Abstract
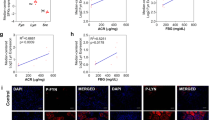
Proximal renal tubular damage is a critical process underlying diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Our previous study shows that prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) reduces the apoptosis of renal tubular cells in DKD rats. But its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study we investigated the protective effects of PGE1 in DKD rats and high glucose (HG, 30 mM)-treated HK-2 proximal tubular cells. Four weeks after uninephrectomized streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats were established, the DKD rats were administered PGE1 (10 µg· kg−1· d−1, iv.) for 10 consecutive days. We showed that PGE1 administration did not change blood glucose levels, but alleviated diabetic kidney injury in the DKD rats, evidenced by markedly reduced proteinuria and renal tubular apoptosis. In the in vitro experiments, PGE1 (0.1–100 µM) significantly enhanced HG-reduced HK-2 cell viability. In HG-treated HK-2 cells, PGE1 (10 µM) significantly suppressed the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and the mitochondrial apoptosis-related protein expressions such as Bim, Bax, caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-3; similar changes were also observed in the kidney of PGE1-treated DKD rats. By using two pharmacological tools-JNK activator anisomycin (AM) and JNK inhibitor SP600125, we revealed that PGE1 blocked HG-triggered activation of JNK/Bim pathway in HK-2 cells; JNK was an upstream regulator of Bim. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that the nephroprotective effects of PGE1 against apoptosis of proximal renal tubule in DKD rats via suppressing JNK-related Bim signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Conserva F, Gesualdo L, Papale M. A systems biology overview on human diabetic nephropathy: from genetic susceptibility to post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:7934504.
Gnudi L. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of diabetic glomerulopathy. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2012;27:2642–9.
Diez-Sampedro A, Lenz O, Fornoni A. Podocytopathy in diabetes: a metabolic and endocrine disorder. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58:637–46.
Suh JH, Miner JH. The glomerular basement membrane as a barrier to albumin. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:470–7.
Zhang XQ, Dong JJ, Cai T, Shen X, Zhou XJ, Liao L. High glucose induces apoptosis via upregulation of Bim expression in proximal tubule epithelial cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:24119–29.
Hasegawa K, Wakino S, Simic P, Sakamaki Y, Minakuchi H, Fujimura K, et al. Renal tubular Sirt1 attenuates diabetic albuminuria by epigenetically suppressing Claudin-1 overexpression in podocytes. Nat Med. 2013;19:1496–504.
Xiao L, Zhu X, Yang S, Liu F, Zhou Z, Zhan M, et al. Rap1 ameliorates renal tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2014;63:1366–80.
Magri CJ, Fava S. The role of tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:551–5.
Kumar D, Robertson S, Burns KD. Evidence of apoptosis in human diabetic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;259:67–70.
Lo CS, Shi Y, Chenier I, Ghosh A, Wu CH, Cailhier JF, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F stimulates Sirtuin-1 gene expression and attenuates nephropathy progression in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2017;66:1964–78.
Cai T, Wu XY, Zhang XQ, Shang HX, Zhang ZW, Liao L, et al. Calcium dobesilate prevents diabetic kidney disease by decreasing bim and inhibiting apoptosis of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36:249–55.
Gilbert RE. Proximal tubulopathy: prime mover and key therapeutic target in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes. 2017;66:791–800.
Akiyama T, Tanaka S. Bim: guardian of tissue homeostasis and critical regulator of the immune system, tumorigenesis and bone biology. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 2011;59:277–87.
Tennant BR, Vanderkruk B, Dhillon J, Dai D, Verchere CB, Hoffman BG. Myt3 suppression sensitizes islet cells to high glucose-induced cell death via Bim induction. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2233.
Shin ES, Huang Q, Gurel Z, Palenski TL, Zaitoun I, Sorenson CM, et al. STAT1-mediated Bim expression promotes the apoptosis of retinal pericytes under high glucose conditions. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e986.
Sionov RV, Vlahopoulos SA, Granot Z. Regulation of Bim in health and disease. Oncotarget. 2015;6:23058–134.
Han H, Cao A, Wang L, Guo H, Zang Y, Li Z, et al. Huangqi decoction ameliorates streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic nephropathy through antioxidant and regulation of the TGF-beta/MAPK/PPAR-gamma signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42:1934–44.
Pan Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Cai L, Ren L, Tang L, et al. Targeting JNK by a new curcumin analog to inhibit NF-κB-mediated expression of cell adhesion molecules attenuates renal macrophage infiltration and injury in diabetic mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79084.
Harris CA, Johnson EM Jr. BH3-only Bcl-2 family members are coordinately regulated by the JNK pathway and require Bax to induce apoptosis in neurons. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:37754–60.
Whitfield J, Neame SJ, Paquet L, Bernard O, Ham J. Dominant-negative c-Jun promotes neuronal survival by reducing BIM expression and inhibiting mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Neuron. 2001;29:629–43.
Putcha GV, Moulder KL, Golden JP, Bouillet P, Adams JA, Strasser A, et al. Induction of BIM, a proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family member, is critical for neuronal apoptosis. Neuron. 2001;29:615–28.
Kawamura T, Akira T, Watanabe M, Kagitani Y. Prostaglandin E1 prevents apoptotic cell death in superficial dorsal horn of rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1023–30.
