Abstract
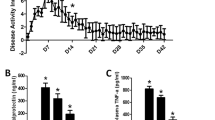
Diosmetin (3',5,7 -trihydroxy-4'-methoxy flavone) is a natural flavonoid compound in the citrus species, it exhibits a variety of pharmacological activities, but little is known of its effects on colitis. In this study we evaluated the therapeutic effects of diosmetin on mouse models of chronic and acute colitis. Chronic colitis was induced in mice by drinking water containing 3% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) from D0 to D8, followed by administration of diosmetin (25, 50 mg · kg−1 · d−1) for another 8 days. Acute colitis was induced by drinking water containing 5% DSS from D0 to D7, the mice concomitantly received diosmetin (25, 50 mg · kg−1 · d−1) from D1 to D7. During the experiments, body weight and disease activity index (DAI) were assessed daily. After the mice were sacrificed, colon tissue and feces samples were collected, and colon length was measured. We showed that in both models, diosmetin administration significantly decreased DAI score and ameliorated microscopic colon tissue damage; increased the expression of tight junction proteins (occludin, claudin-1, and zonula occludens-1), and reduced the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and Cox-2 in colon tissue. We found that diosmetin administration remarkably inhibited colon oxidative damage by adjusting the levels of intracellular and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, GSH-Px, SOD, MDA and GSH in colon tissue. The protection of diosmetin against intestinal epithelial barrier damage and oxidative stress were also observed in LPS-treated Caco-2 and IEC-6 cells in vitro. Furthermore, we demonstrated that diosmetin markedly increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 and reduced the ratio of acetylated NF-κB and NF-κB by activating the circ-Sirt1/Sirt1 axis, which inhibited oxidative stress and inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Diosmetin reversed the effects of si-circSirt1 and si-Sirt1 in LPS-treated Caco-2 and IEC-6 cells. When the gut microbiota was analyzed in the mouse model of colitis, we found that diosmetin administration modulated the abundance of Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria and Firmicutes, which were crucial for inflammatory bowel disease. Our results have linked colitis to the circ-Sirt1/Sirt1 signaling pathway, which is activated by diosmetin. The results imply that diosmetin may be a novel candidate to alleviate DSS-induced colitis and can be a lead compound for future optimization and modification.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
da Silva BC, Lyra AC, Rocha R, Santana GO. Epidemiology, demographic characteristics and prognostic predictors of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:9458–67.
Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Colombel JF. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2017;389:1756–70.
Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2012;380:1606–19.
Patel H, Barr A, Jeejeebhoy KN. Renal effects of long-term treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid. Can J Gastroenterol. 2009;23:170–6.
Zoubek ME, Pinazo-Bandera J, Ortega-Alonso A, Hernández N, Crespo J, Contreras F, et al. Liver injury after methylprednisolone pulses: a disputable cause of hepatotoxicity. A case series and literature review. United European. Gastroenterol J. 2019;7:825–37.
Xu P, Becker H, Elizalde M, Masclee A, Jonkers D. Intestinal organoid culture model is a valuable system to study epithelial barrier function in IBD. Gut. 2018;67:1905–6.
Antoni L, Nuding S, Wehkamp J, Stange EF. Intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:1165–79.
Jäger S, Stange EF, Wehkamp J. Inflammatory bowel disease: an impaired barrier disease. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398:1–12.
Choi W, Yeruva S, Turner JR. Contributions of intestinal epithelial barriers to health and disease. Exp Cell Res. 2017;358:71–77.
France MM, Turner JR. The mucosal barrier at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:307–14.
Bourgonje AR, Feelisch M, Faber KN, Pasch A, Dijkstra G, van Goor H. Oxidative stress and redox-modulating therapeutics in inflammatory bowel disease. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26:1034–46.
