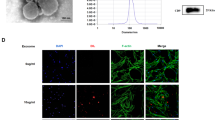
Abstract
Intestinal fibrosis is a common complication of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and is defined as an excessive accumulation of scar tissue in the intestinal wall. Intestinal fibrosis occurs in both forms of IBD: ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting hypoxia-inducing factor (HIF) prolyl-hydroxylases are promising for the development of novel antifibrotic therapies in IBD. Herein, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of hydroxamate of betulinic acid (BHA), a hypoxia mimetic derivative of betulinic acid, against IBD in vitro and in vivo. We showed that BAH (5–20 μM) dose-dependently enhanced collagen gel contraction and activated the HIF pathway in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts; BAH treatment also prevented the loss of trans-epithelial electrical resistance induced by proinflammatory cytokines in Caco-2 cells. In two different murine models (TNBS- and DSS-induced IBD) that cause colon fibrosis, oral administration of BAH (20, 50 mg/kg·d, for 17 days) prevented colon inflammation and fibrosis, as detected using immunohistochemistry and qPCR assays. BAH-treated animals showed a significant reduction of fibrotic markers (Tnc, Col1a2, Col3a1, Timp-1, α-SMA) and inflammatory markers (F4/80+, CD3+, Il-1β, Ccl3) in colon tissue, as well as an improvement in epithelial barrier integrity and wound healing. BHA displayed promising oral bioavailability, no significant activity against a panel of 68 potential pharmacological targets and was devoid of genotoxicity and cardiotoxicity. Taken together, our results provide evidence that oral administration of BAH can alleviate colon inflammation and colitis-associated fibrosis, identifying the enhancement of colon barrier integrity as a possible mechanism of action, and providing a solid rationale for additional clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Liverani E, Scaioli E, Digby RJ, Bellanova M, Belluzzi A. How to predict clinical relapse in inflammatory bowel disease patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:1017–33.
Rieder F, Fiocchi C, Rogler G. Mechanisms, management, and treatment of fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:340–50 e346.
Koutroubakis IE, Ramos-Rivers C, Regueiro M, Koutroumpakis E, Click B, Schoen RE, et al. Persistent or recurrent anemia is associated with severe and disabling inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1760–6.
Lawrance IC, Maxwell L, Doe W. Inflammation location, but not type, determines the increase in TGF-beta1 and IGF-1 expression and collagen deposition in IBD intestine. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2001;7:16–26.
Silverstein MD, Loftus EV, Sandborn WJ, Tremaine WJ, Feagan BG, Nietert PJ, et al. Clinical course and costs of care for Crohn’s disease: Markov model analysis of a population-based cohort. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:49–57.
Rieder F, Fiocchi C. Intestinal fibrosis in IBD-a dynamic, multifactorial process. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:228–35.
Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:417–29.
Annese V, Duricova D, Gower-Rousseau C, Jess T, Langholz E. Impact of new treatments on hospitalisation, surgery, infection, and mortality in IBD: a Focus Paper by the Epidemiology Committee of ECCO. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10:216–25.
Billiet T, Rutgeerts P, Ferrante M, Van Assche G, Vermeire S. Targeting TNF-alpha for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14:75–101.
Kalra J, Lingaraju MC, Mathesh K, Kumar D, Parida S, Singh TU, et al. Betulinic acid alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and visceral pain in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018;391:285–97.
Bildziukevich U, Ozdemir Z, Wimmer Z. Recent achievements in medicinal and supramolecular chemistry of betulinic acid and its derivatives (double dagger). Molecules. 2019;24:3546.
Saneja A, Arora D, Kumar R, Dubey RD, Panda AK, Gupta PN. Therapeutic applications of betulinic acid nanoformulations. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2018;1421:5–18.
Rios JL, Manez S. New pharmacological opportunities for betulinic acid. Planta Med. 2018;84:8–19.
Minassi A, Rogati F, Cruz C, Prados ME, Galera N, Jinenez C, et al. Triterpenoid hydroxamates as HIF prolyl hydrolase inhibitors. J Nat Prod. 2018;81:2235–43.
Taylor CT, Colgan SP. Hypoxia and gastrointestinal disease. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007;85:1295–1300.
Cummins EP, Crean D. Hypoxia and inflammatory bowel disease. Microbes Infect. 2017;19:210–21.
Furuta GT, Turner JR, Taylor CT, Hershberg RM, Comerford K, Narravula S, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent induction of intestinal trefoil factor protects barrier function during hypoxia. J Exp Med. 2001;193:1027–34.
Louis NA, Hamilton KE, Canny G, Shekels LL, Ho SB, Colgan SP. Selective induction of mucin-3 by hypoxia in intestinal epithelia. J Cell Biochem. 2006;99:1616–27.
Kelly CJ, Glover LE, Campbell EL, Kominsky DJ, Ehrentraut SF, Bowers BE, et al. Fundamental role for HIF-1alpha in constitutive expression of human beta defensin-1. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6:1110–8.
