Abstract
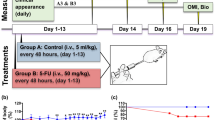
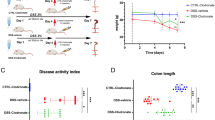
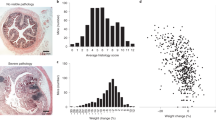
Intestinal mucositis is a common side effect of anticancer regimens that exerts a negative impact on chemotherapy. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a potential therapy for mucositis but efficient product is not available because the enzyme is degraded following oral administration or induces an immune reaction after intravascular infusion. Multi-modified Stable Anti-Oxidant Enzymes® (MS-AOE®) is a new recombinant SOD with better resistance to pepsin and trypsin. We referred it as MS-SOD to distinguish from other SODs. In this study we investigated its potential to alleviate 5-FU-induced intestinal injury and the mechanisms. An intestinal mucositis model was established in C57/BL6 mice by 5-day administration of 5-FU (50 mg/kg every day, ip). MS-SOD (800 IU/10 g, ig) was given once daily for 9 days. 5-FU caused severe mucositis with intestinal morphological damage, bodyweight loss and diarrhea; MS-SOD significantly decreased the severity. 5-FU markedly increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines in the intestine which were ameliorated by MS-SOD. Furthermore, MS-SOD modified intestinal microbes, particularly reduced Verrucomicrobia, compared with the 5-FU group. In Caco2 cells, MS-SOD (250–1000 U/mL) dose-dependently decreased tBHP-induced ROS generation. In RAW264.7 cells, MS-SOD (500 U/mL) had no effect on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines, but inhibited iNOS expression. These results demonstrate that MS-SOD can scavenge ROS at the initial stage of injury, thus play an indirect role in anti-inflammatory and barrier protein protection. In conclusion, MS-SOD attenuates 5-FU-induced intestinal mucositis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation, and influencing microbes. MS-SOD may exert beneficial effect in prevention of intestinal mucositis during chemotherapy in clinic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Rosenthal DI, Mendoza TR, Fuller CD, Hutcheson KA, Wang XS, Hanna EY, et al. Patterns of symptom burden during radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: a prospective analysis using the university of Texas MD anderson cancer center symptom inventory‐head and neck module. Cancer. 2014;120:1975–84.
Harris DJ. Cancer treatment-induced mucositis pain: strategies for assessment and management. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2006;2:251–8.
Swami U, Goel S, Mani S. Therapeutic targeting of CPT-11 induced diarrhea: a case for prophylaxis. Curr Drug Targets. 2013;14:777–97.
Iacovelli R, Pietrantonio F, Palazzo A, Maggi C, Ricchini F, de Braud F, et al. Incidence and relative risk of grade 3 and 4 diarrhoea in patients treated with capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil: a meta-analysis of published trials. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78:1228–37.
Simone NL, Menard C, Soule BP, Albert PS, Guion P, Smith S, et al. Intrarectal amifostine during external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer produces significant improvements in quality of life measured by epic score. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:90–5.
Zhou YF, Sridhar R, Shan L, Sha W, Gu XB, Sukumar S. Loperamide, an FDA-approved antidiarrhea drug, effectively reverses the resistance of multidrug resistant MCF-7/MDR1 human breast cancer cells to doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity. Cancer Invest. 2012;30:119–25.
Deng C, Deng B, Jia LQ, Tan HY. Efficacy of long-acting release octreotide for preventing chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea: protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e014916.
Huang JH, Cao YF, Liao C, Wu LC, Gao F. Effect of histamine-2-receptor antagonists versus sucralfate on stress ulcer prophylaxis in mechanically ventilated patients: a meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials. Crit Care. 2010;14:R194.
Aggarwal BB, Prasad S, Reuter S, Kannappan R, Yadav VR, Park B, et al. Identification of novel anti-inflammatory agents from ayurvedic medicine for prevention of chronic diseases: “Reverse Pharmacology” and “Bedside to Bench” approach. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:1595–653.
Sonis ST. The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:277–84.
Bhattacharyya A, Chattopadhyay R, Mitra S, Crowe SE. Oxidative stress: an essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiol Rev. 2014;94:329–54.
Zhang XC, Epperly MW, Kay MA, Chen ZY, Dixon T, Franicola D, et al. Radioprotection in vitro and in vivo by minicircle plasmid carrying the human manganese superoxide dismutase transgene. Hum Gene Ther. 2008;19:820–6.
Ahlengard S, Tufesson G, Pettersson H, Andersson T. Treatment of traumatic arthritis in the horse with Intra-Articular Orgotein (Palosein”). Equine Vet J. 1978;10:122–4.
Goldberg LD, Crysler C. A single center, pilot, double-blinded, randomized, comparative, prospective clinical study to evaluate improvements in the structure and function of facial skin with tazarotene 0.1% cream alone and in combination with GliSODin® skin nutrients advanced anti-aging formula. Clin Cosmet Invest Dermatol. 2014;7:139–44.
