Abstract
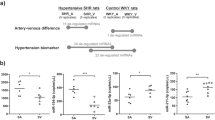
Proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) greatly contributes to vascular remodeling in hypertension. This study is to determine the roles and mechanisms of miR-135a-5p intervention in attenuating VSMC proliferation and vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). MiR-135a-5p level was raised, while fibronectin type III domain-containing 5 (FNDC5) mRNA and protein expressions were reduced in VSMCs of SHRs compared with those of Wistar–Kyoto rats (WKYs). Enhanced VSMC proliferation in SHRs was inhibited by miR-135a-5p knockdown or miR-135a-5p inhibitor, but exacerbated by miR-135a-5p mimic. VSMCs of SHRs showed reduced myofilaments, increased or even damaged mitochondria, increased and dilated endoplasmic reticulum, which were attenuated by miR-135a-5p inhibitor. Dual-luciferase reporter assay shows that FNDC5 was a target gene of miR-135a-5p. Knockdown or inhibition of miR-135a-5p prevented the FNDC5 downregulation in VSMCs of SHRs, while miR-135a-5p mimic inhibited FNDC5 expressions in VSMCs of both WKYs and SHRs. FNDC5 knockdown had no significant effects on VSMC proliferation of WKYs, but aggravated VSMC proliferation of SHRs. Exogenous FNDC5 or FNDC5 overexpression attenuated VSMC proliferation of SHRs, and prevented miR-135a-5p mimic-induced enhancement of VSMC proliferation of SHR. MiR-135a-5p knockdown in SHRs attenuated hypertension, normalized FNDC5 expressions and inhibited vascular smooth muscle proliferation, and alleviated vascular remodeling. These results indicate that miR-135a-5p promotes while FNDC5 inhibits VSMC proliferation in SHRs. Silencing of miR-135a-5p attenuates VSMC proliferation and vascular remodeling in SHRs via disinhibition of FNDC5 transcription. Either inhibition of miR-135a-5p or upregulation of FNDC5 may be a therapeutically strategy in attenuating vascular remodeling and hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Rizzoni D, Agabiti RE. Small artery remodeling in hypertension and diabetes. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2006;8:90–5.
Wang D, Uhrin P, Mocan A, Waltenberger B, Breuss JM, Tewari D, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation as a therapeutic target. Part 1: molecular targets and pathways. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36:1586–607.
Schiffrin EL. Vascular remodeling in hypertension: mechanisms and treatment. Hypertension. 2012;59:367–74.
Brown IAM, Diederich L, Good ME, DeLalio LJ, Murphy SA, Cortese-Krott MM, et al. Vascular smooth muscle remodeling in conductive and resistance arteries in hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38:1969–85.
Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y, et al. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76:441–51.
Dong Y, Liu C, Zhao Y, Ponnusamy M, Li P, Wang K. Role of noncoding RNAs in regulation of cardiac cell death and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75:291–300.
Zhou SS, Jin JP, Wang JQ, Zhang ZG, Freedman JH, Zheng Y, et al. miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:1073–84.
Song XW, Zou LL, Cui L, Li SH, Qin YW, Zhao XX, et al. Plasma miR-451 with echocardiography serves as a diagnostic reference for pulmonary hypertension. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:1208–16.
Ren XS, Tong Y, Qiu Y, Ye C, Wu N, Xiong XQ, et al. MiR155-5p in adventitial fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9:1698795.
Tong Y, Ye C, Ren XS, Qiu Y, Zang YH, Xiong XQ, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) from adventitial fibroblasts of spontaneously hypertensive rats promotes vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Hypertension. 2018;72:881–8.
Zhang Y, Jiang WL, Yang JY, Huang J, Kang G, Hu HB, et al. Downregulation of lysyl oxidase-like 4 LOXL4 by miR-135a-5p promotes lung cancer progression in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:18679–87.
Gao S, Yang D, Huang W, Wang T, Li W. miR-135a-5p affects adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by promoting the Hippo signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11:1347–55.
Guo LM, Ding GF, Xu W, Ge H, Jiang Y, Chen XJ, et al. MiR-135a-5p represses proliferation of HNSCC by targeting HOXA10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19:973–83.
Zhao X, Sun Z, Li H, Jiang F, Zhou J, Zhang L. MiR-135a-5p modulates biological functions of thyroid carcinoma cells via targeting VCAN 3’-UTR. Cancer Biomark. 2017;20:207–16.
Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481:463–8.
Xiong XQ, Chen D, Sun HJ, Ding L, Wang JJ, Chen Q, et al. FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorates glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhances lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852:1867–75.
Liu TY, Shi CX, Gao R, Sun HJ, Xiong XQ, Ding L, et al. Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129:839–50.
Liu TY, Xiong XQ, Ren XS, Zhao MX, Shi CX, Wang JJ, et al. FNDC5 alleviates hepatosteatosis by restoring AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy, fatty acid oxidation, and lipogenesis in mice. Diabetes. 2016;65:3262–75.
Xiong XQ, Geng Z, Zhou B, Zhang F, Han Y, Zhou YB, et al. FNDC5 attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization in obesity. Metabolism. 2018;83:31–41.
