Abstract
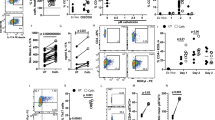
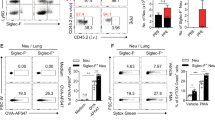
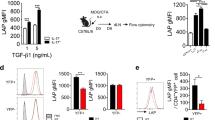
Bergenin is a natural PPARγ agonist that can prevent neutrophil aggregation, and often be used in clinics for treating respiratory diseases. Recent data show that Th17 cells are important for neutrophil aggregation and asthma through secreting IL-17A. In this study, we investigated the effects of bergenin on Th17 differentiation in vitro and subsequent neutrophilic asthma in mice. Naïve T cells isolated from mouse mesenteric lymph nodes were treated with IL-23, TGF-β, and IL-6 to induce Th17 differentiation. We showed that in naïve T cells under Th17-polarizing condition, the addition of bergenin (3, 10, 30 μM) concentration-dependently decreased the percentage of CD4+ IL-17A+ T cells and mRNA expression of specific transcription factor RORγt, and function-related factors IL-17A/F, IL-21, and IL-22, but did not affect the cell vitality and apoptosis. Furthermore, bergenin treatment prevented GLS1-dependent glutaminolysis in the progress of Th17 differentiation, slightly affected the levels of SLC1A5, SLC38A1, GLUD1, GOT1, and GPT2. Glutamine deprivation, the addition of glutamate (1 mM), α-ketoglutarate (1 mM), or GLS1 plasmid all significantly attenuated the above-mentioned actions of bergenin. Besides, we demonstrated that bergenin (3, 10, and 30 μM) concentration-dependently activated PPARγ in naïve T cells, whereas PPARγ antagonist GW9662 and siPPARγ abolished bergenin-caused inhibition on glutaminolysis and Th17 differentiation. Furthermore, we revealed that bergenin inhibited glutaminolysis by regulating the level of CDK1, phosphorylation and degradation of Cdh1, and APC/C-Cdh1-mediated ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of GLS1 after activating PPARγ. We demonstrated a correlation existing among bergenin-affected GLS1-dependent glutaminolysis, PPARγ, “CDK1-APC/C-Cdh1” signaling, and Th17 differentiation. Finally, the therapeutic effect and mechanisms for bergenin-inhibited Th17 responses and neutrophilic asthma were confirmed in a mouse model of neutrophilic asthma by administration of GW9662 or GLS1 overexpression plasmid in vivo. In conclusion, bergenin repressed Th17 differentiation and then alleviated neutrophilic asthma in mice by inhibiting GLS1-dependent glutaminolysis via regulating the “CDK1-APC/C-Cdh1” signaling after activating PPARγ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Yang J, Sundrud MS, Skepner J, Yamagata T. Targeting Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35:493–500.
Baek SY, Lee J, Lee DG, Park MK, Lee J, Kwok SK, et al. Ursolic acid ameliorates autoimmune arthritis via suppression of Th17 and B cell differentiation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35:1177–87.
Ouyang S, Liu C, Xiao J, Chen X, Lui AC, Li X. Targeting IL-17A/glucocorticoid synergy to CSF3 expression in neutrophilic airway diseases. JCI Insight. 2020;5:e132836.
Zhou T, Huang X, Zhou Y, Ma J, Zhou M, Liu Y, et al. Associations between Th17-related inflammatory cytokines and asthma in adults: a case-control study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15502.
Camargo LDN, Righetti RF, Aristóteles LRCRB, Dos Santos TM, de Souza FCR, Fukuzaki S, et al. Effects of anti-IL-17 on inflammation, remodeling, and oxidative stress in an experimental model of asthma exacerbated by LPS. Front Immunol. 2018;8:1835.
Xu W, Chen L, Guo S, Wu L, Zhang J. Intranasal administration of recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis inducing IL-17A autoantibody attenuates airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151581.
Kono M, Yoshida N, Maeda K, Tsokos GC. Transcriptional factor ICER promotes glutaminolysis and the generation of Th17 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:2478–83.
Johnson MO, Wolf MM, Madden MZ, Andrejeva G, Sugiura A, Contreras DC, et al. Distinct regulation of Th17 and Th1 cell differentiation by glutaminase-dependent metabolism. Cell. 2018;175:1780–95.
