement is between 30 and 70 years it is rarely seen in the pediatric age group. To the best of our knowledge, fewer than 20 cases of pediatric aggressive vertebral hemangiomas have been reported. Based on a review of pediatric AVH only 4 patients have been treated with preoperative vascular embolization followed by surgical decompression and stabilization. O-arm navigated AVH excision and vertebroplasty has never been described in the literature; this being the first case. It also aids in the identification of tumor margins along with real-time monitoring of adequate resection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 1 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is not a part of a public repository.
References
Fox MW, Onofrio BM. The natural history and management of symptomatic and asymptomatic vertebral hemangiomas. J Neurosurg. 1993;78:36–45.
Sahajwalla D, Vorona G, Tye G, Harper A, Richard H, Sisler I, et al. Aggressive vertebral hemangioma masquerading as neurological disease in a pediatric patient. Radiol Case Rep. 2021;16:1107–12.
Goraya GS, Singhal S, Paul BS, Paul G. Aggressive vertebral hemangioma: the mystery of spastic legs unveiled by a purple shoulder. Cureus. 2022;14:e21568.
Cloran FJ, Pukenas BA, Loevner LA, Aquino C, Schuster J, Mohan S. Aggressive spinal haemangiomas: imaging correlates to clinical presentation with analysis of treatment algorithm and clinical outcomes. BJR. 2015;88:20140771.
Vasudeva VS, Chi JH, Groff MW. Surgical treatment of aggressive vertebral hemangiomas. FOC. 2016;41:E7.
Barsa P, Frőhlich R, Šercl M, Buchvald P, Suchomel P. The intraoperative portable CT scanner-based spinal navigation: a viable option for instrumentation in the region of cervico-thoracic junction. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:1643–50.
Urrutia J, Postigo R, Larrondo R, Martin AS. Clinical and imaging findings in patients with aggressive spinal hemangioma requiring surgical treatment. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:209–12.
Kato S, Kawahara N, Murakami H, Demura S, Yoshioka K, Okayama T, et al. Surgical management of aggressive vertebral hemangiomas causing spinal cord compression: long-term clinical follow-up of five cases. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15:350–6.
Adeolu AA, Balogun JA, Adeleye AO, Adeoye PO, Okolo CA, Ogbole GI. Management of symptomatic vertebral haemangioma in a resource challenged environment. Childs Nerv Syst. 2010;26:979–82.
Cheung NK, Doorenbosch X, Christie JG. Rapid onset aggressive vertebral haemangioma. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011;27:469–72.
Duprez T, Lokietek W, Clapuyt P, DeMerlier Y, Malghem J, Gadisseux JF. Multiple aggressive vertebral haemangiomas in an adolescent: a case report. Pediatr Radio. 1998;28:51–3.
Singh PK, Chandra PS, Vaghani G, Savarkar DP, Garg K, Kumar R, et al. Management of pediatric single-level vertebral hemangiomas presenting with myelopathy by three-pronged approach (ethanol embolization, laminectomy, and instrumentation): a single-institute experience. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016;32:307–14.
Pretell-Mazzini J, Chikwava KR, Dormans JP. Low back pain in a child associated with acute onset cauda equina syndrome: a rare presentation of an aggressive vertebral hemangioma: a case report. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32:271–6.
Cross JJ, Antoun NM, Laing RJC, Xuereb J. Imaging of compressive vertebral haemangiomas. Eur Radio. 2000;10:997–1002.
Karagoz Guzey F, Emel E, Aycan A, Bas NS, Seyithanoglu MH, Ozkan N, et al. Pediatric vertebral and spinal epidural tumors: a retrospective review of twelve cases. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2008;44:14–21.
Uzunaslan D, Saygin C, Gungor S, Hasiloglu Z, Ozdemir N, Celkan T. Novel use of propranolol for management of pain in children with vertebral hemangioma: report of two cases. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29:855–60.
Pinto DS, Hoisala VR, Gupta P, Sarkar P. Aggressive vertebral body hemangioma causing compressive myelopathy - two case reports. J Orthop Case Rep. 2017;7:7–10.
Doppman JL, Oldfield EH, Heiss JD. Symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: treatment by means of direct intralesional injection of ethanol. Radiology. 2000;214:341–8.
Narayana RV, Pati R, Dalai S. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in painful refractory vertebral hemangiomas. IJOO. 2014;48:163–7.
Zhang P, Liu H, Sun Z, Wang J, Wang G. The application of O-arm and navigation system in precise localization of spinal cord lesions: a case series study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;196:105922.
Nagashima Y, Nishimura Y, Haimoto S, Eguchi K, Awaya T, Ando R, et al. Piecemeal resection of aggressive vertebral hemangioma using real-time navigation-guided drilling technique. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2021;83:861–8.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, project administration; NS: Data curation, writing draft, visualization; SA: Modification of primary draft, investigation, review and editing, project administration; PB: Supervision, project administration; review and editing, SH and PS: Supervision, project administration. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethics committee approval
Approval of the institutional Ethics Committee (Sancheti Hospital Institutional Ethics Committee) has been obtained.
Guidelines
This care report has been prepared in accordance with the CARE – Case report guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kothari, A.R., Situt, N.V., Hadgaonkar, S.R. et al. O-arm navigated excision and vertebroplasty of pediatric aggressive vertebral hemangioma with compressive myelopathy: A case report. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 11, 20 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-025-00717-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-025-00717-x