Saeedi BJ, Kao DJ, Kitzenberg DA, Dobrinskikh E, Schwisow KD, Masterson JC, et al. HIF-dependent regulation of claudin-1 is central to intestinal epithelial tight junction integrity. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:2252–62.
Taylor CT, Doherty G, Fallon PG, Cummins EP. Hypoxia-dependent regulation of inflammatory pathways in immune cells. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3716–24.
Cummins EP, Seeballuck F, Keely SJ, Mangan NE, Callanan JJ, Fallon PG, et al. The hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine is protective in a murine model of colitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:156–65.
Robinson A, Keely S, Karhausen J, Gerich ME, Furuta GT, Colgan SP. Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:145–55.
Marks E, Goggins BJ, Cardona J, Cole S, Minahan K, Mateer S, et al. Oral delivery of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor: AKB-4924 promotes localized mucosal healing in a mouse model of colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:267–75.
Gupta R, Chaudhary AR, Shah BN, Jadhav AV, Zambad SP, Gupta RC, et al. Therapeutic treatment with a novel hypoxia-inducible factor hydroxylase inhibitor (TRC160334) ameliorates murine colitis. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014;7:13–23.
Jeong S, Park H, Hong S, Yum S, Kim W, Jung Y. Lipophilic modification enhances anti-colitic properties of rosmarinic acid by potentiating its HIF-prolyl hydroxylases inhibitory activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;747:114–22.
Manresa MC, Tambuwala MM, Radhakrishnan P, Harnoss JM, Brown E, Cavadas MA, et al. Hydroxylase inhibition regulates inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis through the suppression of ERK-mediated TGF-beta1 signaling. [corrected]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;311:G1076–90.
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K, Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc. 2017;12:1295–309.
Tambuwala MM, Manresa MC, Cummins EP, Aversa V, Coulter IS, Taylor CT. Targeted delivery of the hydroxylase inhibitor DMOG provides enhanced efficacy with reduced systemic exposure in a murine model of colitis. J Control Release. 2015;217:221–7.
Taniguchi CM, Miao YR, Diep AN, Wu C, Rankin EB, Atwood TF, et al. PHD inhibition mitigates and protects against radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity via HIF2. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:236ra264.
Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaelsson E. Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;288:G1328–38.
Viennois E, Tahsin A, Merlin D. Purification of total RNA from DSS-treated murine tissue via lithium chloride precipitation. Bio Protoc. 2018;8:e2829.
Safari A, Parsaei H, Zamani A, Pourabbas B. Semi-automatic algorithm for estimating Cobb Angle. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019;9:317–26.
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, Parkos CA, Madara JL, Hopkins AM, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol. 2003;171:6164–72.
Capaldo CT, Nusrat A. Cytokine regulation of tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788:864–71.
Al-Sadi R, Boivin M, Ma T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front Biosci. 2009;14:2765–78.
Farmer RG. Lower gastrointestinal bleeding in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991;26:93–100.
Glover LE, Colgan SP. Epithelial barrier regulation by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14:S233–6.
Oh SY, Cho KA, Kang JL, Kim KH, Woo SY. Comparison of experimental mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33:333–40.
Semenza GL, Wang GL. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:5447–54.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:5510–4.
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–72.
Ortiz-Barahona A, Villar D, Pescador N, Amigo J, del Peso L. Genome-wide identification of hypoxia-inducible factor binding sites and target genes by a probabilistic model integrating transcription-profiling data and in silico binding site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:2332–45.
Tambuwala MM, Cummins EP, Lenihan CR, Kiss J, Stauch M, Scholz CC, et al. Loss of prolyl hydroxylase-1 protects against colitis through reduced epithelial cell apoptosis and increased barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:2093–101.
Walmsley SR, Chilvers ER, Thompson AA, Vaughan K, Marriott HM, Parker LC, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) is essential for hypoxic regulation of neutrophilic inflammation in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:1053–63.
Di Conza G, Trusso Cafarello S, Loroch S, Mennerich D, Deschoemaeker S, Di Matteo M, et al. The mTOR and PP2A pathways regulate PHD2 phosphorylation to fine-tune HIF1alpha levels and colorectal cancer cell survival under hypoxia. Cell Rep. 2017;18:1699–712.
Fichtner-Feigl S, Fuss IJ, Young CA, Watanabe T, Geissler EK, Schlitt HJ, et al. Induction of IL-13 triggers TGF-beta1-dependent tissue fibrosis in chronic 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis. J Immunol. 2007;178:5859–70.
Cummins EP, Keogh CE, Crean D, Taylor CT. The role of HIF in immunity and inflammation. Mol Asp Med. 2016;47–48:24–34.
Harris AJ, Thompson AR, Whyte MK, Walmsley SR. HIF-mediated innate immune responses: cell signaling and therapeutic implications. Hypoxia (Auckl). 2014;2:47–58.
Lin N, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors: key regulators of myeloid cells during inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3661–71.
Wobben R, Husecken Y, Lodewick C, Gibbert K, Fandrey J, Winning S. Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha for interferon synthesis in mouse dendritic cells. Biol Chem. 2013;394:495–505.