Xu T, Stewart KM, Wang X, Liu K, Xie M, Ryu JK, et al. Metabolic control of Th17 and induced Treg cell balance by an epigenetic mechanism. Nature. 2017;548:228–33.
Wang K, Li YF, Lv Q, Li XM, Dai Y, Wei ZF. Bergenin, acting as an agonist of PPARγ, ameliorates experimental colitis in mice through improving expression of SIRT1, and therefore inhibiting NF-κB-mediated macrophage activation. Front Pharmacol. 2018;8:981.
Yang S, Yu Z, Wang L, Yuan T, Wang X, Zhang X, et al. The natural product bergenin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-kappaB activition. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;200:147–55.
Klotz L, Burgdorf S, Dani I, Saijo K, Flossdorf J, Hucke S, et al. The nuclear receptor PPAR gamma selectively inhibits Th17 differentiation in a T cell-intrinsic fashion and suppresses CNS autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2009;206:2079–89.
Srivastava N, Kollipara RK, Singh DK, Sudderth J, Hu Z, Nguyen H, et al. Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by PPARγ is mediated by a metabolic switch that increases reactive oxygen species levels. Cell Metab. 2014;20:650–61.
Lv Q, Wang K, Qiao S, Yang L, Xin Y, Dai Y, et al. Norisoboldine, a natural AhR agonist, promotes Treg differentiation and attenuates colitis via targeting glycolysis and subsequent NAD+/SIRT1/SUV39H1/H3K9me3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:258.
Abbring S, Verheijden KAT, Diks MAP, Leusink-Muis A, Hols G, Baars T, et al. Raw cow’s milk prevents the development of airway inflammation in a murine house dust mite-induced asthma model. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1045.
Yang Y, Dong P, Zhao J, Zhou W, Zhou Y, Xu Y, et al. PKCλ/ι regulates Th17 differentiation and house dust mite-induced allergic airway inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864:934–41.
Daan de Boer J, Roelofs JJ, de Vos AF, de Beer R, Schouten M, Hommes TJ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide inhibits Th2 lung inflammation induced by house dust mite allergens in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;48:382–9.
Qi Q, Dong Z, Sun Y, Li S, Zhao Z. Protective effect of bergenin against cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression by immunomodulatory effect and antioxidation in Balb/c mice. Molecules. 2018;23:2668.
Xu X, Wang Y, Wei Z, Wei W, Zhao P, Tong B, et al. Madecassic acid, the contributor to the anti-colitis effect of madecassoside, enhances the shift of Th17 toward Treg cells via the PPARγ/AMPK/ACC1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2723.
Celinski K, Dworzanski T, Fornal R, Korolczuk A, Madro A, Slomka M. Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and therapeutic actions of PPAR-gamma agonists rosiglitazone and troglitazone in experimental colitis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;63:631–40.
Qiao X, Zhang L, Gamper AM, Fujita T, Wan Y. APC/C-Cdh1: from cell cycle to cellular differentiation and genomic integrity. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:3904–12.
Crasta K, Lim HH, Giddings TH Jr, Winey M, Surana U. Inactivation of Cdh1 by synergistic action of Cdk1 and polo kinase is necessary for proper assembly of the mitotic spindle. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:665–75.
Lukas C, Sørensen CS, Kramer E, Santoni-Rugiu E, Lindeneg C, Peters JM, et al. Accumulation of cyclin B1 requires E2F and cyclin-A-dependent rearrangement of the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature. 1999;401:815–8.
Yeh SL, Yeh CL, Chan ST, Chuang CH. Plasma rich in quercetin metabolites induces G2/M arrest by upregulating PPAR-γ expression in human A549 lung cancer cells. Planta Med. 2011;77:992–8.
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1133–41.
Han L, Zhang XZ, Wang C, Tang XY, Zhu Y, Cai XY, et al. IgD-Fc-Ig fusion protein, a new biological agent, inhibits T cell function in CIA rats by inhibiting IgD-IgDR-Lck-NF-κB signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:800–12.
Ritchlin CT, Kavanaugh A, Merola JF, Schett G, Scher JU, Warren RB, et al. Bimekizumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results from a 48-week, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2020;395:427–40.
Gabay C, Emery P, van Vollenhoven R, Dikranian A, Alten R, Pavelka K, et al. ADACTA Study Investigators. Tocilizumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (ADACTA): a randomised, double-blind, controlled phase 4 trial. Lancet. 2013;382:1541–50.
