Abstract
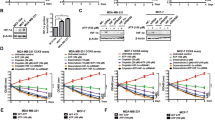
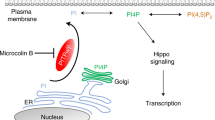
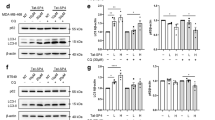
Dysregulation of the Hippo signaling pathway seen in many types of cancer is usually associated with a poor prognosis. Paris saponin VII (PSVII) is a steroid saponin isolated from traditional Chinese herbs with therapeutic action against various human cancers. In this study we investigated the effects of PSVII on human breast cancer (BC) cells and its anticancer mechanisms. We showed that PSVII concentration-dependently inhibited the proliferation of MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-436 and MCF-7 BC cell lines with IC50 values of 3.16, 3.45, and 2.86 μM, respectively, and suppressed their colony formation. PSVII (1.2–1.8 μM) induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in the BC cell lines. PSVII treatment also induced autophagy and promoted autophagic flux in the BC cell lines. PSVII treatment decreased the expression and nuclear translocation of Yes-associated protein (YAP), a downstream transcriptional effector in the Hippo signaling pathway; overexpression of YAP markedly attenuated PSVII-induced autophagy. PSVII-induced, YAP-mediated autophagy was associated with increased active form of LATS1, an upstream effector of YAP. The activation of LATS1 was involved the participation of multiple proteins (including MST2, MOB1, and LATS1 itself) in an MST2-dependent sequential activation cascade. We further revealed that PSVII promoted the binding of LATS1 with MST2 and MOB1, and activated LATS1 in the BC cell lines. Molecular docking showed that PSVII directly bound to the MST2-MOB1-LATS1 ternary complex. Microscale thermophoresis analysis and drug affinity responsive targeting stability assay confirmed the high affinity between PSVII and the MST2-MOB1-LATS1 ternary complex. In mice bearing MDA-MB-231 cell xenograft, administration of PSVII (1.5 mg/kg, ip, 4 times/week, for 4 weeks) significantly suppressed the tumor growth with increased pLATS1, LC3-II and Beclin 1 levels and decreased YAP, p62 and Ki67 levels in the tumor tissue. Overall, this study demonstrates that PSVII is a novel and direct Hippo activator that has great potential in the treatment of BC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
10 December 2024
The original online version of this article was revised: In Figure 3b, there is an error in the image of MCF-7 cells treated with PSVII. We accidentally stored the MDA-MB-231 cells treated with PSVII as the MCF-7 cells treated with PSVII when we took the image. This led to the misuse. The authors state that these corrections do not affect the results or conclusions of this article.
09 January 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01453-y
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Ji JS, Zou X, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:e555–e67.
Ehsan H, Imtiaz H, Sana MK, Sheikh MM, Wahab A. Relapsed breast cancer complicated by isolated brain metastasis. Clin Case Rep. 2021;9:887–90.
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:528–42.
Cao W, Li J, Yang K, Cao D. An overview of autophagy: mechanism, regulation and research progress. Bull Cancer. 2021;108:304–22.
Limpert AS, Lambert LJ, Bakas NA, Bata N, Brun SN, Shaw RJ, et al. Autophagy in cancer: regulation by small molecules. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39:1021–32.
Russo M, Russo GL. Autophagy inducers in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;153:51–61.
Takahashi A, Kimura F, Yamanaka A, Takebayashi A, Kita N, Takahashi K, et al. Metformin impairs growth of endometrial cancer cells via cell cycle arrest and concomitant autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14:53.
Fu H, Wang C, Yang D, Wei Z, Xu J, Hu Z, et al. Curcumin regulates proliferation, autophagy, and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by affecting PI3K and P53 signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:4634–42.
Bi Y, Shen C, Li C, Liu Y, Gao D, Shi C, et al. Inhibition of autophagy induced by quercetin at a late stage enhances cytotoxic effects on glioma cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:3549–60.
Si Y, Ji X, Cao X, Dai X, Xu L, Zhao H, et al. Src inhibits the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway through tyrosine phosphorylation of Lats1. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4868–80.
Han Y. Analysis of the role of the Hippo pathway in cancer. J Transl Med. 2019;17:116.
Dey A, Varelas X, Guan KL. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:480–94.
Cao J, Huang W. Two faces of Hippo: activate or suppress the Hippo pathway in cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2017;28:1079–85.
