Abstract
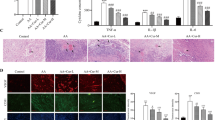
Excessive and abnormal vessel growth plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as cancer. Angiogenesis is one of the hallmarks of cancer growth, invasion, and metastasis. Discovery of novel antiangiogenic agents would provide new insights into the mechanisms of angiogenesis, as well as potential drugs for cancer treatment. In the present study, we investigated the antiangiogenic activity of a series of monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin synthesized previously in our lab. We found that curcumin analog A2 displayed the full potential to be developed as a novel antiangiogenic agent. Curcumin analog A2 at and above 20 μM dramatically inhibited the migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro, new microvessels sprouting from the rat aortic rings ex vivo and newly formed microvessels in chicken chorioallantoic membranes (CAMs) and Matrigel plus in vivo. We further demonstrated that curcumin analog A2 exerted its antiangiogenic activity mainly through inducing endothelial cell death via elevating NADH/NADPH oxidase-derived ROS. Curcumin analog A2 at the antiangiogenic concentrations also triggered autophagy in HUVECs, but this process is neither a pre-requisite for toxicity, leading to the cell death nor a protective response against the toxicity of curcumin analog A2. In conclusion, we demonstrate for the first time the potent antiangiogenic activity of the monocarbonyl curcumin analog A2, which could serve as a promising potential therapeutic agent for the prevention and treatment angiogenesis-related diseases, such as cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 2011;146:873–87.
De Palma M, Biziato D, Petrova TV. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:457–74.
Hida K, Hida Y, Shindoh M. Understanding tumor endothelial cell abnormalities to develop ideal anti-angiogenic therapies. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:459–66.
Noble ME, Endicott JA, Johnson LN. Protein kinase inhibitors: insights into drug design from structure. Science. 2004;303:1800–5.
Rahmani AH, Alsahli MA, Aly SM, Khan MA, Aldebasi YH. Role of curcumin in disease prevention and treatment. Adv Biomed Res. 2018;7:38.
Shanmugam MK, Warrier S, Kumar AP, Sethi G, Arfuso F. Potential role of natural compounds as anti-angiogenic agents in cancer. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017;15:503–19.
El-Azab M, Hishe H, Moustafa Y, El-Awady El-S. Anti-angiogenic effect of resveratrol or curcumin in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;652:7–14.
Gururaj AE, Belakavadi M, Venkatesh DA, Marmé D, Salimath BP. Molecular mechanisms of anti-angiogenic effect of curcumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;297:934–42.
Hewlings SJ, Kalman DS. Curcumin: A review of its’ effects on human health. Foods . 2017;6:E92.
Shimazu K, Inoue M, Sugiyama S, Fukuda K, Yoshida T, Taguchi D, et al. Curcumin analog GOY078, overcomes resistance to tumor angiogenesis inhibitors. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:3285–93.
Sugiyama S, Yoshino Y, Kuriyama S, Inoue M, Komine K, Otsuka K, et al. A curcumin analog, GO-Y078, effectively inhibits angiogenesis through actin disorganization. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16:633–47.
Sun L, Liu J, Lin SS, Shi WT, Zhu J, Liang G, et al. Potent anti-angiogenic activity of B19–a mono-carbonyl analogue of curcumin. Chin J Nat Med. 2014;12:8–14.
Zhao C, Liu Z, Liang G. Promising curcumin-based drug design: mono-carbonyl analogues of curcumin (MACs). Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:2114–35.
Pan Z, Chen C, Zhou Y, Xu F, Xu Y. Synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin as potential anti-tumor agents. Drug Dev Res. 2016;77:43–9.
Pignanelli C, Ma D, Noel M, Ropat J, Mansour F, Curran C, et al. Selective targeting of cancer cells by oxidative vulnerabilities with novel curcumin analogs. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1105.
Song JX, Sun YR, Peluso I, Zeng Y, Yu X, Lu JH, et al. A novel curcumin analog binds to and activates TFEB in vitro and in vivo independent of MTOR inhibition. Autophagy. 2016;12:1372–89.
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973;52:2745–56.
Zhang L, Jing H, Cui L, Li H, Zhou B, Zhou G, et al. 3,4-Dimethoxystilbene, a resveratrol derivative with anti-angiogenic effect, induces both macroautophagy and apoptosis in endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114:697–707.
Zhang L, Wang X, Miao Y, Chen Z, Qiang P, Cui L, et al. Magnetic ferroferric oxide nanoparticles induce vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and inflammation by disturbing autophagy. J Hazard Mater. 2016;304:186–95.
Zhang L, Dai F, Cui L, Jing H, Fan P, Tan X, et al. Novel role for TRPC4 in regulation of macroautophagy by a small molecule in vascular endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1853:377–87.
Patan S. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cancer Treat Res. 2004;117:3–32.
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 2016;12:1–222.
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2977–92.
Ramjiawan RR, Griffioen AW, Duda DG. Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: Is there a role for combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis. 2017;20:185–204.
Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;s386:671–4.
Sakamaki K. Regulation of endothelial cell death and its role in angiogenesis and vascular regression. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2004;1:305–15.
Watson EC, Grant ZL, Coultas L. Endothelial cell apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74:4387–403.
Jiang F. Autophagy in vascular endothelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43:1021–8.
Pathania AS, Wani ZA, Guru SK, Kumar S, Bhushan S, Korkaya H, et al. The anti-angiogenic and cytotoxic effects of the boswellic acid analog BA145 are potentiated by autophagy inhibitors. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:6.
Gurel-Gurevin E, Kiyan HT, Esener OBB, Aydinlik S, Uvez A, Ulukaya E, et al. Chloroquine used in combination with chemotherapy synergistically suppresses growth and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:4011–20.
Nishikawa T, Tsuno NH, Okaji Y, Sunami E, Shuno Y, Sasaki K, et al. The inhibition of autophagy potentiates anti-angiogenic effects of sulforaphane by inducing apoptosis. Angiogenesis. 2010;13:227–38.
Panieri E, Santoro MM. ROS signaling and redox biology in endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:3281–303.
Szewczyk A, Jarmuszkiewicz W, Koziel A, Sobieraj I, Nobik W, Lukasiak A, et al. Mitochondrial mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction. Pharmacol Rep. 2015;67:704–10.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31471296), the Foundation for Key Teacher by Henan University of Technology (No. 001170) and the Research Program for Science and Technology of Henan Province (No. 192102310148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZ designed the study; BL, LSC, BZ, LLZ, ZHL, and LZ performed the study; BL and LZ analyzed the data; LZ wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Cui, Ls., Zhou, B. et al. Monocarbonyl curcumin analog A2 potently inhibits angiogenesis by inducing ROS-dependent endothelial cell death. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40, 1412–1423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0224-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0224-x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Curcuminoids as natural modulators of necroptosis: therapeutic implications
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2025)