Hasan Z, Koizumi SI, Sasaki D, Yamada H, Arakaki N, Fujihara Y, et al. JunB is essential for IL-23-dependent pathogenicity of Th17 cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15628.
Nakaya M, Xiao Y, Zhou X, Chang JH, Chang M, Cheng X, et al. Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation. Immunity. 2014;40:692–705.
Garcia-Vallvé S, Guasch L, Tomas-Hernández S, del Bas JM, Ollendorff V, Arola L, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and ligand choreography: newcomers take the stage. J Med Chem. 2015;58:5381–94.
Yu JH, Long L, Luo ZX, You JR. Effect of PPARγ agonist (rosiglitazone) on the secretion of Th2 cytokine in asthma mice. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017;10:64–68.
Lee EJ, Kwon JE, Park MJ, Jung KA, Kim DS, Kim EK, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates experimental autoimmune arthritis by targeting Th17 and inducing pAMPK and transcriptional corepressor SMILE. Immunol Lett. 2017;188:1–8.
Tian Y, Chen T, Wu Y, Yang L, Wang LJ, Fan XJ, et al. Pioglitazone stabilizes atherosclerotic plaque by regulating the Th17/Treg balance in AMPK-dependent mechanisms. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16:140.
Li W, Zhang Z, Zhang K, Xue Z, Li Y, Zhang Z, et al. Arctigenin suppress Th17 cells and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through AMPK and PPAR-γ/ROR-γt signaling. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:5356–66.
Reynolds MR, Clem BF. Troglitazone suppresses glutamine metabolism through a PPAR-independent mechanism. Biol Chem. 2015;396:937–47.
Fergeson JE, Patel SS, Lockey RF. Acute asthma, prognosis, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:438–47.
Parulekar AD, Kao CC, Diamant Z, Hanania NA. Targeting the interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 pathways in severe asthma: current knowledge and future needs. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018;24:50–55.
Ray A, Kolls JK. Neutrophilic inflammation in asthma and association with disease severity. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:942–54.
Morishima Y, Ano S, Ishii Y, Ohtsuka S, Matsuyama M, Kawaguchi M, et al. Th17-associated cytokines as a therapeutic target for steroid-insensitive asthma. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:609395.
Zhao Y, Huang Y, He J, Li C, Deng W, Ran X, et al. Rosiglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist, attenuates airway inflammation by inhibiting the proliferation of effector T cells in a murine model of neutrophilic asthma. Immunol Lett. 2014;157:9–15.
Meng X, Sun X, Zhang Y, Shi H, Deng W, Liu Y, et al. PPARγ agonist PGZ attenuates OVA-induced airway inflammation and airway remodeling via RGS4 signaling in mouse model. Inflammation. 2018;41:2079–89.
Sun L, Fu J, Lin SH, Sun JL, Xia L, Lin C, et al. Particulate matter of 2.5 μm or less in diameter disturbs the balance of TH17/regulatory T cells by targeting glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in an asthma model. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:402–14.
Zhang J, Fulgar CC, Mar T, Young DE, Zhang Q, Bein KJ, et al. TH17-induced neutrophils enhance the pulmonary allergic response following BALB/c exposure to house dust mite allergen and fine particulate matter from California and China. Toxicol Sci. 2018;164:627–43.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773970) and the 2019 Outstanding Young Backbone Teacher Project of Jiangsu University “Green Blue Project”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZFW and YD designed the study. LY, YZ, YMM, WXY, and YZG performed all the experiments. In addition, LY and YZ prepared the manuscript, which was reviewed and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zheng, Y., Miao, Ym. et al. Bergenin, a PPARγ agonist, inhibits Th17 differentiation and subsequent neutrophilic asthma by preventing GLS1-dependent glutaminolysis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 963–976 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00717-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00717-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Ubiquitin–Proteasome System in Asthma: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Possibilities
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2025)
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus Modulates Lung Inflammation and Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis in a Murine Model of Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2025)
-
A novel method of Francisella infection of epithelial cells using HeLa cells expressing fc gamma receptor
BMC Infectious Diseases (2024)
-
Quantitative investigation of drug-drug interaction between bergenin and vilazodone in rats through UPLC-MS/MS assay
BMC Chemistry (2024)
-
YAP1 inhibits RSL3-induced castration-resistant prostate cancer cell ferroptosis by driving glutamine uptake and metabolism to GSH
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2024)