Abstract
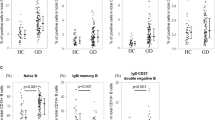
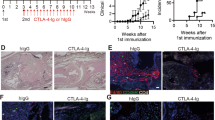
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterized by synovitis and the destruction of small joints. Emerging evidence shows that immunoglobulin D (IgD) stimulation induces T-cell activation, which may contribute to diseases pathogenesis in RA. In this study, we investigated the downstream signaling pathways by which IgD activated T cells as well as the possible role of IgD in the T–B interaction. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy controls and RA patients. We demonstrated that IgD activated T cells through IgD receptor (IgDR)-lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (Lck)-zeta-associated protein 70 (ZAP70)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathways; IgD-induced CD4+ T cells promoted the proliferation of CD19+ B cells in RA patients. A novel fusion protein IgD-Fc-Ig (composed of human IgD-Fc domain and IgG1 Fc domain, which specifically blocked the IgD–IgDR binding) inhibited the coexpression of IgDR and phosphorylated Lck (p-Lck) and the expression levels of p-Lck, p-ZAP70, p-PI3K on CD4+ T cells, and decreased NF-κB nuclear translocation in Jurkat cells. Meanwhile, IgD-Fc-Ig downregulated the expression levels of CD40L on CD4+ T cells as well as CD40, CD86 on CD19+ B cells in RA patients and healthy controls. It also decreased the expression levels of CD40L on CD4+ T cells and CD40 on CD19+ B cells from spleens of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice and reduced IL-17A level in mouse serum. Moreover, administration of IgD-Fc-Ig (1.625–13 mg/kg, iv, twice a week for 4 weeks) in CIA mice dose-dependently decreased the protein expression levels of CD40, CD40L, and IgD in spleens. IgD-Fc-Ig restrains T-cell activation through inhibiting IgD-IgDR-Lck-ZAP70-PI3K-NF-κB signaling, thus inhibiting B-cell activation. Our data provide experimental evidences for application of IgD-Fc-Ig as a highly selective T cell-targeting treatment for RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Sparks JA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:ITC1–16.
Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:685–99.
Bécède M, Alasti F, Gessl I, Haupt L, Kerschbaumer A, Landesmann U, et al. Risk profiling for a refractory course of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;49:211–7.
Preud’homme JL, Petit I, Barra A, Morel F, Lecron JC, Lelièvre E. Structural and functional properties of membrane and secreted IgD. Mol Immunol. 2000;37:871–87.
Chen K, Cerutti A. New insights into the enigma of immunoglobulin D. Immunol Rev. 2010;237:160–79.
Wu Y, Pan W, Hu X, Zhang A, Wei W. The prospects for targeting FcR as a novel therapeutic strategy in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;183:114360.
Chen L, Fan F, Deng J, Xu J, Xu A, Sun C, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of immunoglobulin D myeloma in the novel agent era. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:963–70.
Carballo I, Rabuñal N, Alvela L, Pérez LF, Vidal C, Alonso M, et al. Factors influencing serum concentrations of IgD in the adult population: an observational study in Spain. Scand J Immunol. 2017;85:272–9.
Zhang J, Hu X, Dong X, Chen W, Wu Y, Wei W, et al. Regulation of T cell activities in rheumatoid arthritis by the novel fusion protein IgD-Fc-Ig. Front Immunol. 2020;11:755.
Wu Y, Chen W, Chen H, Zhang L, Huang Q, Wei W, et al. The elevated secreted immunoglobulin D enhanced the activation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e147788.
Chen H, Wu Y, Huang Q, Chen W, Dong J, Wei W. Novel fluorescence based ligand-receptor binding assay: study on IgD receptor. Acta Univ Med Anhui. 2016;51:1105–10.
Amin AR, Tamma SM, Oppenheim JD, Finkelman FD, Kieda C, Coico RF, et al. Specificity of the murine IgD receptor on T cells is for N-linked glycans on IgD molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:9238–42.
Han L, Zhang XZ, Wang C, Tang X, Zhang L, Wei W, et al. IgD-Fc-Ig fusion protein, a new biological agent, inhibits T cell function in CIA rats by inhibiting IgD-IgDR-Lck-NF-κB signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:800–12.
George TC, Fanning SL, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, Medeiros RB, High-fill S, Shimizu Y, et al. Quantitative measurement of nuclear translocation events using similarity analysis of multispectral cellular images obtained in flow. J Immunol Methods. 2006;311:117–29.