Vaccaro A, Kaplan Dor Y, Nambara K, Pollina EA, Lin C, Greenberg ME, et al. Sleep loss can cause death through accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the gut. Cell. 2020;181:1307–28. e1315
Peng Y, Yan Y, Wan P, Chen D, Ding Y, Ran L, et al. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of anthocyanins from the fruits of lycium ruthenicum murray in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;136:96–108.
Marchesi JR, Adams DH, Fava F, Hermes GD, Hirschfield GM, Hold G, et al. The gut microbiota and host health: a new clinical frontier. Gut. 2016;65:330–9.
Hagymási K, Bacsárdi A, Egresi A, Berta E, Tulassay Z, Lengyel G. The role of gut microbiota in chronic liver diseases, and treatment possibilities. Orv Hetil. 2018;159:1465–74.
Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol. 2020;72:558–77.
McNamara BP, Koutsouris A, O’Connell CB, Nougayréde JP, Donnenberg MS, Hecht G. Translocated espf protein from enteropathogenic escherichia coli disrupts host intestinal barrier function. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:621–9.
Li XV, Leonardi I, Iliev ID. Gut mycobiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Immunity. 2019;50:1365–79.
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, et al. Modulation of nf-kappab-dependent transcription and cell survival by the sirt1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004;23:2369–80.
Do MT, Kim HG, Choi JH, Jeong HG. Metformin induces microrna-34a to downregulate the sirt1/pgc-1α/nrf2 pathway, leading to increased susceptibility of wild-type p53 cancer cells to oxidative stress and therapeutic agents. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;74:21–34.
Wellman AS, Metukuri MR, Kazgan N, Xu X, Xu Q, Ren NSX, et al. Intestinal epithelial sirtuin 1 regulates intestinal inflammation during aging in mice by altering the intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:772–86.
Ye YL, Yin J, Hu T, Zhang LP, Wu LY, Pang Z. Increased circulating circular rna_103516 is a novel biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease in adult patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:6273–88.
Liu B, Ye B, Zhu X, Yang L, Li H, Liu N, et al. An inducible circular RNA circKcnt2 inhibits ILC3 activation to facilitate colitis resolution. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4076–90.
Zhu P, Zhu X, Wu J, He L, Lu T, Wang Y, et al. IL-13 secreted by ILC2s promotes the self-renewal of intestinal stem cells through circular RNA circPan3. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:183–94.
Kong P, Yu Y, Wang L, Dou YQ, Zhang XH, Cui Y, et al. circ-Sirt1 controls NF-κB activation via sequence-specific interaction and enhancement of SIRT1 expression by binding to miR-132/212 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:3580–93.
Roowi S, Crozier A. Flavonoids in tropical citrus species. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59:12217–25.
Chen X, Wu Q, Chen Y, Zhang J, Li H, Yang Z, et al. Diosmetin induces apoptosis and enhances the chemotherapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel in non-small cell lung cancer cells via Nrf2 inhibition. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176:2079–94.
Liu Q, Ci X, Wen Z, Peng L. Diosmetin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomol Ther. 2018;26:157–66.
Yang K, Li WF, Yu JF, Yi C, Huang WF. Diosmetin protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice. J Surg Res. 2017;214:69–78.
Mo GL, He Y, Zhang XQ, Lei X, Luo Q. Diosmetin exerts cardioprotective effect on myocardial ischemia injury in neonatal rats by decreasing oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;47:1713–22.
Zaragozá C, Villaescusa L, Monserrat J, Zaragozá F, Álvarez-Mon M. Potential therapeutic anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of dihydroflavones, flavones, and flavonols. Molecules. 2020;25:1017–30.
Suzuki K, Sun X, Nagata M, Kawase T, Yamaguchi H, Sukumaran V, et al. Analysis of intestinal fibrosis in chronic colitis in mice induced by dextran sulfate sodium. Pathol Int. 2011;61:228–38.
Liu Y, Zhao J, Zhao Y, Zong S, Tian Y, Chen S, et al. Therapeutic effects of lentinan on inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:750–60.