Zheng Y, Pan D. The Hippo signaling pathway in development and disease. Dev Cell. 2019;50:264–82.
Calses PC, Crawford JJ, Lill JR, Dey A. Hippo pathway in cancer: aberrant regulation and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Cancer. 2019;5:297–307.
Wu L, Yang X. Targeting the Hippo pathway for breast cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10:422.
Wang BL, Zhang H, Hao XC, Ge ZK, Qiu JR, Zhao YH. Research progress on pharmacological action of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. J Tradit Chin Med. 2018;40:478–81.
Wang BL, Hao XC, Ge ZK, Qiu JR, Zhang H, Zhao YH. Study on HPLC fingerprint of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. Hubei J Tradit Chin Med. 2018;37:225–8.
Lin X, Gajendran B, Varier KM, Liu W, Song J, Rao Q, et al. Paris Saponin VII induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in erythroleukemia cells by a mitochondrial membrane signaling pathway. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;21:498–507.
Tang GE, Niu YX, Li Y, Wu CY, Wang XY, Zhang J. Paris saponin VII enhanced the sensitivity of HepG2/ADR cells to ADR via modulation of PI3K/AKT/MAPK signaling pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020;36:98–106.
Li Y, Sun Y, Fan L, Zhang F, Meng J, Han J, et al. Paris saponin VII inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells through Ras signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;88:150–7.
Zhang W, Zhang D, Ma X, Liu Z, Li F, Wu D. Paris saponin VII suppressed the growth of human cervical cancer Hela cells. Eur J Med Res. 2014;19:41.
Fan L, Li Y, Sun Y, Han J, Yue Z, Meng J, et al. Paris saponin VII inhibits the migration and invasion in human A549 lung cancer cells. Phytother Res. 2015;29:1366–72.
Cheng G, Gao F, Sun X, Bi H, Zhu Y. Paris saponin VII suppresses osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by inhibiting MMP2/9 production via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14:3199–205.
Zhang Y, Huang P, Liu X, Xiang Y, Zhang T, Wu Y, et al. Polyphyllin I inhibits growth and invasion of cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells by partially inhibiting CIP2A/PP2A/Akt signaling axis. J Pharm Sci. 2018;137:305–12.
Ma WJ, Xiang YC, Yang R, Zhang T, Xu JX, Wu YZ, et al. Cucurbitacin B induces inhibitory effects via the CIP2A/PP2A/C-KIT signaling axis in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. J Pharm Sci. 2019;139:304–10.
Liu PF, Xiang YC, Liu XW, Zhang T, Yang R, Chen S, et al. Cucurbitacin B induces the lysosomal degradation of EGFR and suppresses the CIP2A/PP2A/Akt signaling axis in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Molecules. 2019;24:647.
Si Y, Wang J, Liu X, Zhou T, Xiang Y, Zhang T, et al. Ethoxysanguinarine, a novel direct activator of AMP-activated protein kinase, induces autophagy and exhibits therapeutic potential in breast cancer cells. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1503.
Wang Q, Zhang Q, Luan S, Yang K, Zheng M, Li K, et al. Adapalene inhibits ovarian cancer ES-2 cells growth by targeting glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1. Bioorg Chem. 2019;93:103315.
Choi J, Lee YJ, Yoon YJ, Kim CH, Park SJ, Kim SY, et al. Pimozide suppresses cancer cell migration and tumor metastasis through binding to ARPC2, a subunit of the Arp2/3 complex. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:3788–801.
Lee YK, Jun YW, Choi HE, Huh YH, Kaang BK, Jang DJ, et al. Development of LC3/GABARAP sensors containing a LIR and a hydrophobic domain to monitor autophagy. EMBO J. 2017;36:1100–16.
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Pankiv S, Overvatn A, Brech A, Johansen T. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 2009;452:181–97.
Lv X, Li K, Hu Z. Autophagy and pulmonary fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:569–79.
Ni L, Zheng Y, Hara M, Pan D, Luo X. Structural basis for Mob1-dependent activation of the core Mst-Lats kinase cascade in Hippo signaling. Genes Dev. 2015;29:1416–31.
Zhao YZ, Zhang YY, Han H, Fan RP, Hu Y, Zhong L, et al. Advances in the antitumor activities and mechanisms of action of steroidal saponins. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16:732–48.