Hu X, Wu Y, Zhang J, Wei W. T-cells interact with B cells, dendritic cells, and fibroblast-like synoviocytes as hub-like key cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;70:428–34.
Guillaume G, Renaud L, Paul EL. Regulatory mechanisms in T cell receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:485–97.
Courtney AH, Lo WL, Weiss A. TCR signaling: mechanisms of initiation and propagation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018;43:108–23.
Simeoni L. Lck activation: puzzling the pieces together. Oncotarget. 2017;8:102761–2.
Lo WL, Shah NH, Ahsan N, Horkova V, Stepanek O, Salomon AR, et al. Lck promotes Zap70-dependent LAT phosphorylation by bridging Zap70 to LAT. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:733–41.
Ursula B, Burkhart S, Luca S. Beyond TCR signaling: emerging functions of Lck in cancer and immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3500.
Hu J, Luo T, Xi D, Guo K, Hu L, Zhao J, et al. Silencing ZAP70 prevents HSP65-induced reverse cholesterol transport and NF-κB activation in T cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:271–7.
Mendez-Samperio P, Ayala H, Vazquez A. NF-kappa B is involved in regulation of CD40 ligand expression on Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin-activated human T cells. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003;10:376–82.
Ngaotepprutaram T, Kaplan B, Kaminski NE. Impaired NFAT and NF-κB activation are involved in suppression of CD40 ligand expression by Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in human CD4+ T cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;273:209–18.
Dakal TC, Dhabhai B, Agarwal D, Gupta R, Nagda G, Meena AR, et al. Mechanistic basis of co-stimulatory CD40-CD40L ligation mediated regulation of immune responses in cancer and autoimmune disorders. Immunobiology. 2020;225:151899.
Elmetwali T, Salman A, Wei W, Hussain SA, Young LS, Palmer DH. CD40L membrane retention enhances the immunostimulatory effects of CD40 ligation. Sci Rep. 2020;10:342.
Tung CH, Lu MC, Lai NS, Wu SF. Tumor necrosis factor-α blockade treatment decreased CD154 (CD40-ligand) expression in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0183726.
Jodi LK, Sadiye AR, Rachel E, Roland K. Targeting the CD40-CD40L pathway in autoimmune diseases: Humoral immunity and beyond. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;141:92–103.
Elgueta R, Benson MJ, de Vries VC, Wasiuk A, Guo Y, Noelle RJ. Molecular mechanism and function of CD40⁄CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol Rev. 2009;229:152–72.
Lorenzetti R, Janowska I, Smulski CR, Frede N, Henneberger N, Walter L, et al. Abatacept modulates CD80 and CD86 expression and memory formation in human B-cells. J Autoimmun. 2019;101:145–52.
Abbasi M, Mousavi MJ, Jamalzehi S, Alimohammadi R, Bezvan MH, Mohammadi H, et al. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:10018–31.
Bonelli M, Scheinecker C. How does abatacept really work in rheumatoid arthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30:295–300.
Bonelli M, Göschl L, Blüml S, Karonitsch T, Hirahara K, Ferner E, et al. Abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) treatment reduces T cell apoptosis and regulatory T cell suppression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2016;55:710–20.
Du FH, Mills EA, Mao-Draayer Y. Next-generation anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in autoimmune disease treatment. Auto Immun Highlights. 2017;8:12.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81603121; 81673444; 81973332) and the Key Projects of Natural Science Research of Anhui Colleges and Universities (No. KJ2020A0158). The authors acknowledge Professors Li Si and Doctor Fang Wang in the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, for their help in healthy and RA donors recruiting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XXH performed the experiments and wrote the paper. AJZ and WWP participated in the experiments, collected the samples and performed immunohistochemistry experiments. QLX and JYC took part in FACS Aria cell sorting. LLZ and YC helped to revise the paper. YJW designed the study, participated in the experiments, and revised the paper. WW conceived of the study and revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Xx., Zhang, Aj., Pan, Ww. et al. An IgD-Fc-Ig fusion protein restrains the activation of T and B cells by inhibiting IgD-IgDR-Lck signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 387–400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00665-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00665-w
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of essential genes and immune cell infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatics analysis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
PSTPIP2 regulates synovial macrophages polarization and dynamics via ERβ in the joint microenvironment
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2022)