Meng FG, inventors. Novel recombinant high-stability superoxide dismutase and application thereof. China patent. 2016;ZL201610099824.
Hamouda N, Sano T, Oikawa Y, Ozaki T, Shimakawa M, Matsumoto K, et al. Apoptosis, dysbiosis and expression of inflammatory cytokines are sequential events in the development of 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;121:159–68.
Yasuda M, Kato S, Yamanaka N, Iimori M, Matsumoto K, Utsumi D, et al. 5-HT3 receptor antagonists ameliorate 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis by suppression of apoptosis in murine intestinal crypt cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;168:1388–400.
Li HL, Lu L, Wang XS, Qin LY, Wang P, Qiu SP, et al. Alteration of gut microbiota and inflammatory cytokine/chemokine profiles in 5-fluorouracil induced intestinal mucositis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:455.
Liu ZZ, Xi J, Schroder S, Wang WG, Xie TP, Wang ZG, et al. Chimonanthus nitens var. salicifolius aqueous extract protects against 5-fluorouracil induced gastrointestinal mucositis in a mouse model. Evid Based Complement Altemat Med. 2013;2013:789263.
Wright TH, Yazbeck R, Lymn KA, Whitford EJ, Cheah KY, Butler RN, et al. The herbal extract, Iberogast (R), improves jejunal integrity in rats with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-induced mucositis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:923–9.
Al-Sadi R, Khatib K, Guo SH, Ye DM, Youssef M, Ma T. Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;300:G1054–64.
Lin Y, Lin Y, Lin L, Zheng CQ. IL-17/IFN-gamma interactions regulate intestinal inflammation in TNBS-induced acute colitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012;32:548–56.
Hosseini MAS, Mansourabadi AH, Shams A, Hassanzadeh M. The role of interleukin (IL-22) in immune response to human diseases. Int J Epidemiol Res. 2015;2:152–61.
Sakai H, Kai Y, Oguchi A, Kimura M, Tabata S, Yaegashi M, et al. Curcumin inhibits 5-fluorouracil-induced up-regulation of CXCL1 and CXCL2 of the colon associated with attenuation of diarrhoea development. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;119:540–7.
Xu L, He SS, Yin P, Li DY, Mei C, Yu XH, et al. Punicalagin induces Nrf2 translocation and HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt, protecting rat intestinal epithelial cells from oxidative stress. Int J Hyperther. 2016;32:465–73.
Asakura H, Suzuki K, Kitahora T, Morizane T. Is there a link between food and intestinal microbes and the occurrence of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:1794–801.
Forstermann U, Sessa WC. Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:829–37.
Hernandez-Saavedra D, Zhou HF, McCord JM. Anti-inflammatory properties of a chimeric recombinant superoxide dismutase: SOD2/3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005;59:204–8.
Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:330–8.
van der Flier LG, Clevers H. Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:241–60.
Ganesh BP, Klopfleisch R, Loh G, Blaut M. Commensal Akkermansia muciniphila exacerbates gut inflammation in Salmonella typhimurium-infected gnotobiotic mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74963.
Hu CA, Hou Y, Yi D, Qiu Y, Wu G, Kong X, et al. Autophagy and tight junction proteins in the intestine and intestinal diseases. Anim Nutr. 2015;1:43–7.
Weber CR, Shen L, Wu LC, Wang YM, Turner JR. Occludin is required for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated regulation of tight junction (TJ) barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:S64.
Luettig J, Rosenthal R, Barmeyer C, Schulzke JD. Claudin-2 as a mediator of leaky gut barrier during intestinal inflammation. Tissue Barriers. 2015;3:e977176.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National New Drug Creation Program of China (2015ZX09501007-001 to Jian-hua Sun and 2018ZX09201017-004 to Li-kun Gong) and the “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA12050305 to Li-kun Gong).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XXY, YTZ, FGM and LKG designed the research and wrote the manuscript. XXY, HLL, SYW, XLY, and JHS conducted the experiments. HLL contributed to the pathological analysis, and YTZ performed data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Xx., Li, Hl., Zhang, Yt. et al. A new recombinant MS-superoxide dismutase alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 348–357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0295-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0295-8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inflammatory bowel diseases: pathological mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives
Molecular Biomedicine (2026)
-
Recombinant Molecules as a New Frontier in Mucositis Therapy
BioDrugs (2026)
-
Numerical simulation of wormhole propagation in fractured carbonate rocks during acidizing using a simplified Stokes–Brinkman model
Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology (2024)
-
The secreted protein Amuc_1409 from Akkermansia muciniphila improves gut health through intestinal stem cell regulation
Nature Communications (2024)
-
TBHQ attenuates ferroptosis against 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal epithelial cell injury and intestinal mucositis via activation of Nrf2
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2021)