Tyrakis PA, Palazon A, Macias D, Lee KL, Phan AT, Velica P, et al. S-2-hydroxyglutarate regulates CD8+ T-lymphocyte fate. Nature. 2016;540:236–41.
Cho SH, Raybuck AL, Stengel K, Wei M, Beck TC, Volanakis E, et al. Germinal centre hypoxia and regulation of antibody qualities by a hypoxia response system. Nature. 2016;537:234–8.
Giuffrida P, Caprioli F, Facciotti F, Di Sabatino A. The role of interleukin-13 in chronic inflammatory intestinal disorders. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18:549–55.
Fichtner-Feigl S, Kesselring R, Martin M, Obermeier F, Ruemmele P, Kitani A, et al. IL-13 orchestrates resolution of chronic intestinal inflammation via phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Immunol. 2014;192:3969–80.
Rieder F. Managing intestinal fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N. Y). 2018;14:120–2.
Sun Z, Schwenzer A, Rupp T, Murdamoothoo D, Vegliante R, Lefebvre O, et al. Tenascin-C promotes tumor cell migration and metastasis through Integrin alpha9beta1-mediated YAP inhibition. Cancer Res. 2018;78:950–61.
Lowy CM, Oskarsson T. Tenascin C in metastasis: a view from the invasive front. Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9:112–24.
Stidham RW, Higgins PDR. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018;31:168–78.
Keller DS, Windsor A, Cohen R, Chand M. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: review of the evidence. Tech Coloproctol. 2019;23:3–13.
Yang Z, Zhang C, Qi W, Cui C, Cui Y, Xuan Y. Tenascin-C as a prognostic determinant of colorectal cancer through induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and proliferation. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018;105:216–22.
Zhou M, Li M, Liang X, Zhang Y, Huang H, Feng Y, et al. The Significance of serum S100A9 and TNC levels as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. J Cancer. 2019;10:5315–23.
Wiemann J, Heller L, Perl V, Kluge R, Strohl D, Csuk R. Betulinic acid derived hydroxamates and betulin derived carbamates are interesting scaffolds for the synthesis of novel cytotoxic compounds. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;106:194–210.
Wiemann J, Heller L, Csuk R. Targeting cancer cells with oleanolic and ursolic acid derived hydroxamates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26:907–9.
White JR, Phillips F, Monaghan T, Fateen W, Samuel S, Ghosh S, et al. Review article: novel oral-targeted therapies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47:1610–22.
Fukase H, Kajioka T, Oikawa I, Ikeda N, Furuie H. AJM300, a novel oral antagonist of alpha4-integrin, sustains an increase in circulating lymphocytes: a randomised controlled trial in healthy male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86:591–600.
Fukata N, Uchida K, Kusuda T, Koyabu M, Miyoshi H, Fukui T, et al. The effective therapy of cyclosporine A with drug delivery system in experimental colitis. J Drug Target. 2011;19:458–67.
Acknowledgements
We thank Carmen-Cabrero for revising the manuscript. This work was supported by grants RTC-2017–6109–1 (EM) from the Ministry of the Economy and Competition (MINECO) and was co-financed with European Union FEDER funds. This work was also partially supported by Emerald Health Biotechnology España (Cordoba, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MEP, AGM, and JDUB performed in vivo experiments. MEP, BP, and JAC performed in vitro experiments; AM and GA synthesized BAH; and EM and MAC managed and designed the overall study. MEP and EM wrote the manuscript. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
MEP, AGM, and JDUB are employees of Emerald Health Biotechnology. EM is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of Emerald Health Biotechnology. None of the authors have conflicts of interest. GA, AM, and EM have submitted a PCT with the publication number WO2018/069086A.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments with laboratory animals were conducted according to European guidelines (directive 2010/63/EU), and the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation at the University of Cordoba (Cordoba, Spain) that approved all the procedures described in this study (protocol number: 13–03–15–207).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prados, M.E., García-Martín, A., Unciti-Broceta, J.D. et al. Betulinic acid hydroxamate prevents colonic inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42, 1124–1138 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-0497-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-0497-0
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neuroprotective Efficacy of Betulinic Acid Hydroxamate, a B55α/PP2A Activator, in Acute Hypoxia–Ischemia-Induced Brain Damage in Newborn Rats
Translational Stroke Research (2023)
-
Oral administration of turmeric-derived exosome-like nanovesicles with anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving bioactions for murine colitis therapy
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2022)
-
All-in-one theranostic nano-platform based on polymer nanoparticles for BRET/FRET-initiated bioluminescence imaging and synergistically anti-inflammatory therapy for ulcerative colitis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2022)
-
Revisiting fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease: the gut thickens
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2022)
-
Betulinic Acid Hydroxamate is Neuroprotective and Induces Protein Phosphatase 2A-Dependent HIF-1α Stabilization and Post-transcriptional Dephosphorylation of Prolyl Hydrolase 2
Neurotherapeutics (2021)