Yang M, Lin HB, Gong S, Chen PY, Geng LL, Zeng YM, et al. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and NFATc4 in a rat model of experimental colitis. Cytokine. 2014;70:81–86.
Thanou MM, Kotzé AF, Scharringhausen T, Luessen HL, de Boer AG, Verhoef JC, et al. Effect of degree of quaternization of n-trimethyl chitosan chloride for enhanced transport of hydrophilic compounds across intestinal caco-2 cell monolayers. J Control Release. 2000;64:15–25.
Sun X, Yang Q, Rogers CJ, Du M, Zhu MJ. AMPK improves gut epithelial differentiation and barrier function via regulating Cdx2 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:819–31.
Wu H, Chen QY, Wang WZ, Chu S, Liu XX, Liu YJ, et al. Compound sophorae decoction enhances intestinal barrier function of dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis via regulating notch signaling pathway in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110937–51.
Puri P, Liangpunsakul S, Christensen JE, Shah VH, Kamath PS, Gores GJ, et al. The circulating microbiome signature and inferred functional metagenomics in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 2018;67:1284–302.
Dai X, Chen X, Chen Q, Shi L, Liang H, Zhou Z, et al. MicroRNA-193a-3p reduces intestinal inflammation in response to microbiota via down-regulation of colonic PepT1. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:16099–115.
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K, Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc. 2017;12:1295–309.
Rohwer N, Jumpertz S, Erdem M, Egners A, Warzecha KT, Fragoulis A, et al. Non-canonical hif-1 stabilization contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2019;38:5670–85.
Li T, Chen RR, Gong HP, Wang BF, Wu XX, Chen YQ, et al. FGL2 regulates IKK/NF-κB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and lamina propria dendritic cells to attenuate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Mol Immunol. 2020;117:84–93.
Koosha S, Mohamed Z, Sinniah A, Alshawsh MA. Evaluation of anti-tumorigenic effects of diosmetin against human colon cancer xenografts in athymic nude mice. Molecules. 2019;24:2522–33.
Su L, Shen L, Clayburgh DR, Nalle SC, Sullivan EA, Meddings JB, et al. Targeted epithelial tight junction dysfunction causes immune activation and contributes to development of experimental colitis. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:551–63.
Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, et al. Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:1617–26.
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Takano H, et al. Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:4131–42.
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S. Claudin-1 and -2: Novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:1539–50.
Morini J, Babini G, Barbieri S, Baiocco G, Ottolenghi A. The interplay between radioresistant Caco-2 cells and the immune system increases epithelial layer permeability and alters signaling protein spectrum. Front Immunol. 2017;8:223–35.
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Zhu Q, Tan R, Bai D, Bu X, et al. Flavonoid VI-16 protects against dss-induced colitis by inhibiting TXNIP-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages via reducing oxidative stress. Mucosal Immunol. 2019;12:1150–63.
Macias-Ceja DC, Cosín-Roger J, Ortiz-Masiá D, Salvador P, Hernández C, Esplugues JV, et al. Stimulation of autophagy prevents intestinal mucosal inflammation and ameliorates murine colitis. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174:2501–11.
Qian J, Jiang F, Wang B, Yu Y, Zhang X, Yin Z, et al. Ophiopogonin d prevents h2o2-induced injury in primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;128:438–45.
Cao YW, Jiang Y, Zhang DY, Wang M, Chen WS, Su H, et al. Protective effects of penthorum chinense pursh against chronic ethanol-induced liver injury in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;161:92–8.
Maejima Y, Kuroda J, Matsushima S, Ago T, Sadoshima J. Regulation of myocardial growth and death by nadph oxidase. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50:408–16.
Biasi F, Astegiano M, Maina M, Leonarduzzi G, Poli G. Polyphenol supplementation as a complementary medicinal approach to treating inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18:4851–65.