Man S, Gao W, Zhang Y, Huang L, Liu C. Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer agents. Fitoterapia 2010;81:703–14.
Xiang YC, Shen J, Si Y, Liu XW, Zhang L, Wen J, et al. Paris saponin VII, a direct activator of AMPK, induces autophagy and exhibits therapeutic potential in non-small-cell lung cancer. Chin J Nat Med. 2021;19:195–204.
Wu Y, Si Y, Xiang Y, Zhou T, Liu X, Wu M, et al. Polyphyllin I activates AMPK to suppress the growth of non-small-cell lung cancer via induction of autophagy. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;687:108285.
Yin X, Qu C, Li Z, Zhai Y, Cao S, Lin L, et al. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII in beagle dog plasma after oral administration of Rhizoma Paridis extracts by LC-MS-MS. Biomed Chromatogr. 2013;27:343–8.
Tummers B, Green DR. Caspase-8: regulating life and death. Immunol Rev. 2017;277:76–89.
Shen HM, Codogno P. Autophagic cell death: Loch Ness monster or endangered species? Autophagy. 2011;7:457–65.
Feng X, Zhou J, Li J, Hou X, Li L, Chen Y, et al. Tubeimoside I induces accumulation of impaired autophagolysosome against cervical cancer cells by both initiating autophagy and inhibiting lysosomal function. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1117.
Liu K, Ren T, Huang Y, Sun K, Bao X, Wang S, et al. Apatinib promotes autophagy and apoptosis through VEGFR2/STAT3/BCL-2 signaling in osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e3015.
Tang F, Christofori G. The cross-talk between the Hippo signaling pathway and autophagy:implications on physiology and cancer. Cell Cycle. 2020;19:2563–72.
Mo JS, Meng Z, Kim YC, Park HW, Hansen CG, Kim S, et al. Cellular energy stress induces AMPK-mediated regulation of YAP and the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:500–10.
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:132–41.
Totaro A, Zhuang Q, Panciera T, Battilana G, Azzolin L, Brumana G, et al. Cell phenotypic plasticity requires autophagic flux driven by YAP/TAZ mechanotransduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:17848–57.
Wilkinson DS, Jariwala JS, Anderson E, Mitra K, Meisenhelder J, Chang JT, et al. Phosphorylation of LC3 by the Hippo kinases STK3/STK4 is essential for autophagy. Mol Cell. 2015;57:55–68.
Gan W, Dai X, Dai X, Xie J, Yin S, Zhu J, et al. LATS suppresses mTORC1 activity to directly coordinate Hippo and mTORC1 pathways in growth control. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:246–56.
Wienken CJ, Baaske P, Rothbauer U, Braun D, Duhr S. Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis. Nat Commun. 2010;1:100.
Chang J, Kim Y, Kwon HJ. Advances in identification and validation of protein targets of natural products without chemical modification. Nat Prod Rep. 2016;33:719–30.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos 82072928 and 81802387), the Foundation for Innovative Research Group of Hubei Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 2021CFA071), the Foundation for Innovative Research Team of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (No. T201915), the Principal Investigator Grant of Hubei University of Medicine (No. HBMUPI201806), the Innovative Research Program for Graduates (No. YC2021004), the Faculty Development Grants from Hubei University of Medicine (No. 2018QDJZR03), the Scientific and Technological Project of Shiyan City of Hubei Province (Nos 21Y08 and 21Y09), and the National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (Nos 202110929001 and 202110929002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL conceived and planned the experiments. YCX, PP, XWL, XJ, JS, TZ, LZ, FW, YLR, QQY, and HZZ performed the experiment and analyzed the data. YL and YS wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised: In Figure 3b, there is an error in the image of MCF-7 cells treated with PSVII. We accidentally stored the MDA-MB-231 cells treated with PSVII as the MCF-7 cells treated with PSVII when we took the image. This led to the misuse. The authors state that these corrections do not affect the results or conclusions of this article.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Yc., Peng, P., Liu, Xw. et al. Paris saponin VII, a Hippo pathway activator, induces autophagy and exhibits therapeutic potential against human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 1568–1580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00755-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00755-9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Paris saponin VII attenuates psoriasiform inflammation by regulating STAT3/NFκB signaling pathway and Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis
Molecular Medicine (2025)
-
Gracillin suppresses cancer progression through inducing Merlin/LATS protein-protein interaction and activating Hippo signaling pathway
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2025)