Fang WT, Li HJ, Zhou LS. Protective effects of prostaglandin E1 on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by hydrogen peroxide. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31:485–92.
Ma XQ, Fu RF, Feng GQ, Wang ZJ, Ma SG, Weng SA. Hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocyets and the protective effect of prostaglandin E. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005;32:1124–30.
Mou Y, Zhang Y, Guo C, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Zhou X, et al. Integrated treatment of prostaglandin E1 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in diabetic kidney disease rats: possible role of antiapoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37:133–41.
Zhao T, Zhang H, Zhao T, Zhang X, Lu J, Yin T, et al. Intrarenal metabolomics reveals the association of local organic toxins with the progression of diabetic kidney disease. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;60:32–43.
Pari L, Sankaranarayanan C. Beneficial effects of thymoquinone on hepatic key enzymes in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2009;85:830–4.
Sutariya B, Saraf MB. isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-beta pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;198:432–43.
Ling L, Zhang S, Ji Z, Huang H, Yao G, Wang M, et al. Therapeutic effects of lipo-prostaglandin E1 on angiogenesis and neurogenesis after ischemic stroke in rats. Int J Neurosci. 2016;126:469–77.
Huang L, Haylor JL, Hau Z, Jones RA, Vickers ME, Wagner B, et al. Transglutaminase inhibition ameliorates experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009;76:383–94.
Meng XM, Huang XR, Xiao J, Chen HY, Zhong X, Chung AC, et al. Diverse roles of TGF-beta receptor II in renal fibrosis and inflammation in vivo and in vitro. J Pathol. 2012;227:175–88.
Fujii N, Matsuo Y, Matsunaga T, Endo S, Sakai H, Yamaguchi M, et al. Hypotonic stress-induced down-regulation of Claudin-1 and -2 mediated by dephosphorylation and clathrin-dependent endocytosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:24787–99.
Hirai Y, Iyoda M, Shibata T, Kuno Y, Kawaguchi M, Hizawa N, et al. IL-17A stimulates granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production via ERK1/2 but not p38 or JNK in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302:F244–50.
Huang XR, Chung AC, Zhou L, Wang XJ, Lan HY. Latent TGF-beta1 protects against crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:233–42.
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–81.
Subramanian S, Hirsch IB. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Is there a role for glycemic variability? Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18:13.
Abuissa H, O’Keefe J Jr. The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system-based therapy in diabetes prevention and cardiovascular and renal protection. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:1157–66.
Yuan XP, Liu LS, Chen CB, Zhou J, Zheng YT, Wang XP, et al. MicroRNA-423-5p facilitates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by targeting GSTM1 via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncotarget. 2017;8:82064–77.
Yuan J, Shen Y, Yang X, Xie Y, Lin X, Zeng W, et al. Thymosin beta4 alleviates renal fibrosis and tubular cell apoptosis through TGF-beta pathway inhibition in UUO rat models. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18:314.
Li H, Zhu X, Zhang J, Shi J. MicroRNA-25 inhibits high glucose-induced apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via PTEN/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:471–9.
Wu JD, Tao S, Jin X, Jiang LL, Shen Y, Luo Y, et al. PGE1 improves diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016;126:24–8.
Kato M, Yuan H, Xu ZG, Lanting L, Li SL, Wang M, et al. Role of the Akt/FoxO3a pathway in TGF-beta1-mediated mesangial cell dysfunction: a novel mechanism related to diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:3325–35.
Chuang PY, Yu Q, Fang W, Uribarri J, He JC. Advanced glycation endproducts induce podocyte apoptosis by activation of the FOXO4 transcription factor. Kidney Int. 2007;72:965–76.
Xiao HT, Wen B, Ning ZW, Zhai LX, Liao CH, Lin CY, et al. Cyclocarya paliurus tea leaves enhances pancreatic beta cell preservation through inhibition of apoptosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:9155.
O’Reilly LA, Cullen L, Visvader J, Lindeman GJ, Print C, Bath ML, et al. The proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim is expressed in hematopoietic, epithelial, neuronal, and germ cells. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:449–61.
Major CD, Wolf BA. Interleukin-1 beta stimulation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activity in insulin-secreting cells: evidence for cytoplasmic restriction. Diabetes. 2001;50:2721–8.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670757, 81570742); the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2016HQ26); and the Grant for the Development of Science and Technology of Ji-nan City (201602172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL and JJD conceived and designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript; YHZ, YQZ, CCG, LKW, and YJC performed the experiments and analyzed the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yh., Zhang, Yq., Guo, Cc. et al. Prostaglandin E1 attenuates high glucose-induced apoptosis in proximal renal tubular cells by inhibiting the JNK/Bim pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 561–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0314-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0314-9
This article is cited by
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of the NFAT pathway in kidney diseases
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2025)
-
Combination drug therapy prevents CIAKI by suppressing ER stress-induced apoptosis
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Cellular crosstalk of mesangial cells and tubular epithelial cells in diabetic kidney disease
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Klotho protects against diabetic kidney disease via AMPK- and ERK-mediated autophagy
Acta Diabetologica (2021)
-
PM2.5 exposure induced renal injury via the activation of the autophagic pathway in the rat and HK-2 cell
Environmental Sciences Europe (2020)