Kim TW, Shin JS, Chung KS, Lee YG, Baek NI, Lee KT. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of koreanaside a, a lignan isolated from the flower of forsythia koreana, against LPS-induced macrophage activation and DSS-induced colitis mice: The crucial role of AP-1, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT signaling. Cells. 2019;8:1163–81. 8
Zhang F, Yao S, Yuan J, Zhang M, He Q, Yang G, et al. Elevated IL-6 receptor expression on CD4+ T cells contributes to the increased Th17 responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Virol J. 2011;8:270–80.
Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Santiago-Hernández JJ, Pérez-Hernández N, Ramírez-Fuentes S, Fragoso JM, Vargas-Alarcón G. Interleukin 1 β (IL-1β) and il-1 antagonist receptor (IL-1rn) gene polymorphisms are associated with the genetic susceptibility and steroid dependence in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:531–5.
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Cavallo P, Dragone T, Carofiglio V, Panaro MA. Modulation of NF-κB activation by resveratrol in LPS treated human intestinal cells results in downregulation of PGE2 production and Cox-2 expression. Toxicol Vitr. 2012;26:1122–8.
An JH, Li Q, Bhang DH, Song WJ, Youn HY. Tnf-α and inf-γ primed canine stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate experimental murine colitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10:2115–29.
Ni J, Wu GD, Albenberg L, Tomov VT. Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:573–84.
Zuo T, Kamm MA, Colombel JF, Ng SC. Urbanization and the gut microbiota in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:440–52.
Liu F, Smith AD, Solano-Aguilar G, Wang TTY, Pham Q, Beshah E, et al. Mechanistic insights into the attenuation of intestinal inflammation and modulation of the gut microbiome by krill oil using in vitro and in vivo models. Microbiome. 2020;8:83–103.
Fang Y, Chen HQ, Zhang X, Zhang H, Xia J, Ding K, et al. Probiotic administration of lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 attenuates atherosclerotic plaque formation in ApoE–/– mice fed with a high-fat diet. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:3533–41.
Yang W, Yu T, Huang X, Bilotta AJ, Xu L, Lu Y, et al. Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4457–75.
Jeffery IB, O’Toole PW, Öhman L, Claesson MJ, Deane J, Quigley EM, et al. An irritable bowel syndrome subtype defined by species-specific alterations in faecal microbiota. Gut. 2012;61:997–1006.
Soltys K, Stuchlikova M, Hlavaty T, Gaalova B, Budis J, Gazdarica J, et al. Seasonal changes of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin d correlate with the lower gut microbiome composition in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Sci Rep. 2020;10:6024–39.
Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circrna biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015;12:381–8.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant 82070060 and 82072660] and the Foundation of Tianjin Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd [Grant 735-F1025301].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HLL, YYW, XHL, HGZ, and CY designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. HLL, YYW, HR, JHL, and SSZ performed the animal and cell experiments. HLL, YYW, and XHL performed the quantitative real-time PCR and Western blotting assays. ZWL and SBS performed the immunofluorescence experiments. RTZ and BWM performed the histopathological section.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Hl., Wei, Yy., Li, Xh. et al. Diosmetin has therapeutic efficacy in colitis regulating gut microbiota, inflammation, and oxidative stress via the circ-Sirt1/Sirt1 axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 919–932 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00726-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00726-0
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of Diosmetin, Arbutin, and Phenyl Glucoside as Novel Inhibitors from Origanum majorana Targeting Human Cyclooxygenase-2 Enzyme: Insight from Virtual Screening, MD Simulation and Density Functional Theory
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2026)
-
Role of adiponectin and its receptors AdipoR1/2 in inflammatory bowel disease
Cell Communication and Signaling (2025)
-
Study on the effect of modified diosmetin for ulcerative colitis
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine (2025)
-
Diosmetin Attenuates Painful Symptoms Caused by Antineoplastics Paclitaxel and Anastrozole in Mice
Molecular Neurobiology (2025)
-
Diosmetin Ameliorates HFD-induced Cognitive Impairments via Inhibiting Metabolic Disorders, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Male SD Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)