Ling L, Chen D, Tong Y, Zang YH, Ren XS, Zhou H, et al. Fibronectin type III domain containing 5 attenuates inflammasome activation and phenotypic transformation of adventitial fibroblasts in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1104–14.
Liao Q, Qu S, Tang LX, Li LP, He DF, Zeng CY, et al. Irisin exerts a therapeutic effect against myocardial infarction via promoting angiogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40:1314–21.
Sun HJ, Zhao MX, Ren XS, Liu TY, Chen Q, Li YH, et al. Salusin-beta promotes vascular smooth muscle cell migration and intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury via ROS/NFkappaB/MMP-9 pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016;24:1045–57.
Sun HJ, Ren XS, Xiong XQ, Chen YZ, Zhao MX, Wang JJ, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to VSMC phenotypic transformation and proliferation in hypertension. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e3074.
Chen D, Zang YH, Qiu Y, Zhang F, Chen AD, Wang JJ, et al. BCL6 attenuates proliferation and oxidative stress of vascular smooth muscle cells in hypertension. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5018410.
Fan ZD, Zhang L, Shi Z, Gan XB, Gao XY, Zhu GQ. Artificial microRNA interference targeting AT1a receptors in paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension in rats. Gene Ther. 2012;19:810–7.
Zhang LL, Ding L, Zhang F, Gao R, Chen Q, Li YH, et al. Salusin-beta in rostral ventrolateral medulla increases sympathetic outflow and blood pressure via superoxide anions in hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2014;32:1059–67.
Zhang Y, Qian X, Sun X, Lin C, Jing Y, Yao Y, et al. Liuwei Dihuang, a traditional Chinese medicinal formula, inhibits proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via modulation of estrogen receptors. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42:31–40.
Hedin U, Thyberg J. Plasma fibronectin promotes modulation of arterial smooth-muscle cells from contractile to synthetic phenotype. Differentiation. 1987;33:239–46.
Sotomayor-Flores C, Rivera-Mejias P, Vasquez-Trincado C, Lopez-Crisosto C, Morales PE, Pennanen C, et al. Angiotensin-(1-9) prevents cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by controlling mitochondrial dynamics via miR-129-3p/PKIA pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:2586–604.
Pennanen C, Parra V, Lopez-Crisosto C, Morales PE, Del CA, Gutierrez T, et al. Mitochondrial fission is required for cardiomyocyte hypertrophy mediated by a Ca2+-calcineurin signaling pathway. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:2659–71.
Zhang KL, Shen QQ, Fang YF, Sun YM, Ding J, Chen Y. AZD9291 inactivates the PRC2 complex to mediate tumor growth inhibition. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40:1587–95.
Wang D, Ren J, Ren H, Fu JL, Yu D. MicroRNA-132 suppresses cell proliferation in human breast cancer by directly targeting FOXA1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:124–31.
Briet M, Schiffrin EL. Treatment of arterial remodeling in essential hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2013;15:3–9.
Cao RY, Zheng H, Redfearn D, Yang J. FNDC5: a novel player in metabolism and metabolic syndrome. Biochimie. 2019;158:111–6.
Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, Efstathiadou ZA, Makras P, Perakakis N, Kountouras J, et al. Irisin in metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018;59:260–74.
Panati K, Suneetha Y, Narala VR. Irisin/FNDC5—an updated review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20:689–97.
Zhang X, Hu C, Kong CY, Song P, Wu HM, Xu SC, et al. FNDC5 alleviates oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via activating AKT. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:540–55.
Zang YH, Chen D, Zhou B, Chen AD, Wang JJ, Gao XY, et al. FNDC5 inhibits foam cell formation and monocyte adhesion in vascular smooth muscle cells via suppressing NFκB-mediated NLRP3 upregulation. Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;121:106579.
Zhou B, Qiu Y, Wu N, Chen AD, Zhou H, Chen Q, et al. FNDC5 attenuates oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in vascular smooth muscle cells via activating the AMPK-SIRT1 signal pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6384803.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [32071106, 91639105, 31871148, and 81770426].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CY, YT, QC, YHL, YMK, and GQZ designed experiments. CY, YT, NW, GWW, FZ, JZL, HZ, and ADC conducted the experiments. CY, YT, NW, GWW, JYC, JJW, and GQZ performed data and statistical analyses. CY, YT, and GQZ wrote the manuscript, with contributions from all the other authors. GQZ supervised the study. All authors approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, C., Tong, Y., Wu, N. et al. Inhibition of miR-135a-5p attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular remodeling in hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42, 1798–1807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00608-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00608-x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Galangin 3-methyl ether alleviates mouse hypertrophic cardiomyopathy via targeting HDAC2 and subsequently inactivating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2025)
-
MiR-196a-5p hinders vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular remodeling via repressing BACH1 expression
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
MiR-135a-5p regulates window of implantation by suppressing pinopodes development and decidualization of endometrial stromal cells
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2024)
-
Extracellular vesicles in vascular remodeling
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)
-
Chronic infusion of ELABELA alleviates vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats via anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-proliferative effects
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)